Intro
Discover the alarming Tuberculosis death rate worldwide, exploring global TB mortality rates, infection control, and prevention strategies to combat this deadly disease.
The tuberculosis death rate worldwide is a significant public health concern, with the disease being one of the top 10 causes of death globally. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 1.5 million people died from tuberculosis (TB) in 2020, with the majority of these deaths occurring in low- and middle-income countries. The burden of TB is not only limited to the number of deaths but also has a significant impact on the quality of life of those affected, as well as the economic and social stability of communities.
The importance of addressing the tuberculosis death rate worldwide cannot be overstated. TB is a preventable and curable disease, yet it remains a major public health challenge due to various factors such as poverty, lack of access to healthcare, and the rise of drug-resistant strains. The global response to TB has been hampered by inadequate funding, lack of political commitment, and insufficient awareness about the disease. As a result, TB continues to claim millions of lives every year, with the most vulnerable populations, including children, women, and people living with HIV, being disproportionately affected.
The tuberculosis death rate worldwide is a complex issue that requires a comprehensive and multifaceted approach to address. It involves not only improving access to healthcare and strengthening health systems but also addressing the underlying social and economic determinants of health. This includes reducing poverty, improving living conditions, and promoting education and awareness about TB. Furthermore, the development of new diagnostic tools, treatments, and vaccines is crucial to combating the disease and ultimately reducing the tuberculosis death rate worldwide.
Tuberculosis Death Rate Statistics
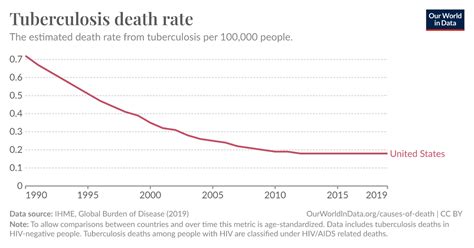
Regional Variations in Tuberculosis Death Rates
The tuberculosis death rate varies significantly across different regions and countries. In Africa, the TB death rate is highest in countries such as South Africa, Nigeria, and Ethiopia, where the disease is often linked to the HIV epidemic. In Southeast Asia, countries such as India, Indonesia, and the Philippines have the highest TB death rates, with the disease being a major public health concern due to the large population and inadequate healthcare infrastructure.Causes of Tuberculosis Death Rate
Impact of Tuberculosis on Global Health
The impact of tuberculosis on global health is significant. TB is a major public health concern, not only due to the number of deaths it causes but also due to its impact on the quality of life of those affected. The disease can cause significant morbidity, including symptoms such as coughing, chest pain, and weight loss, which can lead to reduced productivity and economic instability.Strategies to Reduce Tuberculosis Death Rate
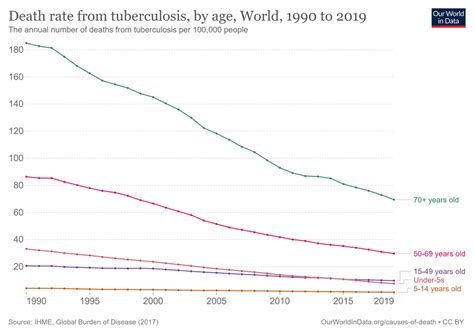
Role of Global Partnerships in Reducing Tuberculosis Death Rate
Global partnerships play a crucial role in reducing the tuberculosis death rate worldwide. Organizations such as the WHO, the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria, and the Stop TB Partnership are working together to coordinate efforts, mobilize resources, and promote research and development to combat TB. These partnerships have helped to increase funding, improve access to healthcare, and promote awareness and education about TB.Challenges in Reducing Tuberculosis Death Rate
Future Directions for Reducing Tuberculosis Death Rate
To achieve the goal of reducing the tuberculosis death rate worldwide, several future directions can be explored. These include: * Increasing funding: Increasing funding for TB research, treatment, and prevention can help to improve access to healthcare and reduce the number of deaths. * Developing new technologies: Developing new technologies, including diagnostic tools and treatments, can help to improve the effectiveness of TB treatment and reduce the risk of drug-resistant TB. * Promoting global partnerships: Promoting global partnerships and collaborations can help to coordinate efforts, mobilize resources, and promote research and development to combat TB.Conclusion and Recommendations

Final Thoughts
The tuberculosis death rate worldwide is a preventable tragedy that can be addressed through a concerted effort from governments, healthcare providers, and communities. By working together, we can reduce the number of deaths from TB and improve the quality of life of those affected. It is essential to prioritize the global response to TB, increase funding, and promote research and development to combat the disease.What is the current tuberculosis death rate worldwide?
+The current tuberculosis death rate worldwide is approximately 17 deaths per 100,000 people, according to the World Health Organization.
What are the main causes of the high tuberculosis death rate?
+The main causes of the high tuberculosis death rate include lack of access to healthcare, poverty, HIV/AIDS, and the rise of drug-resistant TB.
What strategies can be employed to reduce the tuberculosis death rate?
+Strategies to reduce the tuberculosis death rate include improving access to healthcare, strengthening health systems, promoting awareness and education, and developing new diagnostic tools and treatments.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the tuberculosis death rate worldwide and the strategies that can be employed to reduce it. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us. Additionally, we invite you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about this important public health issue. Together, we can work towards reducing the tuberculosis death rate and improving the quality of life of those affected by this disease.
