Intro
Decode liver test results with ease. Learn to interpret liver function tests, understand abnormal results, and discover related liver health issues like liver disease and liver damage.
Liver tests are a crucial diagnostic tool for assessing liver health and detecting potential liver damage or disease. These tests can help identify issues early on, allowing for timely intervention and treatment. However, deciphering liver test results can be a daunting task, especially for those without a medical background. In this article, we will delve into the world of liver tests, exploring the different types of tests, what the results mean, and how to interpret them.
Liver health is essential for overall well-being, as the liver plays a vital role in filtering toxins, regulating metabolism, and producing essential proteins. Liver damage or disease can have severe consequences, including cirrhosis, liver cancer, and even liver failure. Therefore, it is crucial to understand liver test results and take proactive steps to maintain liver health. With the rise of liver diseases, such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), it is more important than ever to be informed about liver health and the tests used to assess it.
The liver is a complex organ, and liver tests are designed to evaluate its various functions. From blood tests to imaging studies, each type of test provides valuable information about liver health. By understanding the different types of liver tests and what the results mean, individuals can take a more active role in managing their liver health. Whether you are concerned about liver disease or simply want to maintain optimal liver function, this article will provide you with the knowledge and tools you need to navigate the world of liver tests.
Liver Function Tests

Types of Liver Function Tests
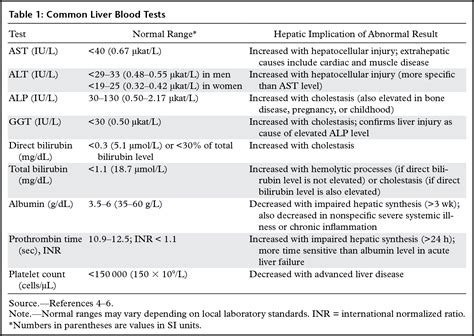
There are several types of LFTs, each measuring different aspects of liver function. These include: * ALT: measures the level of alanine transaminase, an enzyme found primarily in the liver * AST: measures the level of aspartate transaminase, an enzyme found in the liver and other tissues * ALP: measures the level of alkaline phosphatase, an enzyme involved in bone growth and liver function * Bilirubin: measures the level of bilirubin, a pigment produced during the breakdown of red blood cells * Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT): measures the level of GGT, an enzyme involved in amino acid transport * Prothrombin time (PT): measures the time it takes for blood to clot, which can be affected by liver functionInterpreting Liver Test Results
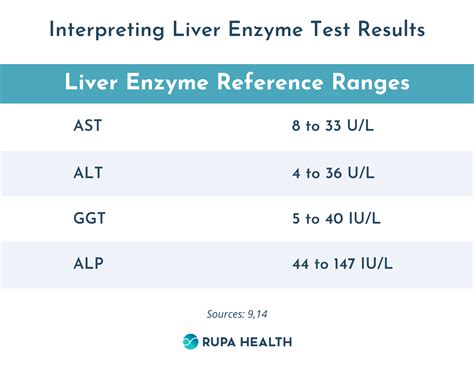
Common Causes of Abnormal Liver Test Results
There are several common causes of abnormal liver test results, including: * Viral hepatitis (e.g., hepatitis B or C) * Alcoholic liver disease * Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) * Medication-induced liver injury * Autoimmune liver disease (e.g., autoimmune hepatitis) * Liver cancerLiver Imaging Tests
Types of Liver Imaging Tests
There are several types of liver imaging tests, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. These include: * Ultrasound: uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the liver * CT scan: uses X-rays and computer technology to produce detailed images of the liver * MRI: uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the liver * Liver biopsy: involves removing a small sample of liver tissue for examination under a microscopeMaintaining Liver Health

Tips for Promoting Liver Health
The following are additional tips for promoting liver health: * Stay hydrated: drink plenty of water to help flush toxins from the liver * Avoid exposure to toxins: limit exposure to environmental toxins, such as pesticides and heavy metals * Get vaccinated: against hepatitis A and B to reduce the risk of liver disease * Manage medications: carefully follow medication instructions and consult with a healthcare provider about potential liver risksLiver Disease Prevention

Common Risk Factors for Liver Disease
The following are common risk factors for liver disease: * Family history: of liver disease * Obesity: increases the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) * Age: liver disease risk increases with age * Sex: men are more likely to develop liver disease than women * Ethnicity: certain ethnic groups, such as Hispanics and African Americans, are at higher risk for liver diseaseWhat are the most common liver function tests?
+The most common liver function tests include alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and bilirubin.
What do abnormal liver test results indicate?
+Abnormal liver test results can indicate liver damage or disease, such as viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
How can I promote liver health?
+Promoting liver health involves eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, managing stress, and getting enough sleep.
What are the common risk factors for liver disease?
+Common risk factors for liver disease include family history, obesity, age, sex, and ethnicity.
How can I reduce the risk of liver disease?
+Reducing the risk of liver disease involves practicing safe sex, avoiding sharing needles, getting screened for liver disease, and managing underlying medical conditions.
In conclusion, understanding liver test results is essential for maintaining liver health and detecting potential liver damage or disease. By knowing the different types of liver tests, what the results mean, and how to interpret them, individuals can take a more active role in managing their liver health. Remember to promote liver health by eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, managing stress, and getting enough sleep. If you have concerns about your liver health or have questions about liver test results, consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance and care. We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from this information and to comment below with any questions or concerns you may have.
