Intro
Discover 5 uses for doxycycline, an antibiotic treating infections, acne, Lyme disease, and more, with its anti-inflammatory properties and benefits in veterinary medicine, periodontitis, and malaria prevention.
Doxycycline is a versatile antibiotic that has been widely used for decades to treat various bacterial infections. Its effectiveness, combined with its relatively low cost and ease of administration, has made it a staple in both human and veterinary medicine. Beyond its primary use as an antibacterial agent, doxycycline has shown promise in treating other conditions, making it a valuable medication in modern healthcare. In this article, we will delve into the uses of doxycycline, exploring both its established applications and its potential in managing different health issues.
The importance of doxycycline lies in its broad-spectrum activity, meaning it can target a wide range of bacteria. This characteristic, along with its ability to penetrate into tissues effectively, makes it particularly useful for treating infections that are difficult to reach with other antibiotics. Moreover, doxycycline's mechanism of action, which involves inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria, contributes to its effectiveness in combating bacterial infections.
Doxycycline's applications extend beyond the realm of bacterial infections, with research indicating its potential in treating certain inflammatory conditions and as an adjunct therapy in managing diseases where inflammation plays a key role. Its ability to modulate the immune response and exhibit anti-inflammatory properties has sparked interest in its use for conditions not traditionally associated with bacterial infections.
Introduction to Doxycycline

Doxycycline is a type of tetracycline antibiotic, a class of broad-spectrum antibiotics that are effective against a wide range of bacteria. It is commonly used to treat various infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and urinary tract infections. The drug works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria, which is essential for the bacteria's growth and replication. This action ultimately leads to the death of the bacteria, thereby resolving the infection.
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacokinetics of doxycycline involve its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. Doxycycline is well-absorbed after oral administration, with its absorption being reduced by the presence of food, especially dairy products. It is widely distributed throughout the body, including into the central nervous system, and is metabolized by the liver. The drug is primarily excreted in the feces, with a smaller amount being excreted in the urine.Uses of Doxycycline
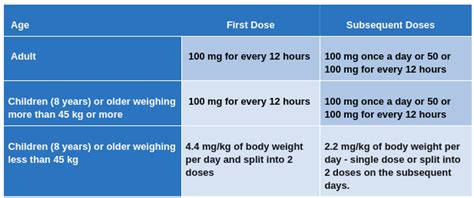
Doxycycline has several established uses, primarily in the treatment of bacterial infections. Some of the key uses include:
- Treatment of Bacterial Infections: Doxycycline is effective against a wide range of bacteria and is used to treat infections such as pneumonia, acne, Lyme disease, and certain sexually transmitted diseases.
- Prevention of Malaria: Doxycycline can be used as a prophylactic measure to prevent malaria in travelers visiting areas where malaria is common.
- Treatment of Inflammatory Conditions: Beyond its antibacterial properties, doxycycline has been found to have anti-inflammatory effects, making it useful in managing conditions like rosacea and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Dental Infections: Doxycycline is often prescribed for the treatment of dental infections, including periodontitis, due to its ability to penetrate into dental tissues effectively.
- Veterinary Medicine: In veterinary medicine, doxycycline is used to treat bacterial infections in animals, showcasing its broad applicability across different species.
Benefits and Side Effects
The benefits of doxycycline include its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of bacteria, its relatively low cost, and its ease of administration. However, like all medications, doxycycline can cause side effects. Common side effects include gastrointestinal upset, photosensitivity, and allergic reactions. Rare but serious side effects can include liver damage and an increased risk of Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) infection.Working Mechanism of Doxycycline
Doxycycline works by binding to the bacterial 30S ribosomal subunit, which is essential for protein synthesis. This binding inhibits the addition of amino acids to the growing peptide chain, thereby preventing the synthesis of proteins necessary for bacterial growth and replication. This mechanism of action is bacteriostatic, meaning it inhibits the growth of bacteria rather than killing them outright. However, in high concentrations or against certain susceptible bacteria, doxycycline can exhibit bactericidal effects, directly killing the bacteria.
Steps for Administration
When administering doxycycline, it is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and administration instructions. This typically involves taking the medication orally, either with or without food, depending on the specific formulation. It is also important to stay hydrated and avoid lying down after taking doxycycline to reduce the risk of esophageal irritation.Practical Examples and Statistical Data
Several studies have highlighted the effectiveness of doxycycline in treating various infections. For instance, in the treatment of acne, doxycycline has been shown to significantly reduce the number of lesions and improve the overall appearance of the skin. In the context of Lyme disease, doxycycline is often the first-line treatment, with studies demonstrating its efficacy in resolving the infection when administered promptly.
Benefits of Early Treatment
Early treatment with doxycycline can significantly improve outcomes for patients with bacterial infections. This is particularly true for conditions like Lyme disease, where prompt antibiotic treatment can prevent long-term complications. Moreover, early treatment can reduce the risk of developing antibiotic-resistant bacteria, a growing concern in global health.SEO Optimization for Doxycycline-Related Content

When creating content related to doxycycline, it is essential to optimize for search engines to ensure visibility and accessibility. This involves using relevant keywords, such as "doxycycline uses," "doxycycline side effects," and "doxycycline dosage," throughout the content. Additionally, incorporating long-tail keywords and phrases related to the specific use or condition being treated can enhance the content's relevance and search engine ranking.
Keyword Density and Synonyms
Maintaining an optimal keyword density, typically between 1% and 2%, is crucial for SEO. This means that for every 100 words of content, the target keyword should appear 1 to 2 times. Using synonyms and related phrases can also help diversify the language and improve the content's readability and SEO relevance.Engagement and Call to Action
As we conclude our exploration of doxycycline and its uses, it is essential to encourage engagement and invite readers to take action. Whether it involves sharing this article with someone who might find it helpful, leaving a comment with questions or experiences, or seeking professional medical advice for a condition that might be treated with doxycycline, every interaction contributes to a more informed and supportive community.
Final Thoughts
In final consideration, doxycycline stands out as a versatile and effective antibiotic with a wide range of applications. Its use extends beyond the treatment of bacterial infections, with potential benefits in managing inflammatory conditions and as part of a comprehensive approach to healthcare. As with any medication, it is crucial to use doxycycline under the guidance of a healthcare professional, ensuring its safe and effective use.What is doxycycline used for?
+Doxycycline is used to treat various bacterial infections, including respiratory, skin, and urinary tract infections. It is also used to prevent malaria and treat certain inflammatory conditions.
How does doxycycline work?
+Doxycycline works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria, which is essential for their growth and replication. This action ultimately leads to the death of the bacteria, resolving the infection.
What are the common side effects of doxycycline?
+Common side effects of doxycycline include gastrointestinal upset, photosensitivity, and allergic reactions. Rare but serious side effects can include liver damage and an increased risk of Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) infection.
