Intro
Discover 5 ways an enlarged salivary gland occurs, including infections, blockages, and tumors, affecting salivary gland function and overall oral health, causing swelling and discomfort.
The salivary glands play a crucial role in our overall health, producing saliva that helps break down food, neutralize acids, and prevent tooth decay. However, there are instances where these glands can become enlarged, leading to discomfort, pain, and difficulty swallowing. Enlarged salivary glands can be caused by various factors, and understanding these causes is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. In this article, we will delve into the world of salivary glands, exploring the possible reasons behind their enlargement and what it means for our health.
The human body has three major salivary glands: the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands. Each gland produces a unique type of saliva that contributes to the digestive process. When these glands become enlarged, it can be a sign of an underlying issue that needs attention. Enlarged salivary glands can be caused by infections, blockages, tumors, or other conditions that affect the gland's ability to function properly. As we explore the possible causes of enlarged salivary glands, it is essential to remember that a proper diagnosis by a healthcare professional is crucial for effective treatment.
The importance of understanding enlarged salivary glands cannot be overstated. Not only can it lead to discomfort and pain, but it can also be a sign of a more serious underlying condition. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of enlarged salivary glands, individuals can seek medical attention early on, preventing further complications and promoting overall health and well-being. In the following sections, we will explore the five ways enlarged salivary glands can happen, discussing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available.
Introduction to Enlarged Salivary Glands

Cause of Enlarged Salivary Glands
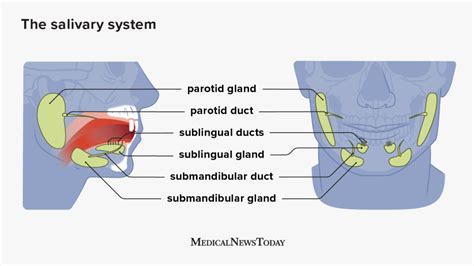
Types of Infections
Infections are a common cause of enlarged salivary glands. Bacterial infections, such as Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae, can cause parotitis, a painful and swollen gland. Viral infections, such as mumps and influenza, can also cause the gland to become inflamed and swollen. Fungal infections, such as candidiasis, can also affect the salivary glands, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems.Symptoms of Enlarged Salivary Glands
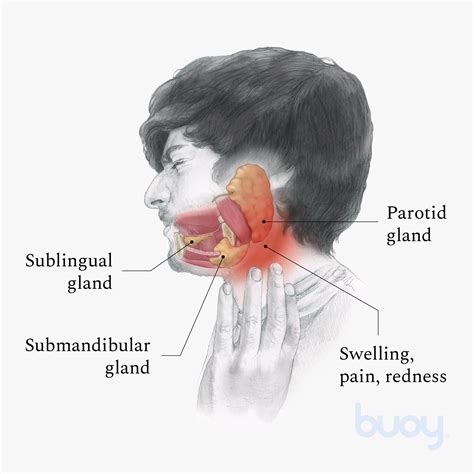
Treatment Options
Treatment for enlarged salivary glands depends on the underlying cause. Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat bacterial infections, while antiviral medications may be used to treat viral infections. Pain management medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, may be recommended to alleviate discomfort and pain. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove blockages or tumors. Alternative therapies, such as massage and warm compresses, may also be used to promote healing and reduce swelling.Diagnosis of Enlarged Salivary Glands
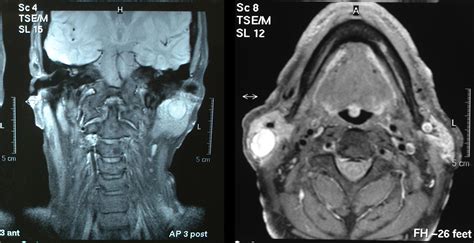
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are an essential part of diagnosing enlarged salivary glands. Ultrasound is a non-invasive test that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the gland. CT scans use X-rays and computer technology to produce detailed images of the gland. MRI scans use magnetic fields and radio waves to produce images of the gland. These tests can help determine if the enlargement is caused by a blockage, tumor, or infection.Prevention of Enlarged Salivary Glands
Good Oral Hygiene
Good oral hygiene is essential for preventing enlarged salivary glands. Brushing and flossing regularly can help prevent bacterial and viral infections. Using an antibacterial mouthwash can also help reduce the risk of infection. Regular dental check-ups can help identify any underlying conditions that may be contributing to the enlargement.Treatment and Management

Alternative Therapies
Alternative therapies, such as massage and warm compresses, can be used to promote healing and reduce swelling. Massage can help increase blood flow to the affected gland, promoting healing and reducing pain. Warm compresses can help reduce swelling and promote drainage. These therapies can be used in conjunction with traditional treatments to promote overall health and well-being.What are the symptoms of enlarged salivary glands?
+The symptoms of enlarged salivary glands include pain and tenderness in the affected gland, swelling and inflammation, difficulty swallowing, and changes in saliva production.
How are enlarged salivary glands diagnosed?
+Diagnosing enlarged salivary glands typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests, such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans.
What are the treatment options for enlarged salivary glands?
+Treatment for enlarged salivary glands depends on the underlying cause and may include antibiotics, antiviral medications, pain management medications, surgery, and alternative therapies, such as massage and warm compresses.
In conclusion, enlarged salivary glands can be caused by a variety of factors, including infections, blockages, tumors, and other conditions. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for promoting overall health and well-being. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of enlarged salivary glands, individuals can seek medical attention early on, preventing further complications and promoting effective treatment. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with enlarged salivary glands in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from this information.
