Intro
Learn about pregnancy blood pressure changes, hypertension risks, and gestational blood pressure management to ensure a healthy pregnancy, preeclampsia prevention, and fetal well-being.
Pregnancy is a complex and multifaceted process that brings about numerous changes in a woman's body. One of the key aspects of pregnancy is the impact it has on blood pressure. Blood pressure changes during pregnancy are a normal occurrence, but they can also be a cause for concern if not properly managed. It is essential for expectant mothers to understand the changes that occur in their blood pressure during pregnancy and how to maintain a healthy blood pressure level.
The importance of monitoring blood pressure during pregnancy cannot be overstated. High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, can lead to complications such as preeclampsia, a condition that can be life-threatening for both the mother and the baby. On the other hand, low blood pressure, or hypotension, can also cause issues, including dizziness and fainting. Therefore, it is crucial for pregnant women to work closely with their healthcare providers to monitor their blood pressure and address any concerns that may arise.
Understanding the changes in blood pressure during pregnancy is vital for expectant mothers. Blood pressure typically decreases during the early stages of pregnancy due to the relaxation of blood vessels, which allows for increased blood flow to the placenta. However, as the pregnancy progresses, blood pressure may increase, and some women may develop hypertension. The exact causes of high blood pressure during pregnancy are not fully understood, but factors such as genetics, obesity, and pre-existing medical conditions can contribute to its development.
Normal Blood Pressure Changes During Pregnancy
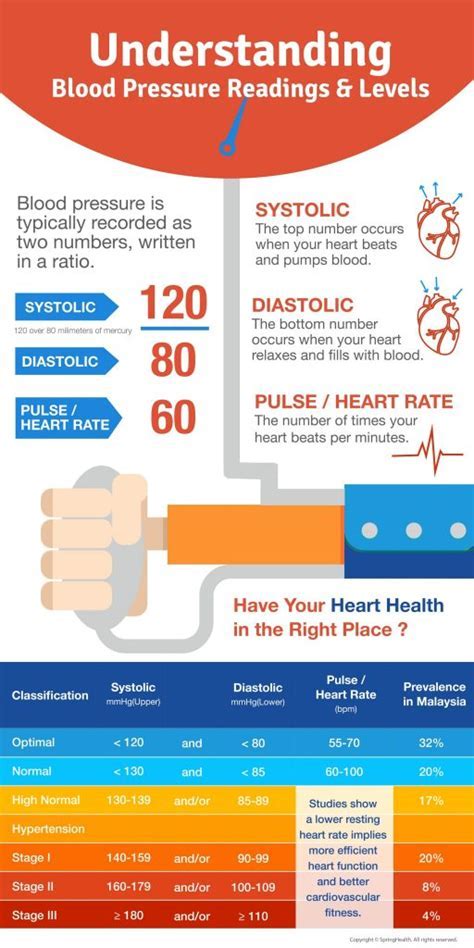
Normal blood pressure changes during pregnancy can vary from woman to woman. In general, blood pressure tends to decrease during the first trimester, reaching its lowest point around 16-18 weeks of gestation. After this point, blood pressure typically begins to rise, returning to pre-pregnancy levels by around 36-40 weeks. However, some women may experience more significant changes in their blood pressure, and it is essential to monitor these changes closely to prevent complications.
Factors Affecting Blood Pressure During Pregnancy
Several factors can influence blood pressure during pregnancy, including: * Genetics: Women with a family history of hypertension are more likely to develop high blood pressure during pregnancy. * Obesity: Excess weight can increase the risk of developing hypertension. * Pre-existing medical conditions: Women with pre-existing medical conditions, such as kidney disease or diabetes, are more likely to experience blood pressure changes during pregnancy. * Age: Women over the age of 35 are at a higher risk of developing hypertension during pregnancy. * Multiple pregnancy: Carrying twins or other multiples can increase the risk of high blood pressure.High Blood Pressure During Pregnancy
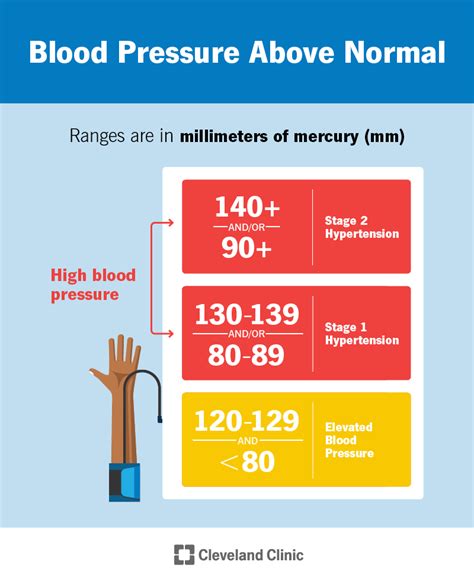
High blood pressure during pregnancy is a significant concern, as it can lead to complications such as preeclampsia. Preeclampsia is a condition characterized by high blood pressure and damage to organs such as the liver and kidneys. If left untreated, preeclampsia can lead to serious complications, including premature birth, low birth weight, and even death. Women who experience high blood pressure during pregnancy should work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their condition and prevent complications.
