Intro
Learn the normal blood glucose level range and understand healthy blood sugar levels, glucose tolerance, and glycemic control to manage diabetes and prediabetes effectively.
Maintaining normal blood glucose levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Blood glucose, also known as blood sugar, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. The level of glucose in the blood is tightly regulated by the body's hormonal and metabolic systems. Understanding the normal range of blood glucose levels is essential for individuals to take preventive measures against diabetes, a condition characterized by elevated blood glucose levels. In this article, we will delve into the importance of maintaining normal blood glucose levels, the factors that influence blood glucose levels, and the steps individuals can take to manage their blood glucose levels effectively.
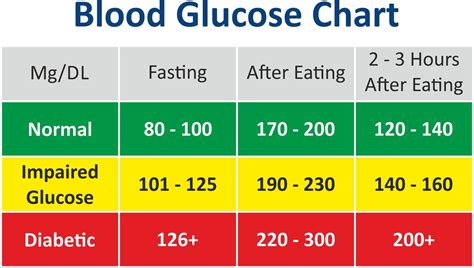
The normal range of blood glucose levels varies throughout the day, depending on factors such as meal times, physical activity, and sleep patterns. Generally, a normal fasting blood glucose level is between 70 and 99 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). After eating, blood glucose levels typically rise, but they should not exceed 140 mg/dL. It is essential to note that these values can vary slightly depending on the individual, their age, and their overall health. For instance, older adults may have slightly higher blood glucose levels due to age-related changes in their metabolic systems.
Blood glucose levels are regulated by a complex interplay of hormones, including insulin and glucagon. Insulin, produced by the pancreas, helps to lower blood glucose levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose by cells. Glucagon, also produced by the pancreas, raises blood glucose levels by stimulating the release of glucose stored in the liver. When blood glucose levels are within the normal range, the body's cells can function optimally, and the risk of developing diabetes-related complications is minimized. Therefore, understanding the factors that influence blood glucose levels and taking steps to maintain normal levels is crucial for overall health and well-being.
Factors Influencing Blood Glucose Levels
Several factors can influence blood glucose levels, including diet, physical activity, stress, and sleep patterns. A diet high in refined carbohydrates, sugar, and saturated fats can lead to elevated blood glucose levels, while a diet rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables can help to regulate blood glucose levels. Regular physical activity, such as walking or jogging, can also help to lower blood glucose levels by increasing the body's sensitivity to insulin. Stress and sleep deprivation can raise blood glucose levels by stimulating the release of stress hormones, such as cortisol, which can increase glucose production in the liver.
Diet and Nutrition
A healthy diet plays a crucial role in maintaining normal blood glucose levels. Foods that are rich in fiber, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, can help to slow the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream, reducing the risk of elevated blood glucose levels. Foods that are high in protein, such as lean meats, fish, and legumes, can also help to regulate blood glucose levels by increasing the body's sensitivity to insulin. On the other hand, foods that are high in added sugars, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats can lead to elevated blood glucose levels and increase the risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.Benefits of Maintaining Normal Blood Glucose Levels

Maintaining normal blood glucose levels has numerous benefits, including reducing the risk of developing diabetes-related complications, such as heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage. Normal blood glucose levels can also improve cognitive function, reduce the risk of depression and anxiety, and enhance overall quality of life. Additionally, maintaining normal blood glucose levels can reduce the risk of developing certain types of cancer, such as pancreatic cancer, and can even help to slow down the aging process.
Reducing the Risk of Diabetes-Related Complications
Diabetes-related complications, such as heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage, can be devastating and even life-threatening. Maintaining normal blood glucose levels can significantly reduce the risk of developing these complications. For instance, studies have shown that individuals with normal blood glucose levels are less likely to develop heart disease, which is a leading cause of death worldwide. Similarly, maintaining normal blood glucose levels can reduce the risk of developing kidney disease, which can lead to end-stage renal disease and the need for dialysis or kidney transplantation.Steps to Maintain Normal Blood Glucose Levels

Maintaining normal blood glucose levels requires a combination of healthy lifestyle habits, including a balanced diet, regular physical activity, stress management, and adequate sleep. Here are some steps individuals can take to maintain normal blood glucose levels:
- Eat a balanced diet that is rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables
- Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking or jogging, for at least 30 minutes a day
- Practice stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga, to manage stress levels
- Get adequate sleep, aiming for 7-8 hours per night
- Monitor blood glucose levels regularly, especially after meals and before bedtime
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
Monitoring blood glucose levels is an essential step in maintaining normal blood glucose levels. Individuals can use a blood glucose meter to measure their blood glucose levels at different times of the day, such as before meals, after meals, and before bedtime. This can help individuals identify patterns and trends in their blood glucose levels, making it easier to make informed decisions about their diet, physical activity, and stress management.Common Mistakes to Avoid

When it comes to maintaining normal blood glucose levels, there are several common mistakes to avoid. These include:
- Consuming high amounts of added sugars and refined carbohydrates
- Not engaging in regular physical activity
- Not getting enough sleep
- Not managing stress levels effectively
- Not monitoring blood glucose levels regularly
- Not seeking medical attention when symptoms of high blood glucose levels occur
Seeking Medical Attention
If individuals experience symptoms of high blood glucose levels, such as increased thirst and urination, blurred vision, or slow healing of cuts and wounds, they should seek medical attention immediately. A healthcare provider can diagnose high blood glucose levels and provide guidance on how to manage them effectively. In some cases, medication may be necessary to regulate blood glucose levels.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, maintaining normal blood glucose levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. By understanding the factors that influence blood glucose levels and taking steps to maintain normal levels, individuals can reduce their risk of developing diabetes-related complications and improve their overall quality of life. We invite readers to share their experiences and tips on maintaining normal blood glucose levels in the comments section below. Additionally, we encourage readers to share this article with friends and family members who may be interested in learning more about blood glucose levels and how to manage them effectively.
What is the normal range of blood glucose levels?
+The normal range of blood glucose levels is between 70 and 99 mg/dL for fasting blood glucose and less than 140 mg/dL for postprandial blood glucose.
What factors can influence blood glucose levels?
+Several factors can influence blood glucose levels, including diet, physical activity, stress, and sleep patterns.
How can I maintain normal blood glucose levels?
+Maintaining normal blood glucose levels requires a combination of healthy lifestyle habits, including a balanced diet, regular physical activity, stress management, and adequate sleep.
