Intro
Manage diabetes with our comprehensive sugar level guide, covering normal ranges, monitoring, and control methods to help regulate blood glucose levels, prevent complications, and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Maintaining a healthy blood sugar level is crucial for individuals with diabetes. Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body processes glucose, a type of sugar that serves as a primary source of energy for the body. When left unmanaged, diabetes can lead to serious complications, including heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. In this article, we will delve into the world of diabetes sugar levels, exploring the importance of monitoring and managing blood glucose levels, and providing tips and strategies for maintaining a healthy balance.
The importance of managing diabetes cannot be overstated. With the rising prevalence of diabetes worldwide, it is essential for individuals with the condition to take an active role in managing their blood sugar levels. This involves working closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan, making lifestyle changes, and monitoring blood glucose levels regularly. By taking control of their diabetes, individuals can reduce their risk of developing complications and improve their overall quality of life.
For individuals with diabetes, understanding the concept of blood sugar levels is vital. Blood sugar levels refer to the amount of glucose present in the blood at any given time. In individuals without diabetes, the body is able to regulate blood sugar levels through the production of insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps to facilitate the uptake of glucose by cells. However, in individuals with diabetes, the body is either unable to produce enough insulin or is unable to effectively use the insulin it produces, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
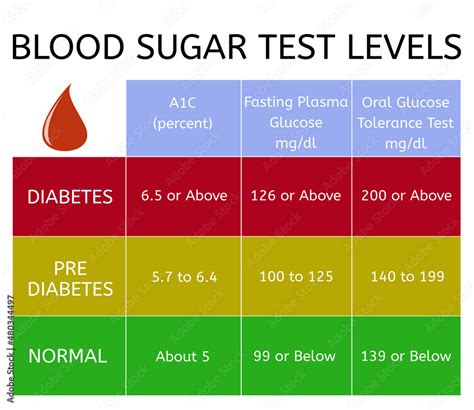
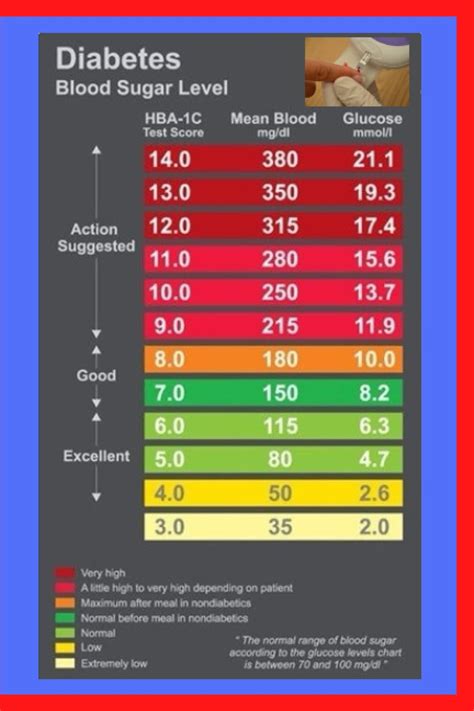
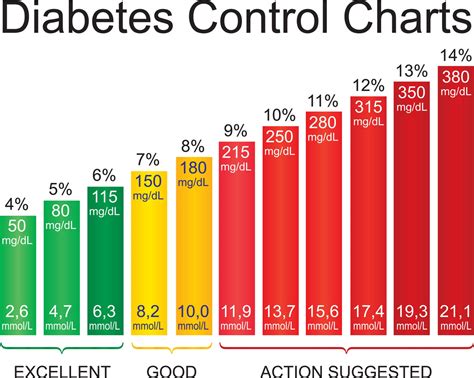
Understanding blood sugar levels is essential for individuals with diabetes. Blood sugar levels are typically measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) and are categorized into several different ranges. Normal blood sugar levels typically range from 70 to 140 mg/dL, although this can vary slightly depending on the individual and the time of day. In individuals with diabetes, blood sugar levels can fluctuate significantly, and it is not uncommon for levels to exceed 200 mg/dL.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Normal blood sugar levels are typically defined as follows: * Fasting blood sugar levels: 70-100 mg/dL * Postprandial blood sugar levels (after eating): Less than 140 mg/dL * Bedtime blood sugar levels: 100-140 mg/dLDiabetes Sugar Level Monitoring
Monitoring blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect of diabetes management. There are several ways to monitor blood sugar levels, including:
- Fingerstick testing: This involves pricking the finger with a small needle to collect a blood sample, which is then placed on a test strip and read using a glucose meter.
