Intro
Learn about 5 diabetes sugar levels, including normal, prediabetes, and diabetic ranges, and understand blood glucose monitoring, sugar control, and healthy targets to manage diabetes effectively.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes. Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and managing sugar levels is essential to prevent complications and improve quality of life. In this article, we will delve into the importance of monitoring and controlling diabetes sugar levels, exploring the benefits, working mechanisms, and steps to achieve optimal glucose management.
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels, which can lead to damage to various organs and tissues in the body. There are different types of diabetes, including type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes, each with distinct causes and symptoms. Regardless of the type, managing diabetes sugar levels is vital to prevent long-term complications, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
Effective diabetes management involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels. By understanding the factors that affect glucose levels, individuals with diabetes can make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and treatment plans. This knowledge enables them to take control of their condition, reducing the risk of complications and improving their overall well-being.
Understanding Diabetes Sugar Levels
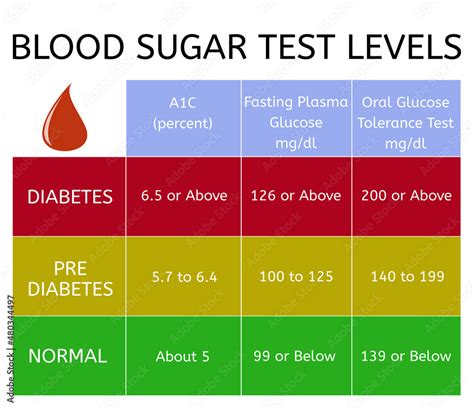
To manage diabetes effectively, it is essential to understand the concept of blood sugar levels. Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is a type of sugar that serves as the primary source of energy for the body's cells. In individuals with diabetes, the body either cannot produce enough insulin, a hormone that regulates glucose levels, or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. As a result, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Normal blood sugar levels vary throughout the day, depending on factors such as meal times, physical activity, and sleep patterns. In general, a normal fasting blood sugar level is between 70 and 99 mg/dL, while a normal postprandial (after meal) blood sugar level is less than 140 mg/dL. For individuals with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends the following target blood sugar levels: * Fasting blood sugar: 80-130 mg/dL * Postprandial blood sugar: Less than 180 mg/dLFactors Affecting Diabetes Sugar Levels
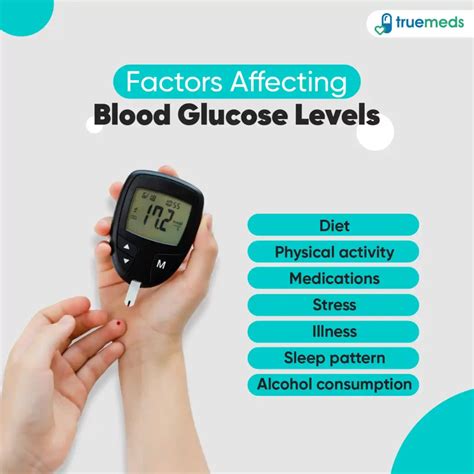
Several factors can affect diabetes sugar levels, including:
- Diet: The type and amount of carbohydrates consumed can impact blood sugar levels. Foods high in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats can cause blood sugar spikes.
- Physical activity: Regular exercise can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Medication: Certain medications, such as metformin and sulfonylureas, can help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Stress: Stress can raise blood sugar levels by stimulating the release of stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline.
- Sleep: Poor sleep quality and duration can disrupt blood sugar regulation and insulin sensitivity.
Monitoring Diabetes Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes. There are several ways to monitor blood sugar levels, including: * Fingertip blood glucose testing: This involves pricking the fingertip with a lancet to collect a blood sample, which is then tested using a glucose meter. * Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM): This involves wearing a small device that measures blood sugar levels continuously throughout the day. * Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) testing: This involves a blood test that measures average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.Managing Diabetes Sugar Levels
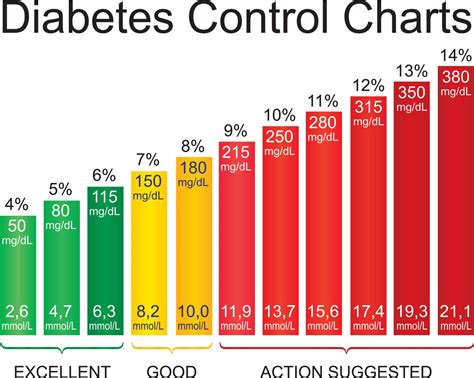
Managing diabetes sugar levels involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medication. The following are some strategies for managing diabetes sugar levels:
- Eat a healthy, balanced diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Engage in regular physical activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week.
