Intro
Discover 5 effective ways to treat ulcers, including natural remedies, dietary changes, and medications, to alleviate symptoms and promote healing for stomach ulcers, peptic ulcers, and gastric ulcers.
Treating ulcers effectively is crucial for alleviating the discomfort and pain they cause, as well as preventing potential complications. Ulcers, which are open sores that develop on the inside lining of the stomach and the upper portion of the small intestine, can be caused by a variety of factors including infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), long-term use of anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen and aspirin, excessive acid production in the stomach, and stress. Understanding the different methods to treat ulcers can help individuals manage their condition better and improve their quality of life.
The importance of treating ulcers cannot be overstated. If left untreated, ulcers can lead to serious health issues such as bleeding, perforation, and narrowing of the stomach or duodenal outlet. Furthermore, the discomfort and pain from ulcers can significantly impact an individual's ability to eat, sleep, and engage in daily activities. Therefore, it is essential to explore the various treatment options available for ulcers, including lifestyle changes, medications, and alternative therapies.
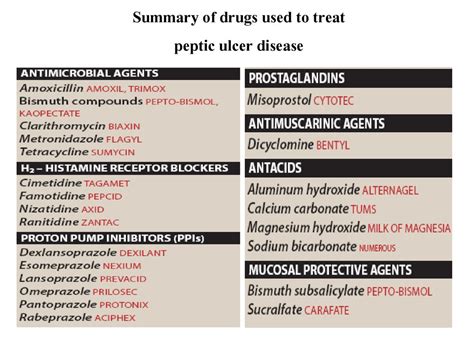
Effective treatment of ulcers often involves a combination of medical interventions and lifestyle modifications. For instance, medications such as antacids, histamine-2 (H2) blockers, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) can help reduce stomach acid and protect the stomach lining, allowing ulcers to heal. Additionally, making dietary changes, managing stress, and avoiding irritants like alcohol and tobacco can also play a crucial role in the healing process. By adopting a comprehensive approach to treatment, individuals can not only alleviate their symptoms but also prevent future occurrences of ulcers.
Understanding Ulcers
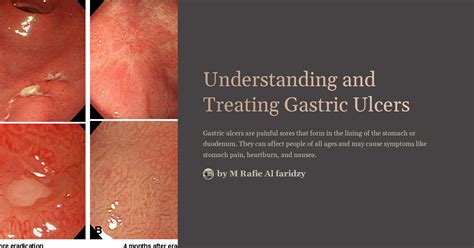
Causes and Symptoms of Ulcers
The causes of ulcers can vary significantly from one individual to another. Infection with H. pylori is a common cause, as this bacterium can weaken the protective mucous coating of the stomach and duodenum, making them more susceptible to acid. The use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is another frequent cause, as these medications can interfere with the production of the stomach's protective lining. Symptoms of ulcers may include burning stomach pain, feeling bloated or full, nausea and vomiting, and in severe cases, vomiting blood or black tarry stools. Recognizing these symptoms early on can facilitate prompt treatment and prevent complications.Treatment Options for Ulcers
Lifestyle Modifications for Ulcer Management
Lifestyle modifications play a critical role in the management and prevention of ulcers. Dietary changes, for example, can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing. Foods that are high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help reduce symptoms, while foods that are high in fat, spicy, or acidic may exacerbate them. Avoiding irritants like tobacco and alcohol is also essential, as these substances can delay healing and increase the risk of complications. Furthermore, practicing stress-reducing techniques and getting adequate sleep can help manage the physical and emotional aspects of ulcer disease.Medications for Ulcer Treatment
Alternative Therapies for Ulcers
In addition to conventional medical treatments, several alternative therapies have been explored for their potential in managing ulcers. These include probiotics, which can help restore the balance of gut bacteria; licorice extract, which may protect the stomach lining; and certain herbal remedies, which have anti-inflammatory properties. While these alternatives may offer some benefits, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before using them, especially in combination with conventional treatments, to ensure safety and efficacy.Surgical Interventions for Ulcer Complications
Prevention of Ulcer Recurrence
Preventing the recurrence of ulcers is as important as treating the initial condition. This involves maintaining the lifestyle modifications and medical treatments that were effective in healing the ulcers. Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is crucial to monitor the healing process and adjust the treatment plan as necessary. Additionally, being aware of the signs of ulcer recurrence and seeking medical attention promptly can help prevent complications and ensure timely intervention.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts on Ulcer Management
Ultimately, the key to successful ulcer management is a combination of prompt medical attention, adherence to treatment plans, and long-term lifestyle changes. By working closely with healthcare providers and taking an active role in their care, individuals can overcome the challenges of ulcer disease and look forward to a healthier, more comfortable future. Whether through conventional treatments, alternative therapies, or a combination of both, there is hope for healing and prevention of ulcers, underscoring the importance of ongoing research and patient education in this field.What are the most common symptoms of ulcers?
+The most common symptoms of ulcers include burning stomach pain, feeling bloated or full, nausea and vomiting, and in severe cases, vomiting blood or black tarry stools.
How are ulcers typically treated?
+Ulcers are typically treated with a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical interventions, including medications that reduce acid production, protect the stomach lining, or eradicate H. pylori infection.
Can ulcers be prevented?
+Yes, ulcers can be prevented by avoiding NSAIDs, quitting smoking, reducing alcohol consumption, managing stress, and eating a balanced diet that is low in fat and high in fiber.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with ulcer treatment. Have you found any specific lifestyle modifications or medical interventions to be particularly effective? What challenges have you faced in managing your condition, and how have you overcome them? Your insights can help others who are navigating the complexities of ulcer disease, and we encourage you to join the conversation by commenting below. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can work towards raising awareness and promoting better understanding and management of ulcers.
