Intro
Identify 5 UTI symptoms, including burning sensations, frequent urination, and abdominal pain, to seek timely treatment for urinary tract infections, bladder issues, and kidney problems, and learn about causes, diagnosis, and remedies for effective relief.
Urinary tract infections, commonly referred to as UTIs, are a prevalent health issue affecting millions of people worldwide. UTIs occur when bacteria, fungi, or viruses infect the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Understanding the symptoms of UTIs is crucial for early detection, treatment, and prevention of complications. In this article, we will delve into the common symptoms of UTIs, explore their causes, and discuss the importance of seeking medical attention.
The urinary tract is designed to prevent bacterial invasion, but under certain conditions, these defenses can fail. When this happens, the bacteria can multiply, leading to an infection. Women are more prone to UTIs due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria easier access to the bladder. However, UTIs can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. Recognizing the symptoms of a UTI is the first step towards effective treatment and recovery.
UTIs can manifest in various ways, ranging from mild to severe. The symptoms can vary depending on the location of the infection within the urinary tract. For instance, an infection in the lower urinary tract, which includes the bladder and urethra, may cause different symptoms than an infection in the upper urinary tract, which includes the kidneys. Common symptoms of a UTI include a burning sensation while urinating, frequent urination, and a strong urge to urinate even when the bladder is not full.
Understanding UTI Symptoms
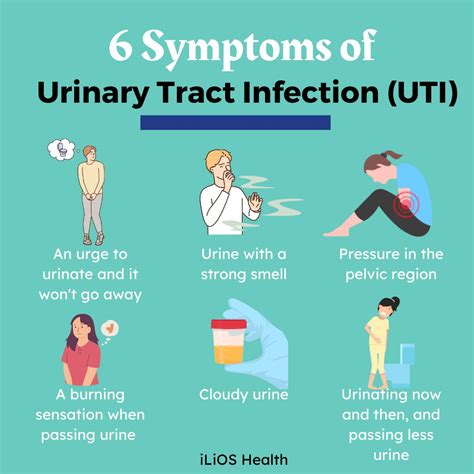
Common Symptoms of UTIs
Some of the most common symptoms of UTIs include: - A strong, persistent urge to urinate - A burning sensation while urinating - Passing frequent, small amounts of urine - Cloudy, dark, or strong-smelling urine - Blood in the urine - Pelvic pain, especially in the center of the pelvis and around the area of the pubic bone Understanding these symptoms is crucial for diagnosing and treating UTIs effectively.Causes of UTIs
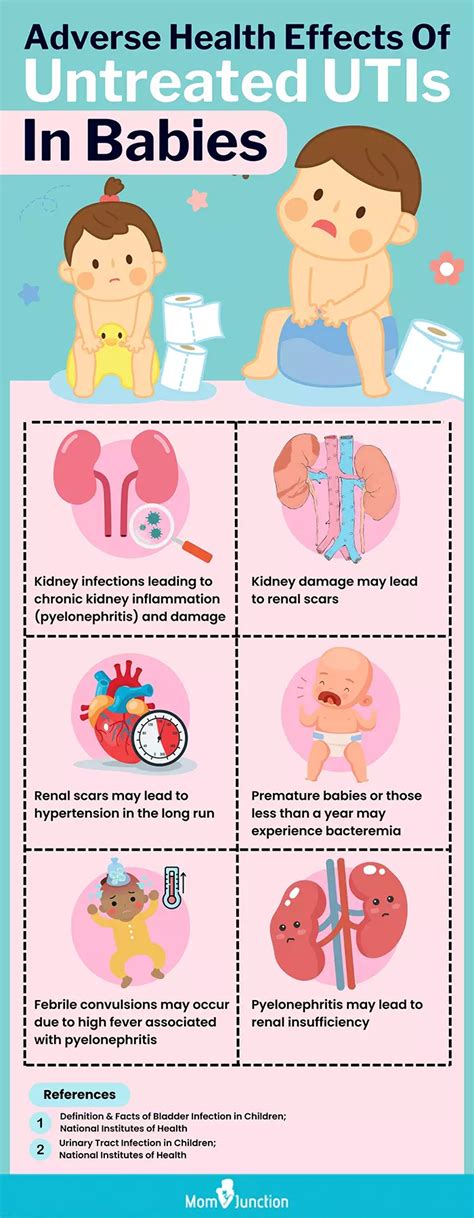
Risk Factors for UTIs
Several factors can increase the risk of developing a UTI, including: - Sexual activity: Sex can push bacteria into the urethra. - Use of certain birth control methods: Diaphragms, spermicides, and catheters can increase the risk. - Menopause: Decreased estrogen levels can cause changes in the urinary tract, making it more susceptible to infection. - Abnormalities in the urinary tract: Any obstruction in the urinary tract, such as kidney stones, can increase the risk of UTIs.Treatment and Prevention of UTIs

Preventive Measures for UTIs
Preventing UTIs involves making lifestyle changes and adopting habits that reduce the risk of infection. Some preventive measures include: - Drinking plenty of water to help flush out bacteria - Urinating when the need arises, rather than delaying - Wiping from front to back after using the toilet to prevent bacteria from entering the urethra - Avoiding the use of scented soaps, bubble baths, and douches, which can irritate the urethraComplications of Untreated UTIs
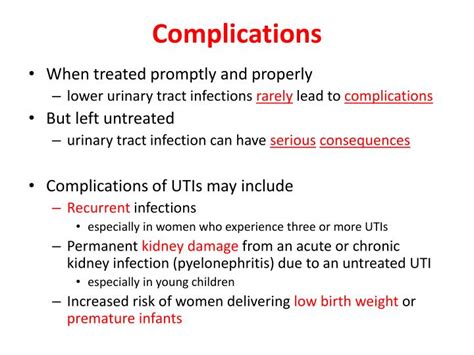
Seeking Medical Attention
If symptoms of a UTI are present, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider. They can diagnose the infection through a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as urinalysis. Prompt treatment can help alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and improve quality of life.Living with UTIs

Recurrent UTIs
Recurrent UTIs, defined as having two or more UTIs in a six-month period, can be challenging to manage. Strategies for managing recurrent UTIs include: - Long-term, low-dose antibiotic therapy - Self-initiated treatment at the onset of symptoms - Preventive measures, such as drinking cranberry juice and taking vitamin C supplementsConclusion and Future Directions

Future Research
Ongoing and future research into UTIs focuses on several key areas, including: - Development of new diagnostic tools for rapid and accurate detection of UTIs - Investigation of alternative treatments, such as phage therapy and probiotics - Studies on the role of the urinary microbiome in health and diseaseWhat are the most common symptoms of a UTI?
+The most common symptoms of a UTI include a burning sensation while urinating, frequent urination, and a strong urge to urinate even when the bladder is not full.
How are UTIs treated?
+UTIs are typically treated with antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the infection. It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by the doctor.
Can UTIs be prevented?
+Yes, UTIs can be prevented by drinking plenty of water, urinating when the need arises, practicing good hygiene, and avoiding the use of scented soaps and bubble baths.
As we conclude our discussion on UTIs, we invite readers to share their experiences and questions regarding urinary tract infections. Your comments and insights can help others understand the importance of recognizing UTI symptoms and seeking medical attention. Together, we can work towards better urinary health and well-being. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Let's engage in a conversation about UTIs and how we can prevent and manage these infections effectively.