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM): This involves wearing a small device that measures blood glucose levels continuously throughout the day.
- Urine testing: This involves testing urine for the presence of ketones, which can indicate high blood sugar levels.
Tips for Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
* Test blood sugar levels at the same time each day to establish a routine * Use a glucose meter that is accurate and easy to use * Keep a log of blood sugar levels to track progress and identify patterns * Work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized monitoring planManaging Diabetes Sugar Levels
Managing diabetes sugar levels involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Some tips for managing diabetes sugar levels include:
- Eating a healthy, balanced diet that is low in sugar and refined carbohydrates
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming
- Taking medications as prescribed by a healthcare provider
- Getting enough sleep and managing stress
Benefits of Managing Diabetes Sugar Levels
* Reduces risk of complications, such as heart disease and kidney damage * Improves overall quality of life * Increases energy levels and reduces fatigue * Supports weight management and reduces risk of obesityDiabetes Sugar Level Targets

Diabetes sugar level targets vary depending on the individual and the type of diabetes. In general, the American Diabetes Association recommends the following targets:
- Fasting blood sugar levels: Less than 130 mg/dL
- Postprandial blood sugar levels (after eating): Less than 180 mg/dL
- A1c levels (average blood sugar levels over 2-3 months): Less than 7%
Strategies for Achieving Diabetes Sugar Level Targets
* Work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan * Monitor blood sugar levels regularly and adjust treatment plan as needed * Make lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activity * Take medications as prescribed by a healthcare providerCommon Diabetes Complications
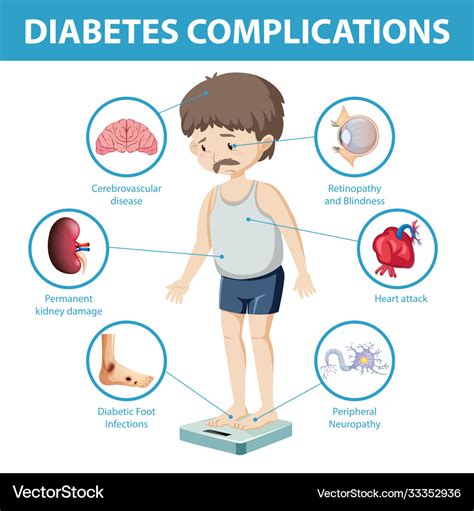
If left unmanaged, diabetes can lead to a range of serious complications, including:
- Heart disease: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and increase risk of heart disease
- Kidney damage: High blood sugar levels can damage kidneys and increase risk of kidney disease
- Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves and increase risk of neuropathy
- Blindness: High blood sugar levels can damage eyes and increase risk of blindness
Preventing Diabetes Complications
* Manage blood sugar levels through lifestyle changes and medical interventions * Monitor blood pressure and cholesterol levels * Get regular check-ups with a healthcare provider * Stay up-to-date on recommended vaccinations and screeningsDiabetes Sugar Level Management Tips

Managing diabetes sugar levels requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Some tips for managing diabetes sugar levels include:
- Eat a healthy, balanced diet that is low in sugar and refined carbohydrates
- Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming
- Get enough sleep and manage stress
- Take medications as prescribed by a healthcare provider
Additional Resources
* American Diabetes Association: [www.diabetes.org](http://www.diabetes.org) * Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: [www.cdc.gov/diabetes](http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes) * National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: [www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes](http://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes)Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, managing diabetes sugar levels is a crucial aspect of diabetes management. By understanding blood sugar levels, monitoring levels regularly, and making lifestyle changes, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of complications and improve their overall quality of life. If you or a loved one has diabetes, it is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan and stay up-to-date on the latest research and recommendations.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with diabetes sugar level management in the comments below. What strategies have you found to be most effective in managing your blood sugar levels? What challenges have you faced, and how have you overcome them? By sharing your story, you can help others who are living with diabetes and inspire them to take control of their condition.
What is the normal range for blood sugar levels?
+Normal blood sugar levels typically range from 70 to 140 mg/dL, although this can vary slightly depending on the individual and the time of day.
How often should I monitor my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of blood sugar monitoring will depend on the individual and their treatment plan. It is generally recommended to monitor blood sugar levels at least 2-3 times per day, although this may vary depending on the individual's needs.
What are the risks of unmanaged diabetes?
+Unmanaged diabetes can lead to a range of serious complications, including heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and blindness.
