Intro
Learn about D Dimer blood test results, understanding elevated levels, and its relation to blood clotting, thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism diagnosis, with insights into normal ranges and abnormal test outcomes.
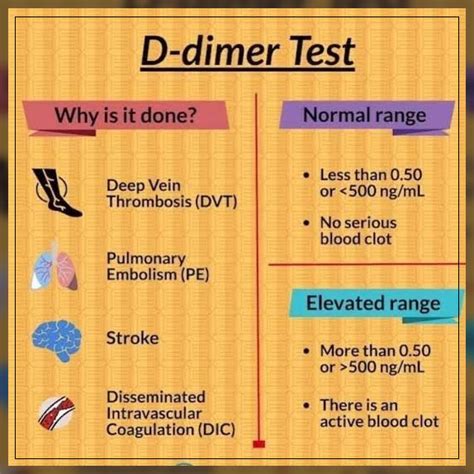
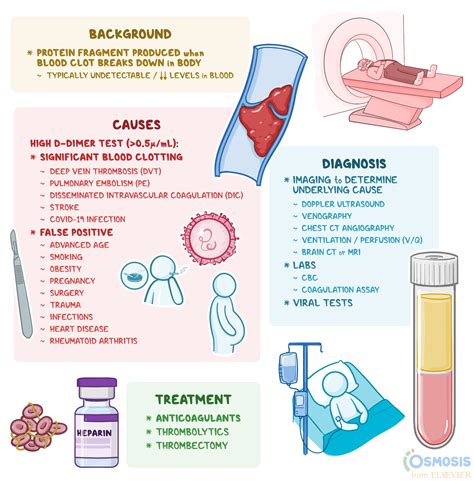
The D-dimer blood test has become a crucial diagnostic tool in the medical field, particularly in detecting and managing conditions related to blood clotting. It's essential to understand the significance of this test and how its results can impact patient care. The D-dimer test measures the levels of a protein fragment called D-dimer in the blood, which is produced when a blood clot dissolves. Elevated D-dimer levels can indicate the presence of a blood clot, making this test a vital component of diagnostic protocols for various conditions, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), and disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC).
The importance of the D-dimer blood test lies in its ability to help healthcare providers diagnose and manage blood clotting disorders effectively. Blood clots can be life-threatening if left untreated, and early detection is crucial for preventing complications. The D-dimer test is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests, such as imaging studies, to confirm the presence of a blood clot. By understanding the results of the D-dimer test, healthcare providers can make informed decisions about patient care, including the need for anticoagulant therapy or further testing.
The D-dimer blood test is a relatively simple and non-invasive procedure that involves collecting a blood sample from a patient's vein. The sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where the levels of D-dimer are measured. The results of the test are typically reported as either positive or negative, with positive results indicating elevated D-dimer levels. However, the interpretation of D-dimer test results can be complex, and healthcare providers must consider various factors, including the patient's medical history, symptoms, and other laboratory results. In this article, we will delve into the details of the D-dimer blood test, its applications, and the interpretation of its results.
D Dimer Test Overview
How the D Dimer Test Works
The D-dimer test works by detecting the presence of D-dimer in the blood. When a blood clot forms, it is made up of platelets, fibrinogen, and other clotting factors. As the clot dissolves, the fibrinogen is broken down into smaller fragments, including D-dimer. The D-dimer test measures the levels of these fragments in the blood, which can indicate the presence of a blood clot. The test is highly sensitive, meaning that it can detect even small amounts of D-dimer in the blood. However, the test is not specific, meaning that elevated D-dimer levels can be caused by various conditions, including recent surgery, trauma, or inflammation.Interpreting D Dimer Test Results
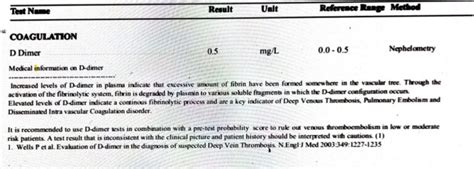
- A D-dimer level of less than 250 ng/mL is generally considered negative.
