Intro
Discover the ultimate Computed Tomography Scan Guide, covering CT scan basics, preparation, and benefits, with related imaging techniques like X-rays and MRI scans, for accurate diagnoses and treatments.
The use of computed tomography (CT) scans has become increasingly prevalent in the medical field, revolutionizing the way doctors diagnose and treat various health conditions. With its ability to produce high-resolution images of the body's internal structures, CT scans have become an essential tool for medical professionals. As technology continues to advance, CT scans are becoming more sophisticated, allowing for faster and more accurate diagnoses. In this article, we will delve into the world of CT scans, exploring their benefits, working mechanisms, and the various types of scans available.
CT scans are a crucial diagnostic tool, enabling doctors to visualize internal injuries, detect diseases, and monitor treatment progress. The technology uses a combination of X-rays and computer algorithms to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. These images can be used to diagnose a wide range of conditions, from broken bones and internal injuries to cancer and cardiovascular disease. With the help of CT scans, doctors can develop more effective treatment plans, improving patient outcomes and saving lives.
The importance of CT scans cannot be overstated, as they have become a vital component of modern medicine. By providing high-resolution images of the body's internal structures, CT scans enable doctors to diagnose conditions that may be difficult or impossible to detect using other diagnostic tools. Additionally, CT scans are non-invasive, reducing the risk of complications and making them a safer alternative to more invasive procedures. As medical technology continues to evolve, the role of CT scans in diagnosis and treatment will only continue to grow.
Introduction to Computed Tomography Scans
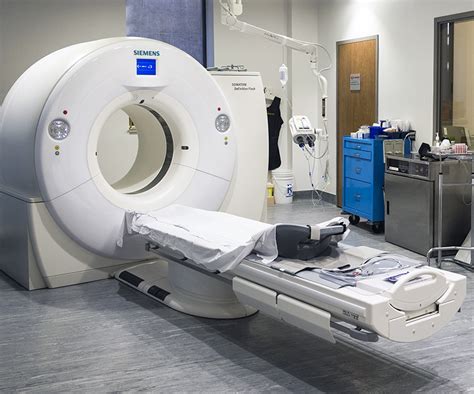
How CT Scans Work
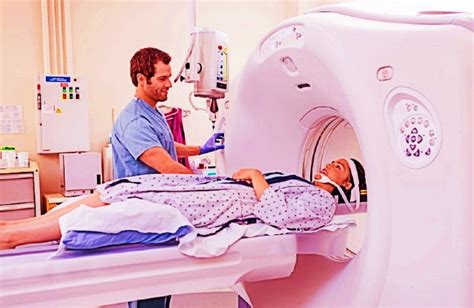
The process of undergoing a CT scan is relatively straightforward. The patient lies on a table that slides into the CT scanner, a large, doughnut-shaped machine. The scanner uses a rotating X-ray beam to capture images of the body from different angles. These images are then reconstructed using computer algorithms, creating detailed cross-sectional images of the body's internal structures. The entire process typically takes only a few minutes, although the exact time may vary depending on the type of scan and the area of the body being imaged.Types of Computed Tomography Scans
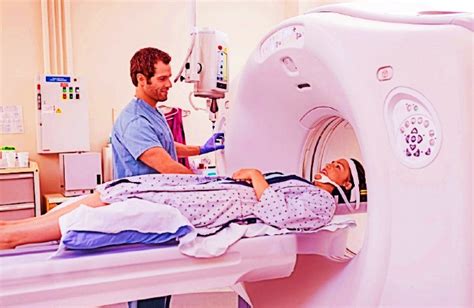
Benefits of Computed Tomography Scans
