Intro
Discover the potential risks of diuretics, including dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and kidney damage, and learn how to manage diuretics side effects, interactions, and long-term consequences with proper medication and lifestyle adjustments.
Diuretics are a type of medication that helps remove excess fluid from the body by increasing urine production. They are commonly used to treat conditions such as high blood pressure, heart failure, and edema. However, like all medications, diuretics can have side effects, some of which can be serious. In this article, we will explore the different types of diuretics, their uses, and their potential side effects.
Diuretics work by increasing the amount of urine produced by the kidneys, which helps to remove excess fluid from the body. This can be beneficial for people with conditions such as high blood pressure, where excess fluid can put extra strain on the heart and blood vessels. Diuretics can also be used to treat conditions such as edema, where excess fluid builds up in the body's tissues. However, diuretics can have side effects, and it is essential to understand these potential side effects to minimize their impact.
The use of diuretics is a common practice in the medical field, and they are often prescribed to patients with cardiovascular diseases. Diuretics can help to reduce blood pressure, improve heart function, and decrease the risk of heart failure. However, it is crucial to weigh the benefits of diuretics against their potential side effects. In this article, we will delve into the world of diuretics, exploring their uses, benefits, and potential side effects.
Types of Diuretics
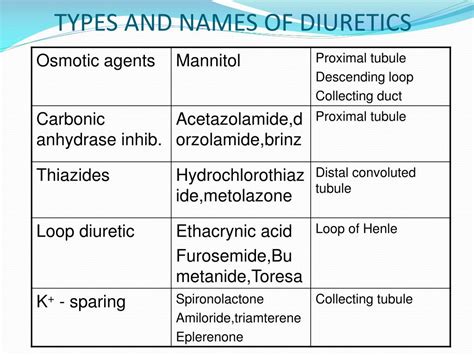
Thiazide Diuretics
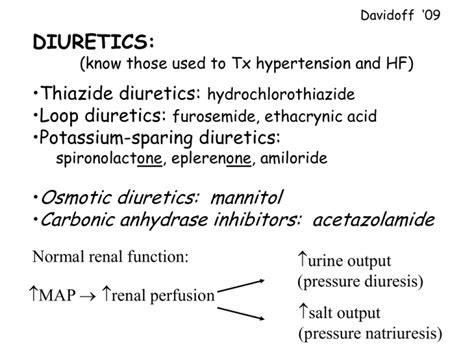
Thiazide diuretics are one of the most commonly used types of diuretics. They are often prescribed to treat high blood pressure, edema, and heart failure. Thiazide diuretics work by inhibiting the reabsorption of sodium and chloride in the kidneys, which helps to increase urine production. However, thiazide diuretics can have side effects, such as hypokalemia (low potassium levels), hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), and increased uric acid levels.Loop Diuretics
Loop diuretics are another type of diuretic that works by inhibiting the reabsorption of sodium, chloride, and potassium in the kidneys. Loop diuretics are often prescribed to treat edema, heart failure, and nephrotic syndrome. However, loop diuretics can have side effects, such as hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia (low magnesium levels), and ototoxicity (hearing loss).Potassium-Sparing Diuretics
Potassium-sparing diuretics work by inhibiting the reabsorption of sodium and water in the kidneys, while sparing potassium. Potassium-sparing diuretics are often prescribed to treat edema, heart failure, and hypertension. However, potassium-sparing diuretics can have side effects, such as hyperkalemia (high potassium levels), gynecomastia (breast tissue growth in men), and hirsutism (excessive hair growth).Common Side Effects of Diuretics

Increased Urination
One of the most common side effects of diuretics is increased urination. This can be inconvenient, especially for people who have to urinate frequently during the night. However, increased urination is a sign that the diuretic is working effectively.Dehydration
Dehydration is another common side effect of diuretics. Diuretics can cause the body to lose too much fluid, leading to dehydration. Symptoms of dehydration include dry mouth, dark urine, and dizziness.Electrolyte Imbalance
Diuretics can also cause an electrolyte imbalance, which can lead to serious health problems. Electrolytes, such as potassium, sodium, and chloride, are essential for maintaining proper fluid balance in the body. An electrolyte imbalance can cause muscle cramps, fatigue, and dizziness.Rare but Serious Side Effects of Diuretics

Hypokalemic Paralysis
Hypokalemic paralysis is a rare but serious side effect of diuretics. It occurs when the body loses too much potassium, leading to muscle weakness and paralysis.Torsades de Pointes
Torsades de pointes is a type of irregular heartbeat that can be caused by diuretics. It occurs when the heart's electrical activity becomes abnormal, leading to a rapid and irregular heartbeat.Minimizing the Side Effects of Diuretics

Taking the Medication as Directed
Taking the medication as directed is crucial to minimizing the side effects of diuretics. It is essential to follow the dosage instructions and take the medication at the same time every day.Monitoring Electrolyte Levels
Monitoring electrolyte levels regularly is essential to preventing electrolyte imbalances. Electrolyte levels can be monitored through regular blood tests.Conclusion and Final Thoughts
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with diuretics in the comments section below. Have you or a loved one taken diuretics? What were your experiences with the medication? Do you have any questions or concerns about diuretics? Share your story and let's start a conversation.
What are diuretics used for?
+Diuretics are used to treat conditions such as high blood pressure, heart failure, and edema. They work by increasing urine production, which helps to remove excess fluid from the body.
What are the common side effects of diuretics?
+The common side effects of diuretics include increased urination, dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, hypokalemia, hyperglycemia, and increased uric acid levels.
How can I minimize the side effects of diuretics?
+To minimize the side effects of diuretics, it is essential to take the medication as directed, monitor electrolyte levels regularly, stay hydrated, avoid excessive salt intake, exercise regularly, and manage stress.
