Intro
Unlock the secrets of CO2 blood test results, understanding bicarbonate levels, pH balance, and respiratory function to diagnose conditions like respiratory acidosis and alkalosis, and discover how to interpret your CO2 test report accurately.
The importance of understanding CO2 blood test results cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in assessing the overall health and well-being of an individual. A CO2 blood test, also known as a bicarbonate test, measures the level of carbon dioxide in the blood, which is essential for maintaining the body's acid-base balance. The test is commonly used to diagnose and monitor various medical conditions, such as respiratory and kidney diseases, and to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment. In this article, we will delve into the world of CO2 blood test results, exploring what they mean, how they are interpreted, and what factors can influence them.
The CO2 blood test is a simple and non-invasive procedure that involves drawing a blood sample from a vein in the arm. The sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where the level of CO2 is measured in units of milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). The normal range for CO2 levels in the blood is typically between 23 and 29 mEq/L, although this can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the individual's age and health status. Understanding the normal range and how to interpret CO2 blood test results is essential for healthcare professionals and patients alike, as it can help identify potential health problems and guide treatment decisions.
The CO2 blood test is an essential tool for diagnosing and monitoring a range of medical conditions, including respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and pneumonia, as well as kidney diseases like chronic kidney disease (CKD) and kidney failure. The test can also be used to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment for these conditions, as well as to monitor the body's response to changes in diet, medication, or other factors that can affect CO2 levels. By understanding the significance of CO2 blood test results, individuals can take a more active role in managing their health and making informed decisions about their care.
Understanding CO2 Blood Test Results

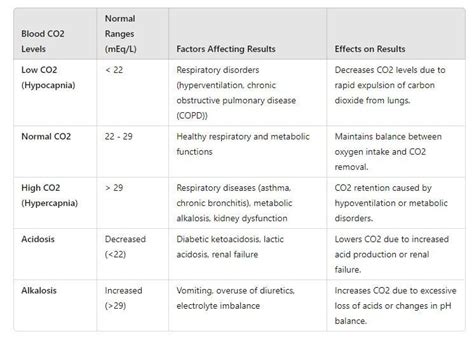
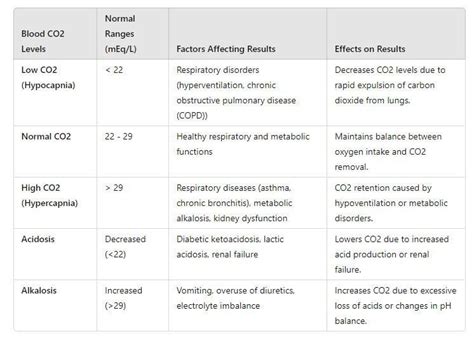
To interpret CO2 blood test results, it is essential to understand the normal range and how it relates to the body's acid-base balance. The normal range for CO2 levels in the blood is typically between 23 and 29 mEq/L, although this can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the individual's age and health status. A CO2 level within this range indicates that the body's acid-base balance is within normal limits. However, if the CO2 level is outside of this range, it can indicate a range of potential health problems, including respiratory and kidney diseases.
Normal CO2 Levels
A normal CO2 level is typically between 23 and 29 mEq/L, although this can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the individual's age and health status. A CO2 level within this range indicates that the body's acid-base balance is within normal limits. Normal CO2 levels are essential for maintaining proper bodily functions, including nerve and muscle function, as well as the health of the kidneys and liver.Abnormal CO2 Levels
An abnormal CO2 level can indicate a range of potential health problems, including respiratory and kidney diseases. If the CO2 level is too high, it can indicate a condition known as respiratory acidosis, which occurs when the lungs are not able to remove enough CO2 from the blood. This can be caused by a range of factors, including COPD, pneumonia, and other respiratory diseases. On the other hand, if the CO2 level is too low, it can indicate a condition known as respiratory alkalosis, which occurs when the lungs are removing too much CO2 from the blood. This can be caused by a range of factors, including hyperventilation, asthma, and other respiratory diseases.Factors That Influence CO2 Blood Test Results

There are several factors that can influence CO2 blood test results, including diet, medication, and underlying medical conditions. For example, a diet that is high in fruits and vegetables can increase CO2 levels, while a diet that is high in meat and dairy products can decrease CO2 levels. Certain medications, such as diuretics and steroids, can also affect CO2 levels. Additionally, underlying medical conditions, such as kidney disease and respiratory disease, can also influence CO2 blood test results.