CT scans offer a number of benefits, including: * High-resolution images: CT scans provide detailed images of the body's internal structures, enabling doctors to diagnose conditions with greater accuracy. * Non-invasive: CT scans are non-invasive, reducing the risk of complications and making them a safer alternative to more invasive procedures. * Fast and convenient: CT scans are relatively quick, typically taking only a few minutes to complete. * Wide range of applications: CT scans can be used to diagnose a wide range of conditions, from broken bones and internal injuries to cancer and cardiovascular disease.Preparation and Procedure
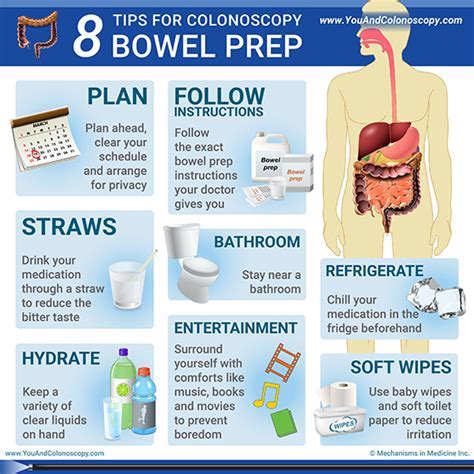
Risks and Complications
While CT scans are generally safe, there are some risks and complications associated with the procedure. These may include: * Radiation exposure: CT scans use X-rays, which can expose patients to radiation. * Allergic reactions: Some patients may be allergic to the contrast material used in CT scans. * Kidney damage: The contrast material used in CT scans can cause kidney damage in some patients.Computed Tomography Scan Results
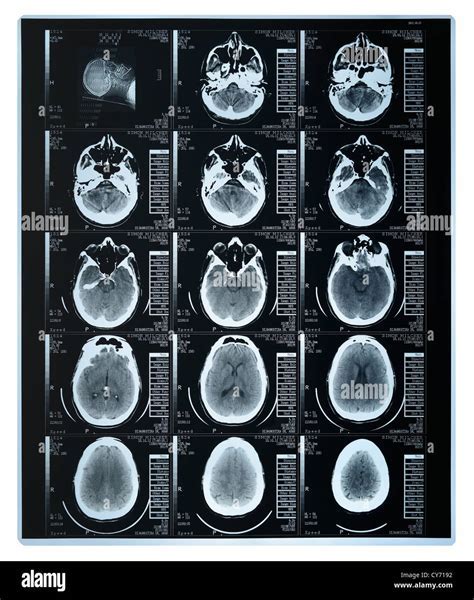
Common Uses of Computed Tomography Scans
CT scans have a wide range of applications, including: * Diagnosing diseases: CT scans can be used to diagnose a wide range of diseases, from cancer and cardiovascular disease to kidney stones and liver disease. * Monitoring treatment: CT scans can be used to monitor treatment progress, helping doctors to adjust treatment plans as needed. * Guiding biopsies: CT scans can be used to guide biopsies, helping doctors to locate and sample abnormal tissue.Future of Computed Tomography Scans
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, CT scans are a vital diagnostic tool, enabling doctors to visualize internal injuries, detect diseases, and monitor treatment progress. With their high-resolution images, non-invasive nature, and wide range of applications, CT scans are an essential component of modern medicine. As technology continues to advance, the role of CT scans in diagnosis and treatment will only continue to grow. If you have any questions or concerns about CT scans, be sure to speak with your doctor or a qualified medical professional.What is a CT scan?
+A CT scan is a medical imaging test that uses X-rays and computer algorithms to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body's internal structures.
How do I prepare for a CT scan?
+Before undergoing a CT scan, patients may be required to prepare in certain ways, such as fasting, removing jewelry and clothing, and drinking contrast material.
What are the risks and complications associated with CT scans?
+While CT scans are generally safe, there are some risks and complications associated with the procedure, such as radiation exposure, allergic reactions, and kidney damage.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive guide to CT scans, including their benefits, working mechanisms, and types of scans available. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more about CT scans, please don't hesitate to comment below or share this article with others. By working together, we can promote greater understanding and awareness of this vital diagnostic tool.
