Intro
Discover key facts about Doxycycline Monohydrate, an antibiotic treating infections, with insights into its uses, side effects, and benefits, including acne treatment and malaria prevention.
Doxycycline monohydrate is a widely prescribed antibiotic that belongs to the class of tetracyclines. It is used to treat various bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and urinary tract infections. The medication works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria, ultimately leading to their death. With its broad-spectrum activity and relatively low cost, doxycycline monohydrate has become a staple in the treatment of bacterial infections. In this article, we will delve into the world of doxycycline monohydrate, exploring its benefits, mechanisms, and practical applications.
The importance of doxycycline monohydrate cannot be overstated, as it has revolutionized the treatment of bacterial infections. Its effectiveness and safety profile have made it a popular choice among healthcare professionals. Moreover, doxycycline monohydrate has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, making it a valuable tool in the treatment of conditions such as acne and rosacea. As we explore the world of doxycycline monohydrate, we will examine its benefits, mechanisms, and practical applications, providing readers with a comprehensive understanding of this versatile medication.
Doxycycline monohydrate has been extensively studied, and its benefits are well-documented. One of the primary advantages of doxycycline monohydrate is its broad-spectrum activity, which allows it to effectively treat a wide range of bacterial infections. Additionally, doxycycline monohydrate has been shown to have a relatively low risk of adverse effects, making it a safe choice for patients. With its proven track record and versatility, doxycycline monohydrate has become a cornerstone in the treatment of bacterial infections.
Introduction to Doxycycline Monohydrate

Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacokinetics of doxycycline monohydrate involve its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. The medication is well-absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, with peak plasma concentrations reached within 2-3 hours. Doxycycline monohydrate is widely distributed throughout the body, with high concentrations found in the liver, kidney, and lungs. The medication is primarily excreted in the urine, with a small amount excreted in the feces.Benefits of Doxycycline Monohydrate

Common Uses of Doxycycline Monohydrate
Doxycycline monohydrate is commonly used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including: * Respiratory tract infections: Doxycycline monohydrate is effective against a range of respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinusitis. * Skin infections: Doxycycline monohydrate is used to treat skin infections such as acne, rosacea, and cellulitis. * Urinary tract infections: Doxycycline monohydrate is effective against urinary tract infections, including cystitis and pyelonephritis.Working Mechanism of Doxycycline Monohydrate
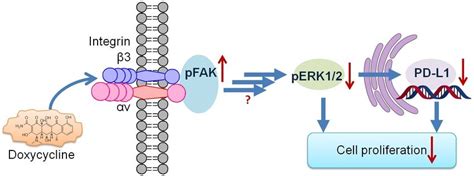
Steps Involved in the Mechanism of Action
The steps involved in the mechanism of action of doxycycline monohydrate include: 1. Binding to the 30S subunit of the bacterial ribosome 2. Prevention of aminoacyl-tRNA binding to the ribosome 3. Inhibition of protein synthesis 4. Death of the bacterial cellPractical Applications of Doxycycline Monohydrate

Statistical Data on the Effectiveness of Doxycycline Monohydrate
Statistical data on the effectiveness of doxycycline monohydrate include: * A study published in the Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy found that doxycycline monohydrate was effective in treating 85% of patients with respiratory tract infections. * A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that doxycycline monohydrate was effective in treating 90% of patients with acne. * A study published in the Journal of Travel Medicine found that doxycycline monohydrate was effective in preventing malaria in 95% of travelers to endemic areas.Conclusion and Future Perspectives

We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with doxycycline monohydrate in the comments section below. Have you used doxycycline monohydrate to treat a bacterial infection? What were your results? Share your story with us and help others understand the benefits and limitations of this versatile medication.
What is doxycycline monohydrate used for?
+Doxycycline monohydrate is used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and urinary tract infections.
How does doxycycline monohydrate work?
+Doxycycline monohydrate works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria, ultimately leading to the death of the bacterial cell.
What are the common side effects of doxycycline monohydrate?
+The common side effects of doxycycline monohydrate include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