Managing High Blood Pressure During Pregnancy
Managing high blood pressure during pregnancy requires a comprehensive approach. Some strategies for managing high blood pressure include: * Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress can help to reduce blood pressure. * Medications: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help lower blood pressure. * Close monitoring: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help to monitor blood pressure and prevent complications.Low Blood Pressure During Pregnancy

Low blood pressure during pregnancy can also be a concern, as it can cause dizziness, fainting, and other symptoms. Low blood pressure is typically defined as a systolic pressure of less than 90 mmHg or a diastolic pressure of less than 60 mmHg. Women who experience low blood pressure during pregnancy should discuss their symptoms with their healthcare provider, as they may need to make lifestyle modifications or receive treatment to manage their condition.
Causes of Low Blood Pressure During Pregnancy
The exact causes of low blood pressure during pregnancy are not fully understood, but several factors can contribute to its development, including: * Dehydration: Inadequate fluid intake can lead to low blood pressure. * Blood loss: Significant blood loss during pregnancy or childbirth can cause low blood pressure. * Medications: Certain medications, such as those used to treat high blood pressure, can cause low blood pressure as a side effect.Preeclampsia and Blood Pressure Changes

Preeclampsia is a serious condition that can occur during pregnancy, characterized by high blood pressure and damage to organs such as the liver and kidneys. Preeclampsia can cause significant changes in blood pressure, and it is essential to monitor blood pressure closely to prevent complications. Women who experience preeclampsia may need to receive treatment, including medications and close monitoring, to manage their condition and prevent serious complications.
Symptoms of Preeclampsia
The symptoms of preeclampsia can vary, but they may include: * High blood pressure * Protein in the urine * Severe headaches * Vision changes * Abdominal pain * Nausea and vomitingMonitoring Blood Pressure During Pregnancy
Monitoring blood pressure during pregnancy is crucial to prevent complications. Women should work closely with their healthcare providers to monitor their blood pressure and address any concerns that may arise. Some strategies for monitoring blood pressure include:
- Regular check-ups: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help to monitor blood pressure and prevent complications.
- Home monitoring: Women may be advised to monitor their blood pressure at home using a blood pressure monitor.
- Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help to reduce blood pressure.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of blood pressure changes during pregnancy is essential to prevent complications. Women who experience changes in their blood pressure should discuss their symptoms with their healthcare provider, as they may need to receive treatment or make lifestyle modifications to manage their condition.Complications of Unmanaged Blood Pressure
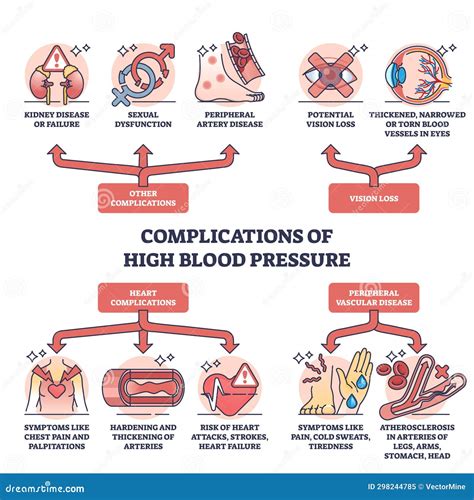
Unmanaged blood pressure during pregnancy can lead to serious complications, including:
- Preeclampsia: High blood pressure can cause damage to organs such as the liver and kidneys.
- Premature birth: High blood pressure can increase the risk of premature birth.
- Low birth weight: High blood pressure can increase the risk of low birth weight.
- Stillbirth: Unmanaged blood pressure can increase the risk of stillbirth.
Preventing Complications
Preventing complications of unmanaged blood pressure requires a comprehensive approach. Women should work closely with their healthcare providers to monitor their blood pressure and address any concerns that may arise. Some strategies for preventing complications include: * Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help to reduce blood pressure. * Medications: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help lower blood pressure. * Close monitoring: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help to monitor blood pressure and prevent complications.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, blood pressure changes during pregnancy are a normal occurrence, but they can also be a cause for concern if not properly managed. It is essential for expectant mothers to understand the changes that occur in their blood pressure during pregnancy and how to maintain a healthy blood pressure level. By working closely with their healthcare providers and making lifestyle modifications, women can reduce their risk of complications and ensure a healthy pregnancy.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with blood pressure changes during pregnancy in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about blood pressure changes during pregnancy.
What are the normal blood pressure changes during pregnancy?
+Normal blood pressure changes during pregnancy can vary from woman to woman. In general, blood pressure tends to decrease during the first trimester, reaching its lowest point around 16-18 weeks of gestation. After this point, blood pressure typically begins to rise, returning to pre-pregnancy levels by around 36-40 weeks.
What are the symptoms of preeclampsia?
+The symptoms of preeclampsia can vary, but they may include high blood pressure, protein in the urine, severe headaches, vision changes, abdominal pain, and nausea and vomiting.
How can I manage high blood pressure during pregnancy?
+Managing high blood pressure during pregnancy requires a comprehensive approach. Some strategies for managing high blood pressure include lifestyle modifications, medications, and close monitoring. Women should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized plan for managing their blood pressure.
