Intro
Discover how antibiotics effectively treat ear infections, alleviating symptoms and preventing complications, with 5 proven methods, including middle ear infection treatment and otitis media management, using antibacterial medications to combat bacterial ear infections.
Ear infections are a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide, particularly children. The primary cause of ear infections is bacterial or viral infections, which can lead to inflammation and fluid buildup in the middle ear. Antibiotics are often prescribed to treat ear infections, especially those caused by bacterial infections. In this article, we will explore the five ways antibiotics treat ear infections and provide an in-depth look at the benefits, working mechanisms, and steps involved in the treatment process.
Ear infections can be painful and debilitating, causing symptoms such as ear pain, fever, and difficulty hearing. If left untreated, ear infections can lead to serious complications, including permanent hearing loss, meningitis, and brain abscess. Therefore, it is essential to seek medical attention if you or your child is experiencing symptoms of an ear infection. Antibiotics are a crucial part of the treatment process, and understanding how they work can help you make informed decisions about your health.
The importance of treating ear infections cannot be overstated. Ear infections can have a significant impact on quality of life, causing pain, discomfort, and difficulty communicating. Moreover, untreated ear infections can lead to long-term health consequences, including hearing loss and developmental delays in children. By understanding the role of antibiotics in treating ear infections, you can take the first step towards seeking effective treatment and preventing long-term health problems.
Understanding Ear Infections
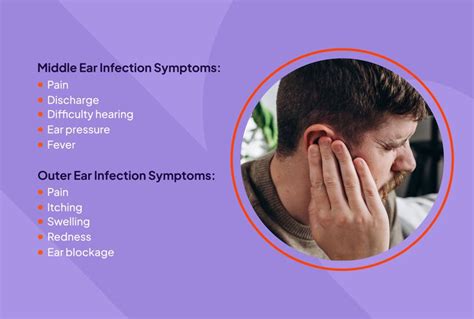
Causes of Ear Infections
Ear infections are often caused by bacterial or viral infections, such as the common cold, flu, or respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Other factors that can increase the risk of ear infections include allergies, sinus infections, and exposure to cigarette smoke. In children, ear infections are often caused by the presence of adenoids, which are small glands located in the back of the throat that can trap bacteria and viruses. Additionally, children who attend daycare or preschool are more likely to develop ear infections due to increased exposure to germs.How Antibiotics Treat Ear Infections
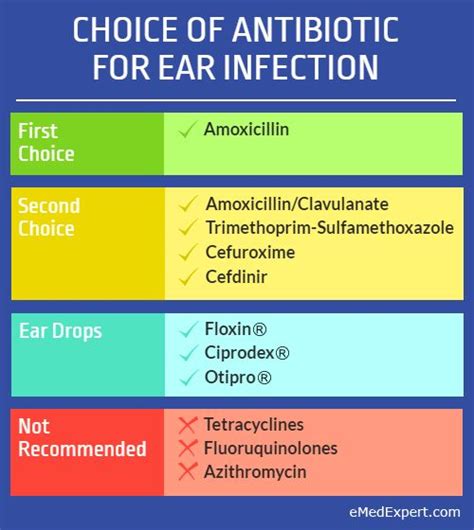
Types of Antibiotics Used to Treat Ear Infections
There are several types of antibiotics that can be used to treat ear infections, including amoxicillin, azithromycin, and clarithromycin. The type of antibiotic prescribed will depend on the severity of the infection, the age and health of the patient, and any allergies or sensitivities to certain medications. In some cases, a doctor may prescribe a broad-spectrum antibiotic that can target a range of bacteria, while in other cases, a narrow-spectrum antibiotic may be prescribed to target a specific type of bacteria.Benefits of Antibiotics in Treating Ear Infections

Steps Involved in the Treatment Process
The steps involved in the treatment process for ear infections typically include: 1. Diagnosis: A doctor will diagnose the ear infection by performing a physical exam and reviewing the patient's medical history. 2. Prescription: A doctor will prescribe an antibiotic to treat the ear infection, depending on the severity of the infection and the age and health of the patient. 3. Administration: The patient will take the antibiotic as directed, usually for a period of 7-10 days. 4. Follow-up: The patient will follow up with the doctor to ensure that the infection has cleared and to monitor for any potential side effects.Practical Examples and Statistical Data

Common Misconceptions About Antibiotics and Ear Infections
There are several common misconceptions about antibiotics and ear infections, including: * Antibiotics are always necessary: Antibiotics are not always necessary to treat ear infections, as some infections may be caused by viruses, which do not respond to antibiotics. * Antibiotics can cure all ear infections: Antibiotics cannot cure all ear infections, as some infections may be caused by resistant bacteria or other underlying conditions. * Antibiotics have no side effects: Antibiotics can have side effects, such as diarrhea, nausea, and allergic reactions, which can range from mild to severe.Conclusion and Next Steps

We hope this article has provided you with valuable information about the role of antibiotics in treating ear infections. If you have any questions or comments, please do not hesitate to reach out. Share this article with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the importance of treating ear infections.
What are the symptoms of an ear infection?
+Ear infections can cause symptoms such as ear pain, fever, difficulty hearing, and discharge from the ear.
How long does it take for antibiotics to work?
+Antibiotics can start to work within 24-48 hours, but it may take several days to a week to fully recover from an ear infection.
Can ear infections be prevented?
+While ear infections cannot be completely prevented, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk, such as practicing good hygiene, avoiding exposure to cigarette smoke, and getting vaccinated against the flu and other respiratory illnesses.