- A D-dimer level of 250-500 ng/mL is considered borderline.
- A D-dimer level of greater than 500 ng/mL is considered positive.
D Dimer Test Results in Different Conditions
The D-dimer test can be used to diagnose and manage various conditions related to blood clotting. The following are some examples of how the D-dimer test can be used in different conditions:- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): A positive D-dimer test result can indicate the presence of a blood clot in the deep veins of the legs.
- Pulmonary embolism (PE): A positive D-dimer test result can indicate the presence of a blood clot in the lungs.
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC): A positive D-dimer test result can indicate the presence of a blood clotting disorder that affects the entire body.
Applications of the D Dimer Test
- Diagnosing blood clotting disorders: The D-dimer test can be used to diagnose conditions such as DVT, PE, and DIC.
- Monitoring anticoagulant therapy: The D-dimer test can be used to monitor the effectiveness of anticoagulant therapy in patients with blood clotting disorders.
- Evaluating patients with suspected blood clots: The D-dimer test can be used to evaluate patients who present with symptoms of a blood clot, such as leg pain or shortness of breath.
Limitations of the D Dimer Test
While the D-dimer test is a valuable diagnostic tool, it has several limitations. The test is not specific, meaning that elevated D-dimer levels can be caused by various conditions, including recent surgery, trauma, or inflammation. Additionally, the test may not detect all types of blood clots, particularly those that are small or located in unusual areas. Therefore, the D-dimer test should be used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests, such as imaging studies, to confirm the presence of a blood clot.D Dimer Test and Other Diagnostic Tests
- Imaging studies: Imaging studies, such as ultrasound or CT scans, can be used to visualize the blood clot and confirm its presence.
- Blood tests: Other blood tests, such as the prothrombin time (PT) or partial thromboplastin time (PTT), can be used to evaluate the patient's blood clotting function.
- Physical examination: A physical examination can be used to evaluate the patient's symptoms and signs, such as leg pain or swelling.
Combining the D Dimer Test with Other Diagnostic Tests
Combining the D-dimer test with other diagnostic tests can improve the accuracy of diagnosis and treatment. For example, a patient who presents with symptoms of a blood clot may undergo a D-dimer test, followed by an imaging study to confirm the presence of a clot. The results of these tests can be used to guide treatment, including anticoagulant therapy or further testing.Conclusion and Future Directions

The D-dimer test has the potential to improve patient outcomes by allowing for early detection and treatment of blood clotting disorders. However, further research is needed to fully understand the benefits and limitations of the test. By continuing to develop and refine the D-dimer test, healthcare providers can improve patient care and reduce the risk of complications associated with blood clotting disorders.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about the D-dimer blood test in the comments below. If you have undergone a D-dimer test or have experience with blood clotting disorders, we would love to hear about your experience. Your feedback and insights can help us better understand the needs and concerns of patients and healthcare providers, and can inform future research and development of the D-dimer test.
What is the D-dimer test used for?
+The D-dimer test is used to diagnose and manage conditions related to blood clotting, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), and disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC).
How is the D-dimer test performed?
+The D-dimer test involves collecting a blood sample from a patient's vein and sending it to a laboratory for analysis.
What do the results of the D-dimer test mean?
+The results of the D-dimer test can indicate the presence of a blood clot, with elevated D-dimer levels suggesting the presence of a clot. However, the test is not specific, and elevated D-dimer levels can be caused by various conditions.
Can the D-dimer test be used to monitor anticoagulant therapy?
+Yes, the D-dimer test can be used to monitor the effectiveness of anticoagulant therapy in patients with blood clotting disorders.
What are the limitations of the D-dimer test?
+The D-dimer test has several limitations, including its lack of specificity and sensitivity. The test may not detect all types of blood clots, and elevated D-dimer levels can be caused by various conditions.
