Intro
Discover the importance of a CT Brain Scan, utilizing computed tomography to diagnose brain injuries, strokes, and tumors, with detailed images and expert analysis for accurate neurologic care and treatment.
The importance of medical imaging in diagnosing and treating various health conditions cannot be overstated. One of the most critical diagnostic tools in modern medicine is the CT brain scan. This non-invasive procedure uses computerized tomography (CT) technology to produce detailed cross-sectional images of the brain, allowing doctors to visualize its structure and identify any abnormalities. The CT brain scan has revolutionized the field of neurology, enabling healthcare professionals to diagnose and treat a wide range of brain-related disorders, from strokes and tumors to injuries and infections.
The CT brain scan is a vital diagnostic tool that has saved countless lives by providing doctors with a clear and accurate picture of the brain's anatomy. This information is essential in diagnosing conditions such as cerebral hemorrhages, aneurysms, and arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), which can be life-threatening if left untreated. The scan can also help doctors monitor the progression of neurological diseases, such as multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease, allowing them to adjust treatment plans accordingly. Furthermore, the CT brain scan can aid in the diagnosis of mental health disorders, such as depression and anxiety, by identifying any underlying brain abnormalities that may be contributing to these conditions.
The use of CT brain scans has become increasingly common in recent years, and their importance cannot be overstated. According to the American College of Radiology, over 70 million CT scans are performed annually in the United States alone, with a significant proportion of these being brain scans. The widespread adoption of CT brain scans is a testament to their effectiveness in diagnosing and treating a wide range of brain-related disorders. As medical technology continues to evolve, it is likely that the use of CT brain scans will become even more prevalent, leading to improved patient outcomes and a better understanding of the human brain.
How CT Brain Scans Work
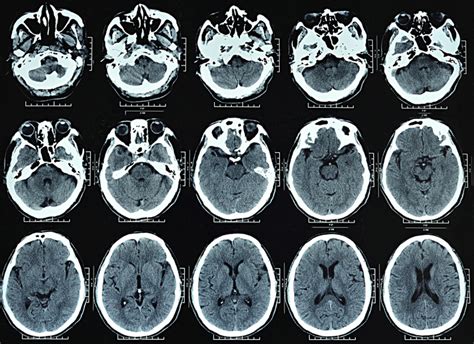
CT brain scans use a combination of X-rays and computer technology to produce detailed images of the brain. The process begins with the patient lying on a table that slides into a large, doughnut-shaped machine called a CT scanner. The scanner is equipped with X-ray detectors and emitters that rotate around the patient's head, taking multiple images from different angles. These images are then transmitted to a computer, which uses sophisticated algorithms to reconstruct the data into detailed cross-sectional images of the brain. The resulting images can be viewed on a computer screen or printed out for further analysis.
Preparation and Procedure
The preparation and procedure for a CT brain scan are relatively straightforward. Patients are typically asked to arrive at the hospital or imaging center 30 minutes prior to the scheduled scan time. They will be required to remove any metal objects, such as jewelry or glasses, and change into a hospital gown. The scan itself usually takes around 10-15 minutes to complete, during which time the patient will be asked to remain still and hold their breath for short periods. In some cases, a contrast agent may be administered to enhance the visibility of certain brain structures or abnormalities.Benefits of CT Brain Scans
The benefits of CT brain scans are numerous and well-documented. Some of the most significant advantages include:
- Rapid diagnosis: CT brain scans can provide doctors with a quick and accurate diagnosis, allowing them to initiate treatment promptly.
- High accuracy: The detailed images produced by CT brain scans enable doctors to identify even small abnormalities, reducing the risk of misdiagnosis.
- Non-invasive: CT brain scans are a non-invasive procedure, eliminating the need for surgery or other invasive diagnostic techniques.
- Cost-effective: Compared to other diagnostic imaging modalities, such as MRI or PET scans, CT brain scans are relatively affordable.
Common Uses of CT Brain Scans
CT brain scans have a wide range of applications in modern medicine. Some of the most common uses include: * Diagnosing strokes and cerebral hemorrhages * Identifying brain tumors and cysts * Monitoring the progression of neurological diseases, such as multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer's disease * Evaluating head injuries and trauma * Diagnosing mental health disorders, such as depression and anxietyRisks and Side Effects
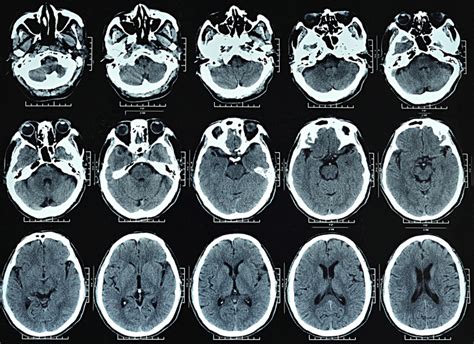
While CT brain scans are generally considered safe, there are some potential risks and side effects to be aware of. These include:
- Radiation exposure: CT brain scans use X-rays, which can increase the risk of radiation-induced cancer.
- Contrast agent reactions: In rare cases, patients may experience an allergic reaction to the contrast agent used during the scan.
- Claustrophobia: The enclosed space of the CT scanner can cause anxiety or claustrophobia in some patients.
- Kidney damage: The contrast agent used in CT brain scans can cause kidney damage in patients with pre-existing kidney disease.
Minimizing Risks and Side Effects
To minimize the risks and side effects associated with CT brain scans, patients can take several precautions. These include: * Informing their doctor about any allergies or sensitivities * Avoiding the use of contrast agents if possible * Staying hydrated to reduce the risk of kidney damage * Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation, to reduce anxiety and claustrophobiaFuture Developments in CT Brain Scans

The field of CT brain scans is constantly evolving, with new technologies and techniques being developed to improve image quality and diagnostic accuracy. Some of the most promising future developments include:
- High-resolution CT scanners: New scanner designs that can produce higher-resolution images, allowing for more detailed visualization of brain structures.
- Artificial intelligence: The use of AI algorithms to analyze CT brain scan images, enabling doctors to diagnose conditions more quickly and accurately.
- Functional CT scans: The development of functional CT scans that can measure brain activity and function, rather than just structure.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, CT brain scans are a vital diagnostic tool that has revolutionized the field of neurology. Their ability to provide detailed images of the brain has enabled doctors to diagnose and treat a wide range of brain-related disorders, from strokes and tumors to injuries and infections. As medical technology continues to evolve, it is likely that the use of CT brain scans will become even more prevalent, leading to improved patient outcomes and a better understanding of the human brain. If you or a loved one has been referred for a CT brain scan, it is essential to understand the procedure, benefits, and risks involved. By working closely with your healthcare team, you can ensure that you receive the best possible care and achieve optimal results.What is a CT brain scan?
+A CT brain scan is a non-invasive medical imaging procedure that uses computerized tomography (CT) technology to produce detailed cross-sectional images of the brain.
What are the benefits of CT brain scans?
+The benefits of CT brain scans include rapid diagnosis, high accuracy, non-invasive procedure, and cost-effectiveness.
What are the risks and side effects of CT brain scans?
+The risks and side effects of CT brain scans include radiation exposure, contrast agent reactions, claustrophobia, and kidney damage.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of CT brain scans and their importance in modern medicine. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others. By working together, we can promote greater awareness and understanding of this vital diagnostic tool and its role in improving patient outcomes.
