Intro
Identify 5 ear infection symptoms, including ear pain, discharge, and hearing loss, to seek timely treatment and prevent complications like tinnitus, vertigo, and eardrum damage, and learn about ear health and infection management.
Ear infections are a common health issue that affects people of all ages, but they are most prevalent among children. These infections occur when bacteria or viruses invade the middle ear, causing inflammation and fluid buildup. Recognizing the symptoms of an ear infection is crucial for seeking timely medical attention and preventing potential complications. In this article, we will delve into the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for ear infections, as well as provide valuable insights and practical advice for managing and preventing these infections.
Ear infections can be painful and debilitating, affecting not only the infected individual but also their loved ones. The symptoms of an ear infection can vary depending on the severity of the infection and the age of the affected person. Some common symptoms include ear pain, fever, and difficulty hearing. It is essential to be aware of these symptoms to ensure prompt medical attention and prevent long-term damage to the ears.
The importance of recognizing ear infection symptoms cannot be overstated. Early detection and treatment can significantly reduce the risk of complications, such as permanent hearing loss, balance problems, and speech development delays in children. Moreover, understanding the causes and risk factors of ear infections can help individuals take preventive measures to minimize their likelihood of developing these infections.
Introduction to Ear Infections
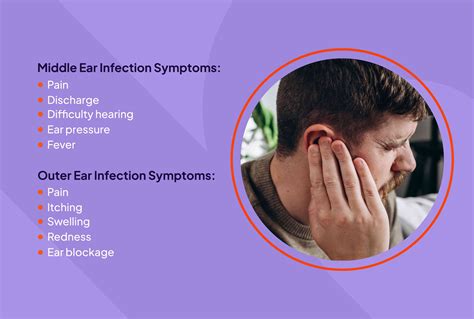
Types of Ear Infections
There are several types of ear infections, including acute otitis media (AOM), otitis media with effusion (OME), and chronic otitis media. AOM is the most common type, characterized by a sudden onset of symptoms, such as ear pain, fever, and difficulty hearing. OME, on the other hand, is a condition where fluid remains in the middle ear after an infection has resolved, often causing no symptoms but potentially affecting hearing. Chronic otitis media refers to a recurring or persistent ear infection that can lead to more severe complications.Causes and Risk Factors
Prevention and Management
Preventing ear infections requires a combination of good hygiene practices, a healthy lifestyle, and awareness of the risk factors. Some preventive measures include practicing good hand hygiene, avoiding close contact with individuals who have a cold or flu, getting vaccinated against flu and pneumococcal disease, and avoiding exposure to cigarette smoke. Managing an ear infection typically involves a course of antibiotics, pain relief medication, and home remedies, such as applying a warm compress to the affected ear.Symptoms of Ear Infections
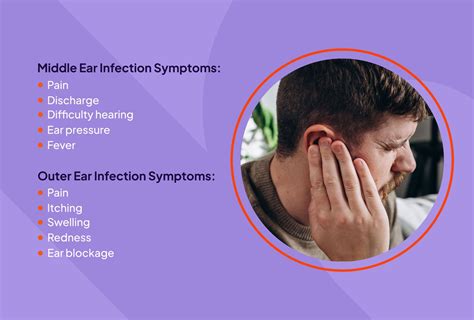
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing an ear infection typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as an otoscopy or tympanometry. Treatment options depend on the severity and type of infection, as well as the age and overall health of the affected individual. Antibiotics are often prescribed to treat bacterial ear infections, while pain relief medication and home remedies can help manage symptoms. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to drain the middle ear or insert ear tubes to alleviate fluid buildup.Complications of Ear Infections

Preventing Future Infections
Preventing future ear infections requires a combination of good hygiene practices, a healthy lifestyle, and awareness of the risk factors. Some preventive measures include: * Practicing good hand hygiene * Avoiding close contact with individuals who have a cold or flu * Getting vaccinated against flu and pneumococcal disease * Avoiding exposure to cigarette smoke * Using earplugs or earmuffs in loud environments * Drying the ears thoroughly after bathing or swimmingConclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with ear infections in the comments section below. Have you or a loved one ever had an ear infection? What were your symptoms, and how did you manage them? Your input can help others who may be going through a similar experience. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please share it with your friends and family on social media.
What are the most common symptoms of an ear infection?
+The most common symptoms of an ear infection include ear pain, fever, difficulty hearing, and drainage or discharge from the ear.
How can I prevent ear infections?
+Preventing ear infections requires a combination of good hygiene practices, a healthy lifestyle, and awareness of the risk factors. Some preventive measures include practicing good hand hygiene, avoiding close contact with individuals who have a cold or flu, getting vaccinated against flu and pneumococcal disease, and avoiding exposure to cigarette smoke.
What are the potential complications of untreated ear infections?
+If left untreated or poorly managed, ear infections can lead to several complications, including permanent hearing loss, speech development delays, balance problems, mastoiditis, meningitis, and brain abscess.
How are ear infections diagnosed?
+Diagnosing an ear infection typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as an otoscopy or tympanometry.
What are the treatment options for ear infections?
+Treatment options for ear infections depend on the severity and type of infection, as well as the age and overall health of the affected individual. Antibiotics are often prescribed to treat bacterial ear infections, while pain relief medication and home remedies can help manage symptoms.