- Take medication as prescribed: Work with your healthcare provider to develop a medication plan that helps regulate blood sugar levels.
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly: Use a glucose meter or CGM to track blood sugar levels and make adjustments to your treatment plan as needed.
Benefits of Managing Diabetes Sugar Levels
Managing diabetes sugar levels can have numerous benefits, including: * Reduced risk of complications: High blood sugar levels can damage organs and tissues, leading to complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. * Improved quality of life: Managing diabetes sugar levels can improve energy levels, reduce symptoms, and enhance overall well-being. * Increased life expectancy: Studies have shown that individuals with diabetes who manage their blood sugar levels effectively can live longer, healthier lives.Common Complications of Unmanaged Diabetes Sugar Levels
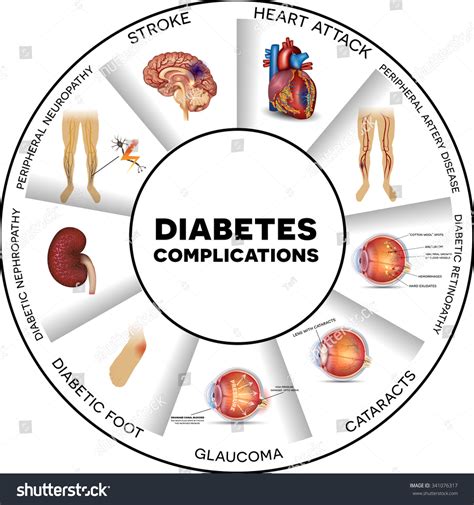
Unmanaged diabetes sugar levels can lead to several complications, including:
- Heart disease: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, increasing the risk of heart disease.
- Kidney damage: Diabetes is the leading cause of kidney failure, accounting for approximately 40% of all cases.
- Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet.
- Blindness: Diabetes is the leading cause of blindness in adults, accounting for approximately 10% of all cases.
Preventing Complications
Preventing complications of unmanaged diabetes sugar levels involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medication. The following are some strategies for preventing complications: * Work with your healthcare provider: Develop a treatment plan that includes regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, medication, and lifestyle modifications. * Eat a healthy, balanced diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. * Engage in regular physical activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week.Current Research and Developments

Current research and developments in diabetes management are focused on improving treatment options and outcomes for individuals with diabetes. Some of the current research areas include:
- Stem cell therapy: Researchers are exploring the use of stem cells to repair or replace damaged pancreatic cells, which could potentially cure type 1 diabetes.
- Artificial pancreas: Researchers are developing an artificial pancreas, which is a device that can automatically monitor and regulate blood sugar levels.
- Personalized medicine: Researchers are working on developing personalized treatment plans that take into account an individual's unique genetic profile, medical history, and lifestyle.
Future Directions
The future of diabetes management looks promising, with several new technologies and treatments on the horizon. Some of the future directions include: * Gene editing: Researchers are exploring the use of gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR, to develop new treatments for diabetes. * Immunotherapy: Researchers are working on developing immunotherapies that can help regulate the immune system and prevent autoimmune attacks on pancreatic cells. * Bionic pancreas: Researchers are developing a bionic pancreas, which is a device that can automatically monitor and regulate blood sugar levels.What are the symptoms of high blood sugar levels?
+High blood sugar levels can cause symptoms such as increased thirst and urination, blurred vision, fatigue, and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
How often should I monitor my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of monitoring blood sugar levels depends on the individual and their treatment plan. Generally, it is recommended to monitor blood sugar levels at least 4-6 times per day.
What are the benefits of managing diabetes sugar levels?
+Managing diabetes sugar levels can reduce the risk of complications, improve quality of life, and increase life expectancy.
In conclusion, managing diabetes sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes. By understanding the factors that affect glucose levels, monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, and making lifestyle modifications, individuals with diabetes can take control of their condition and reduce the risk of complications. We encourage readers to share their experiences and tips for managing diabetes sugar levels in the comments below. Additionally, we invite readers to share this article with others who may benefit from this information. By working together, we can improve diabetes management and reduce the risk of complications.
