Intro
The medical condition known as DISH, which stands for Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis, is a fascinating and complex topic that has garnered significant attention in the medical community. As a condition that affects the skeletal system, DISH is characterized by the abnormal growth of bone tissue, leading to a range of symptoms and complications. In this article, we will delve into the world of DISH, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and more. Whether you are a medical professional or simply someone looking to learn more about this condition, this article aims to provide a comprehensive and informative guide to DISH.
The importance of understanding DISH cannot be overstated, as it is a condition that can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life. With its ability to cause chronic pain, stiffness, and limited mobility, DISH can be a debilitating condition that affects not only the physical health but also the mental and emotional well-being of those affected. Furthermore, DISH is often associated with other health conditions, such as diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease, making it a critical condition to understand and manage. As we explore the world of DISH, we will examine the latest research and findings, providing insights into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available.
As we begin our journey into the world of DISH, it is essential to understand the basics of this condition. DISH is a type of skeletal disorder that is characterized by the abnormal growth of bone tissue, leading to the formation of new bone in areas where it is not normally found. This can result in a range of symptoms, including chronic pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. While the exact causes of DISH are still not fully understood, research suggests that it may be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. With its ability to affect anyone, regardless of age or background, DISH is a condition that requires attention and understanding from medical professionals and the general public alike.
What is DISH?
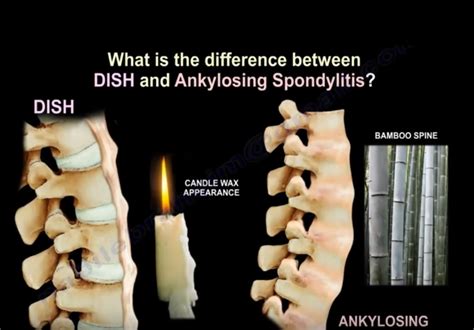
Causes of DISH
The causes of DISH are still not fully understood, but research suggests that it may be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some of the possible causes of DISH include: * Genetic predisposition: Research suggests that DISH may be inherited, with certain genetic mutations increasing the risk of developing the condition. * Hormonal imbalances: Hormonal imbalances, such as an excess of growth hormone, may contribute to the development of DISH. * Inflammatory conditions: Certain inflammatory conditions, such as arthritis, may increase the risk of developing DISH. * Trauma: Trauma to the affected area may trigger the development of DISH.Symptoms of DISH

Diagnosis of DISH
The diagnosis of DISH typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests. Some of the tests used to diagnose DISH include: * X-rays: X-rays can help to identify the abnormal growth of bone tissue and the formation of new bone. * CT scans: CT scans can provide more detailed images of the affected area, helping to confirm the diagnosis. * MRI scans: MRI scans can help to identify any underlying conditions that may be contributing to the development of DISH. * Blood tests: Blood tests can help to rule out other conditions that may be causing the symptoms.Treatment Options for DISH

Complications of DISH
DISH can cause a range of complications, including: * Chronic pain: DISH can cause chronic pain, which can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life. * Limited mobility: The formation of new bone can limit mobility and flexibility, making it difficult to perform daily activities. * Increased risk of fractures: The abnormal growth of bone tissue can increase the risk of fractures, particularly in older adults. * Associated health conditions: DISH is often associated with other health conditions, such as diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease.Living with DISH

Future Directions for DISH Research
Research into DISH is ongoing, with scientists and healthcare professionals working to better understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available. Some of the future directions for DISH research include: * Investigating the genetic causes of DISH: Researchers are working to identify the genetic mutations that contribute to the development of DISH. * Developing new treatment options: Researchers are working to develop new treatment options, such as medications and therapies, to help manage the symptoms of DISH. * Improving diagnosis: Researchers are working to improve diagnosis, developing new tests and imaging techniques to help identify DISH earlier and more accurately.What is the main cause of DISH?
+The main cause of DISH is still not fully understood, but research suggests that it may be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
What are the symptoms of DISH?
+The symptoms of DISH can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the location of the affected area, but common symptoms include chronic pain, stiffness, limited mobility, and swelling.
How is DISH diagnosed?
+DISH is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans.
What are the treatment options for DISH?
+The treatment options for DISH typically depend on the severity of the condition and the location of the affected area, but common treatment options include pain management, physical therapy, surgery, and lifestyle modifications.
Can DISH be prevented?
+While there is no guaranteed way to prevent DISH, maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, and managing stress can help to reduce the risk of developing the condition.
As we conclude our journey into the world of DISH, we hope that this article has provided a comprehensive and informative guide to this complex and fascinating condition. Whether you are a medical professional or simply someone looking to learn more about DISH, we encourage you to share this article with others and to continue exploring the latest research and findings on this topic. By working together, we can better understand DISH and develop new and effective treatment options to help manage its symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected. So, take a moment to share your thoughts and experiences with DISH in the comments below, and let's work together to create a community of support and understanding for those living with this condition.
