Intro
Boost heart health with a tailored diet plan, incorporating cardiovascular-friendly foods, reducing inflammation, and promoting overall wellness through a balanced nutrition approach.
Maintaining a healthy heart is crucial for overall well-being, and one of the most effective ways to achieve this is through a well-planned diet. A heart-healthy diet plan focuses on consuming foods that are rich in nutrients, fiber, and healthy fats, while limiting the intake of processed and high-sodium foods. By making informed food choices, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing heart disease, which is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. In this article, we will delve into the importance of a heart health diet plan, its benefits, and provide a comprehensive guide on how to implement it.
A heart health diet plan is essential for maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system. It helps to lower blood pressure, improve blood lipid profiles, and prevent the formation of blood clots. A well-planned diet can also aid in weight management, which is critical for reducing the risk of heart disease. Furthermore, a heart-healthy diet has been shown to reduce the risk of stroke, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. With the increasing prevalence of heart disease, it is essential to adopt a healthy diet plan that promotes overall cardiovascular well-being.
The benefits of a heart health diet plan are numerous, and it is never too early or too late to start making positive changes to one's diet. By incorporating heart-healthy foods into their diet, individuals can experience significant improvements in their overall health and well-being. A heart health diet plan can help to increase energy levels, improve mental clarity, and enhance physical performance. Additionally, it can aid in reducing inflammation, improving digestion, and boosting the immune system. With the right guidance and support, anyone can adopt a heart health diet plan that suits their lifestyle and preferences.
Understanding the Key Components of a Heart Health Diet Plan
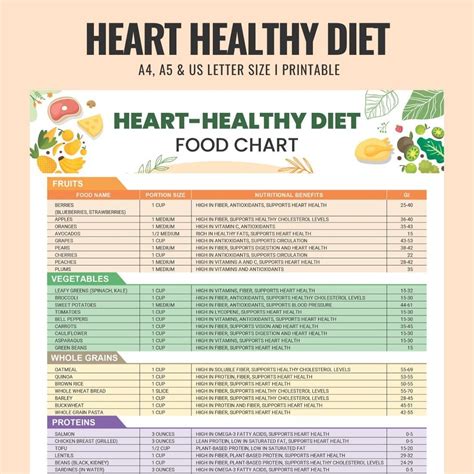
A heart health diet plan typically consists of a variety of foods from all food groups. The key components of a heart-healthy diet include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which help to protect the heart and blood vessels from damage. Whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole-wheat bread, provide sustained energy and fiber, which can help to lower cholesterol levels. Lean proteins, including poultry, fish, and legumes, are essential for building and repairing heart tissue. Healthy fats, such as those found in nuts, seeds, and avocados, help to lower bad cholesterol and increase good cholesterol.
Importance of Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are some of the most nutritious foods that can be included in a heart health diet plan. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which help to protect the heart and blood vessels from damage. The American Heart Association recommends consuming at least 5 servings of fruits and vegetables per day. Some of the best fruits and vegetables for heart health include berries, leafy greens, citrus fruits, and cruciferous vegetables. Berries, such as blueberries and strawberries, are rich in antioxidants and fiber, which can help to lower blood pressure and improve blood lipid profiles. Leafy greens, including spinach and kale, are rich in vitamins and minerals, which can help to reduce inflammation and improve cardiovascular health.Creating a Personalized Heart Health Diet Plan

Creating a personalized heart health diet plan involves setting realistic goals and making sustainable lifestyle changes. The first step is to assess your current diet and identify areas for improvement. Keep a food diary to track your eating habits and identify patterns and triggers. Next, set specific and achievable goals, such as increasing fruit and vegetable intake or reducing sodium consumption. Develop a meal plan that includes a variety of heart-healthy foods and limits processed and high-sodium foods. It is also essential to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water and limiting sugary drinks.
Meal Planning and Grocery Shopping
Meal planning and grocery shopping are critical components of a heart health diet plan. Plan your meals in advance to ensure that you have a steady supply of heart-healthy ingredients. Make a grocery list and stick to it to avoid impulse purchases. Shop the perimeter of the grocery store, where fresh produce, meats, and dairy products are typically located. Avoid the center aisles, where processed and packaged foods are often found. Consider shopping at local farmers' markets or joining a community-supported agriculture (CSA) program to access fresh, seasonal produce.Common Mistakes to Avoid in a Heart Health Diet Plan

There are several common mistakes to avoid when creating a heart health diet plan. One of the most significant mistakes is not drinking enough water. Staying hydrated is essential for maintaining healthy blood flow and blood pressure. Another mistake is consuming too much sodium, which can increase blood pressure and cardiovascular risk. Limit sodium intake to less than 2,300 milligrams per day, and choose low-sodium options whenever possible. Additionally, avoid consuming too much added sugar, which can increase triglycerides and cardiovascular risk. Limit added sugar intake to less than 10% of daily calorie intake.
Overcoming Challenges and Staying Motivated
Overcoming challenges and staying motivated are critical components of a successful heart health diet plan. One of the most significant challenges is staying on track with a busy schedule. Plan ahead by preparing meals in advance and keeping healthy snacks on hand. Another challenge is avoiding unhealthy foods, such as those high in sodium and added sugar. Identify triggers and develop strategies to avoid or manage them. Stay motivated by tracking progress, celebrating successes, and seeking support from friends, family, or a registered dietitian.Sustaining a Heart Health Diet Plan Long-Term

Sustaining a heart health diet plan long-term requires commitment, patience, and persistence. One of the most effective strategies is to focus on progress, not perfection. Don't be too hard on yourself if you slip up – simply get back on track and keep moving forward. Another strategy is to find healthy alternatives to your favorite foods. For example, if you love pizza, try making a healthier version at home with whole-wheat crust and plenty of vegetables. Additionally, stay connected with friends and family who support your healthy lifestyle choices, and consider joining a community or support group to stay motivated and inspired.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting the Plan
Monitoring progress and adjusting the plan as needed is critical for sustaining a heart health diet plan long-term. Keep track of your food intake, physical activity, and health markers, such as blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Use a food diary or mobile app to track your progress and identify areas for improvement. Adjust your plan as needed to stay on track and overcome challenges. Consider working with a registered dietitian or healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan that meets your unique needs and goals.What are the key components of a heart health diet plan?
+A heart health diet plan typically consists of a variety of foods from all food groups, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
How can I create a personalized heart health diet plan?
+Create a personalized heart health diet plan by assessing your current diet, setting realistic goals, and making sustainable lifestyle changes. Consider working with a registered dietitian or healthcare provider to develop a plan that meets your unique needs and goals.
What are some common mistakes to avoid in a heart health diet plan?
+Common mistakes to avoid in a heart health diet plan include not drinking enough water, consuming too much sodium, and eating too much added sugar. Limit sodium intake to less than 2,300 milligrams per day, and choose low-sodium options whenever possible.
In conclusion, a heart health diet plan is a critical component of maintaining overall cardiovascular well-being. By understanding the key components of a heart health diet plan, creating a personalized plan, and avoiding common mistakes, individuals can reduce their risk of heart disease and improve their overall health. Remember to stay hydrated, limit sodium and added sugar intake, and focus on progress, not perfection. With the right guidance and support, anyone can adopt a heart health diet plan that suits their lifestyle and preferences. We invite you to share your experiences, ask questions, and provide feedback on this article. Together, we can create a community that supports and promotes heart-healthy lifestyles.
