Intro
Jaundice in newborns is a common condition that affects many infants in the first few weeks of life. It is characterized by a yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes, caused by a buildup of bilirubin in the blood. While it can be a concerning condition for new parents, there are several effective treatments and home remedies that can help alleviate the symptoms and prevent complications. In this article, we will delve into the world of jaundice in newborns, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Jaundice is a relatively common condition that affects approximately 60% of full-term newborns and 80% of premature infants. It typically appears in the first few days of life and resolves on its own within a week or two. However, in some cases, jaundice can persist or worsen, requiring medical attention. The good news is that with prompt treatment, most babies with jaundice can recover fully and go on to lead healthy lives.
The causes of jaundice in newborns are multifaceted and can be attributed to several factors. One of the primary reasons is the breakdown of red blood cells, which releases bilirubin into the bloodstream. Normally, the liver would process and eliminate bilirubin, but in newborns, the liver may not be mature enough to handle this task efficiently. Other factors that can contribute to jaundice include premature birth, breastfeeding difficulties, and certain medical conditions such as hemolytic disease.
Understanding Jaundice in Newborns
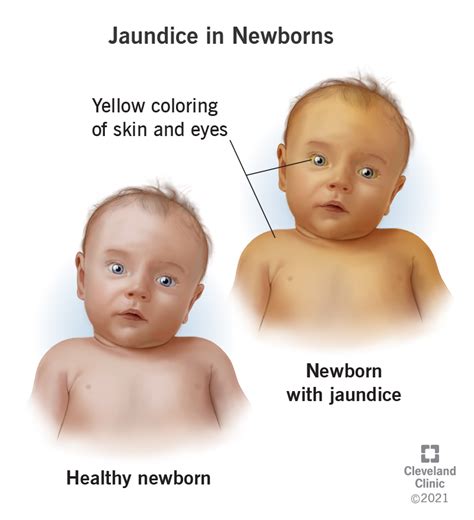
To understand jaundice in newborns, it's essential to recognize the symptoms and signs. These can include yellowish skin and eyes, dark urine, pale stools, and a lack of appetite. In severe cases, jaundice can lead to complications such as kernicterus, a condition that can cause brain damage and developmental delays.
Causes of Jaundice
The causes of jaundice in newborns can be broadly categorized into two main types: physiological and pathological. Physiological jaundice is the most common type and occurs when the liver is still maturing and unable to process bilirubin effectively. Pathological jaundice, on the other hand, is caused by underlying medical conditions such as infections, hemolytic disease, or genetic disorders.Treatment Options for Jaundice

Fortunately, there are several treatment options available for jaundice in newborns. These can range from simple home remedies to more intensive medical interventions. Some of the most common treatments include phototherapy, which involves exposing the baby to special lights that help break down bilirubin, and exchange transfusions, which involve replacing the baby's blood with donor blood to reduce bilirubin levels.
Home Remedies for Jaundice
In addition to medical treatments, there are several home remedies that can help alleviate the symptoms of jaundice in newborns. These can include increasing breastfeeding frequency, ensuring adequate hydration, and using sunlight therapy. Sunlight therapy involves exposing the baby to indirect sunlight, which can help break down bilirubin.Prevention and Complications
While jaundice in newborns can be treated effectively, it's essential to prevent complications from arising. This can involve regular check-ups with a healthcare provider, monitoring bilirubin levels, and seeking medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen. In severe cases, jaundice can lead to complications such as kernicterus, which can have long-term effects on a child's development and cognitive abilities.
Risk Factors for Jaundice
Certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of jaundice in newborns. These can include premature birth, low birth weight, and breastfeeding difficulties. Additionally, babies with a family history of jaundice or those who have undergone certain medical procedures may be at higher risk.Diagnosis and Testing

Diagnosing jaundice in newborns typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. These can include blood tests to measure bilirubin levels, liver function tests, and ultrasound scans to rule out underlying medical conditions.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
After diagnosis, it's essential to monitor the baby's condition closely and follow up with regular check-ups. This can involve tracking bilirubin levels, monitoring for signs of complications, and adjusting treatment plans as necessary.Coping with Jaundice
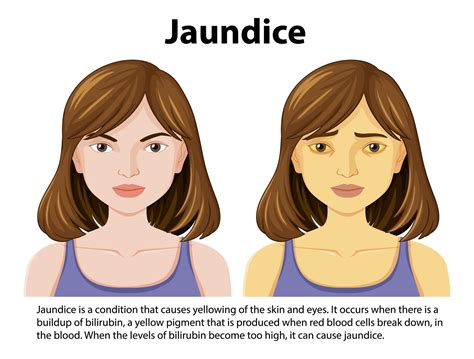
Coping with jaundice in newborns can be challenging for new parents. It's essential to seek support from healthcare providers, family, and friends. Additionally, joining support groups or online forums can connect parents with others who have experienced similar situations.
Emotional Support
Receiving emotional support is crucial for new parents coping with jaundice in their newborn. This can involve counseling, therapy, or simply talking to loved ones about their concerns and feelings.Future Outlook

The future outlook for babies with jaundice is generally positive. With prompt treatment and proper care, most infants can recover fully and lead healthy lives. However, in severe cases, jaundice can have long-term effects on a child's development and cognitive abilities.
Long-Term Effects
In some cases, jaundice can have long-term effects on a child's development and cognitive abilities. This can include learning disabilities, attention deficits, and behavioral problems. However, with early intervention and proper care, these effects can be minimized.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, jaundice in newborns is a common condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, new parents can take the necessary steps to ensure their baby receives the best possible care. If you suspect your baby has jaundice, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with jaundice in newborns in the comments section below. Your input can help others who may be going through similar situations. Additionally, please share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
What are the symptoms of jaundice in newborns?
+The symptoms of jaundice in newborns include yellowish skin and eyes, dark urine, pale stools, and a lack of appetite.
How is jaundice in newborns diagnosed?
+Jaundice in newborns is typically diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, including blood tests and liver function tests.
What are the treatment options for jaundice in newborns?
+The treatment options for jaundice in newborns include phototherapy, exchange transfusions, and home remedies such as increasing breastfeeding frequency and ensuring adequate hydration.
Can jaundice in newborns be prevented?
+While jaundice in newborns cannot be completely prevented, certain risk factors can be minimized, such as premature birth and breastfeeding difficulties.
What are the long-term effects of jaundice in newborns?
+In severe cases, jaundice can have long-term effects on a child's development and cognitive abilities, including learning disabilities, attention deficits, and behavioral problems.