Diet and CO2 Levels
Diet can play a significant role in influencing CO2 blood test results. A diet that is high in fruits and vegetables can increase CO2 levels, while a diet that is high in meat and dairy products can decrease CO2 levels. This is because fruits and vegetables are high in bicarbonate, which can increase CO2 levels, while meat and dairy products are high in acid, which can decrease CO2 levels.Medication and CO2 Levels
Certain medications can also affect CO2 levels. For example, diuretics, which are used to treat high blood pressure and kidney disease, can decrease CO2 levels by increasing the amount of bicarbonate in the urine. Steroids, which are used to treat a range of conditions, including asthma and arthritis, can also affect CO2 levels by increasing the amount of bicarbonate in the blood.CO2 Blood Test Results and Health
CO2 blood test results can provide valuable insights into an individual's health and well-being. By understanding the normal range and how to interpret CO2 blood test results, individuals can take a more active role in managing their health and making informed decisions about their care. For example, if an individual has a high CO2 level, they may need to make lifestyle changes, such as increasing their physical activity or changing their diet, to help lower their CO2 level and reduce their risk of developing related health problems.
CO2 Blood Test Results and Respiratory Disease
CO2 blood test results can be particularly useful in diagnosing and monitoring respiratory diseases, such as COPD and pneumonia. By measuring the level of CO2 in the blood, healthcare professionals can determine if the lungs are functioning properly and if the body's acid-base balance is within normal limits. If the CO2 level is too high, it can indicate a condition known as respiratory acidosis, which occurs when the lungs are not able to remove enough CO2 from the blood.CO2 Blood Test Results and Kidney Disease
CO2 blood test results can also be useful in diagnosing and monitoring kidney diseases, such as CKD and kidney failure. By measuring the level of CO2 in the blood, healthcare professionals can determine if the kidneys are functioning properly and if the body's acid-base balance is within normal limits. If the CO2 level is too low, it can indicate a condition known as metabolic acidosis, which occurs when the kidneys are not able to remove enough acid from the blood.Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, understanding CO2 blood test results is essential for maintaining good health and well-being. By interpreting CO2 blood test results correctly, individuals can identify potential health problems and take steps to prevent or manage them. If you have any concerns about your CO2 blood test results or would like to learn more about how to interpret them, it is essential to speak with a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized guidance and support to help you understand your results and make informed decisions about your care.
What is a normal CO2 level in the blood?
+A normal CO2 level in the blood is typically between 23 and 29 mEq/L, although this can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the individual's age and health status.
What does a high CO2 level indicate?
+A high CO2 level can indicate a condition known as respiratory acidosis, which occurs when the lungs are not able to remove enough CO2 from the blood. This can be caused by a range of factors, including COPD, pneumonia, and other respiratory diseases.
What does a low CO2 level indicate?
+A low CO2 level can indicate a condition known as respiratory alkalosis, which occurs when the lungs are removing too much CO2 from the blood. This can be caused by a range of factors, including hyperventilation, asthma, and other respiratory diseases.
How can I lower my CO2 level if it is too high?
+If your CO2 level is too high, you may need to make lifestyle changes, such as increasing your physical activity or changing your diet, to help lower your CO2 level and reduce your risk of developing related health problems. It is essential to speak with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and support.
How can I raise my CO2 level if it is too low?
+If your CO2 level is too low, you may need to make lifestyle changes, such as increasing your bicarbonate intake or changing your diet, to help raise your CO2 level and reduce your risk of developing related health problems. It is essential to speak with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and support.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of CO2 blood test results and their significance in maintaining good health and well-being. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional. Additionally, we invite you to share this article with others who may benefit from this information, and to leave a comment below with any thoughts or feedback you may have. By working together, we can promote better health and well-being for all.
