Intro
Monitor and manage diabetic blood glucose levels with our comprehensive guide, covering normal range, testing, and control strategies to prevent complications, including hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia, and maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
Maintaining healthy blood glucose levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes. Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and managing blood sugar levels is essential to prevent complications and improve quality of life. In this article, we will delve into the world of diabetic blood glucose levels, exploring the importance of monitoring, the factors that affect blood sugar levels, and providing practical tips for managing diabetes.
The importance of monitoring blood glucose levels cannot be overstated. Regular monitoring helps individuals with diabetes understand how their body responds to different foods, physical activity, and medications. By tracking blood sugar levels, individuals can identify patterns and make informed decisions to maintain healthy levels. Furthermore, monitoring blood glucose levels helps to prevent complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
Effective management of diabetes requires a comprehensive approach that includes a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and medication (if prescribed). A healthy diet plays a vital role in managing blood sugar levels, and individuals with diabetes should focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins. Regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, can also help to lower blood sugar levels and improve overall health.
Understanding Blood Glucose Levels
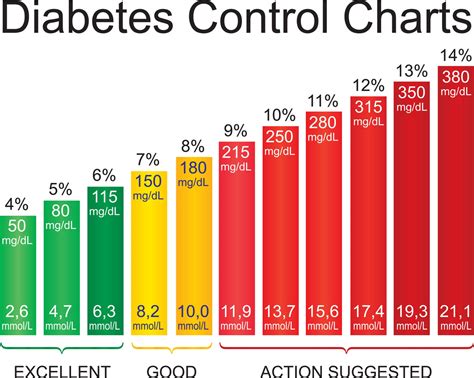
Blood glucose levels refer to the amount of glucose (sugar) present in the blood. In individuals with diabetes, the body either cannot produce enough insulin (type 1 diabetes) or cannot effectively use insulin (type 2 diabetes), leading to high blood sugar levels. The American Diabetes Association recommends the following blood glucose levels for individuals with diabetes:
- Fasting blood glucose: less than 130 mg/dL
- Before meals: 70-130 mg/dL
- After meals: less than 180 mg/dL
- At bedtime: 100-140 mg/dL
Factors That Affect Blood Glucose Levels
Several factors can affect blood glucose levels, including: * Diet: Consuming high-carbohydrate or high-sugar foods can raise blood sugar levels. * Physical activity: Regular physical activity can lower blood sugar levels. * Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and certain antibiotics, can raise blood sugar levels. * Stress: Stress can raise blood sugar levels by releasing hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline. * Sleep: Poor sleep quality or duration can affect blood sugar levels.Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
Monitoring blood glucose levels is a crucial aspect of diabetes management. There are several ways to monitor blood glucose levels, including:
- Fingerstick testing: This involves pricking the finger with a lancet to collect a blood sample, which is then placed on a test strip and read by a glucose meter.
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM): This involves wearing a small device that measures glucose levels throughout the day and night.
- Urine testing: This involves testing urine for ketones, which can indicate high blood sugar levels.
Tips for Managing Blood Glucose Levels
Here are some practical tips for managing blood glucose levels: * Eat a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. * Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, to help lower blood sugar levels. * Take medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider. * Get enough sleep and practice stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing. * Monitor blood glucose levels regularly and adjust your treatment plan as needed.Complications of Unmanaged Diabetes
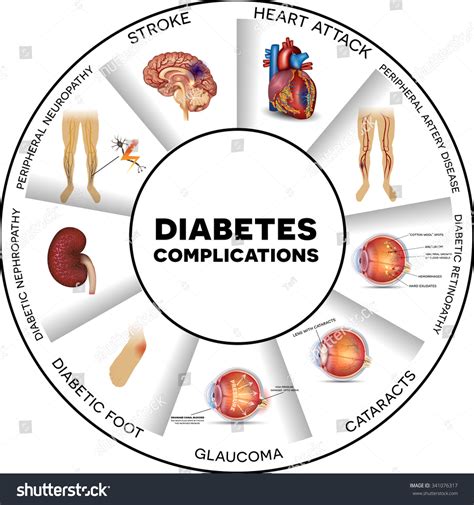
Unmanaged diabetes can lead to several complications, including:
- Heart disease: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of heart disease.
- Kidney damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys and increase the risk of kidney failure.
- Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves and cause numbness, tingling, and pain.
- Blindness: High blood sugar levels can damage the eyes and increase the risk of blindness.
- Amputations: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves and blood vessels, increasing the risk of amputations.
Preventing Complications
Preventing complications requires a comprehensive approach that includes: * Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels * Maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine * Taking medications as prescribed * Getting enough sleep and practicing stress-reducing techniques * Regular check-ups with your healthcare providerLifestyle Changes for Managing Diabetes

Making lifestyle changes is essential for managing diabetes. Here are some tips:
- Eat a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, to help lower blood sugar levels.
- Get enough sleep and practice stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing.
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
Stress Management
Stress can raise blood sugar levels, so it's essential to manage stress effectively. Here are some tips: * Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation. * Engage in regular physical activity to help reduce stress. * Get enough sleep to help regulate stress hormones. * Connect with friends and family to build a support network. * Consider seeking professional help if you're struggling to manage stress.Medications for Managing Diabetes
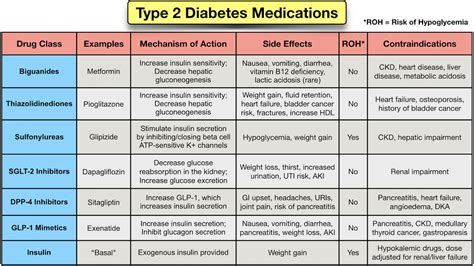
Medications can help manage diabetes by lowering blood sugar levels. Here are some common medications used to treat diabetes:
- Metformin: This medication helps lower blood sugar levels by improving insulin sensitivity.
- Sulfonylureas: These medications stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin.
- Meglitinides: These medications stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin.
- Thiazolidinediones: These medications improve insulin sensitivity.
- GLP-1 receptor agonists: These medications help lower blood sugar levels by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing glucose production in the liver.
Insulin Therapy
Insulin therapy is often necessary for individuals with type 1 diabetes and some individuals with type 2 diabetes. Here are some tips for managing insulin therapy: * Work with your healthcare provider to determine the best insulin regimen for your needs. * Monitor blood glucose levels regularly to adjust your insulin dosage. * Use an insulin pump or inject insulin via a syringe or pen. * Rotate injection sites to avoid lipodystrophy.What is the normal range for blood glucose levels?
+The normal range for blood glucose levels is between 70-130 mg/dL for individuals with diabetes.
How often should I monitor my blood glucose levels?
+The frequency of monitoring blood glucose levels depends on your individual needs and treatment plan. Typically, individuals with diabetes monitor their blood glucose levels at least 4-6 times per day.
What are the complications of unmanaged diabetes?
+Unmanaged diabetes can lead to several complications, including heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, blindness, and amputations.
In conclusion, managing diabetic blood glucose levels requires a comprehensive approach that includes regular monitoring, a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and medication (if prescribed). By understanding the factors that affect blood glucose levels and making lifestyle changes, individuals with diabetes can maintain healthy blood sugar levels and prevent complications. We encourage you to share this article with friends and family members who may be affected by diabetes, and to comment below with any questions or concerns you may have. Remember, managing diabetes is a journey, and with the right tools and support, you can take control of your health and thrive.
