Intro
Discover how earwax buildup causes blockages, leading to hearing loss, earaches, and tinnitus, and learn effective removal methods to clear ear canal blockages and prevent earwax impaction.
Earwax is a natural substance produced by the glands in the ear canal, playing a crucial role in protecting the ears from dirt, dust, and bacteria. However, excessive earwax can cause a blockage, leading to discomfort, hearing loss, and other complications. It is essential to understand the importance of earwax and the potential risks associated with its accumulation. In this article, we will delve into the world of earwax, exploring its functions, the causes of blockages, and the various methods of prevention and treatment.
The ears are self-cleaning organs, and earwax helps to facilitate this process. It traps dirt, dust, and other small particles, preventing them from entering the ear canal and causing damage. Earwax also has antimicrobial properties, which help to prevent the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms. However, when earwax accumulates excessively, it can cause a blockage, leading to a range of symptoms, including ear fullness, hearing loss, and itching.
Earwax blockages can be caused by various factors, including the use of cotton swabs, which can push earwax deeper into the ear canal, rather than removing it. Other causes include the production of excessive earwax, narrow ear canals, and the use of earplugs or hearing aids. It is crucial to address earwax blockages promptly, as they can lead to more severe complications, such as ear infections, eardrum perforation, and permanent hearing loss.
Understanding Earwax
Functions of Earwax
Earwax has several functions, including: * Protecting the ears from dirt, dust, and bacteria * Trapping small particles, preventing them from entering the ear canal * Providing antimicrobial properties, which help to prevent the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms * Helping to regulate the pH balance of the ear canal * Assisting in the removal of dead skin cells and other debris from the ear canalCauses of Earwax Blockages
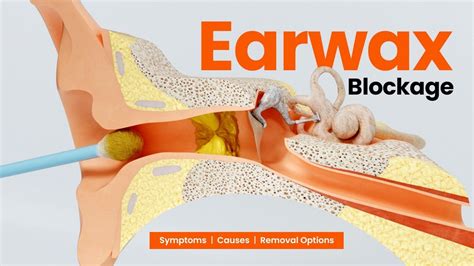
Symptoms of Earwax Blockages
The symptoms of earwax blockages can vary, depending on the severity of the blockage. Common symptoms include: * Ear fullness or a feeling of pressure in the ear * Hearing loss or muffled hearing * Itching or discomfort in the ear * Ringing or buzzing in the ear (tinnitus) * Coughing or throat discomfort * Vertigo or dizzinessPrevention of Earwax Blockages

Treatment of Earwax Blockages
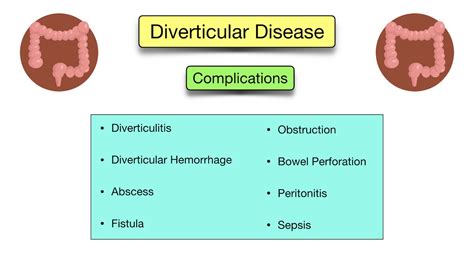
Treating earwax blockages requires a gentle and careful approach. Here are some treatment options: * Ear drops or earwax dissolvers to help soften and remove earwax * Microsuction, a procedure that uses a small vacuum device to remove earwax * Irrigation, a procedure that uses a gentle stream of water to remove earwax * Manual removal, a procedure that uses a specialized tool to remove earwaxComplications of Earwax Blockages
Diagnosis of Earwax Blockages
Diagnosing earwax blockages requires a thorough examination of the ear canal. Here are some diagnostic methods: * Otoscopy, a procedure that uses a specialized tool to visualize the ear canal * Tympanometry, a procedure that measures the movement of the eardrum * Audiometry, a procedure that measures hearing lossConclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with earwax blockages in the comments section below. Have you ever experienced an earwax blockage? How did you treat it? Share your story and help others understand the importance of ear health.
What is earwax and what is its function?
+Earwax, also known as cerumen, is a natural substance produced by the ceruminous glands in the ear canal. Its function is to protect the ears from dirt, dust, and bacteria, and to provide antimicrobial properties that help prevent the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms.
What are the symptoms of earwax blockages?
+The symptoms of earwax blockages can vary, depending on the severity of the blockage. Common symptoms include ear fullness or a feeling of pressure in the ear, hearing loss or muffled hearing, itching or discomfort in the ear, ringing or buzzing in the ear (tinnitus), coughing or throat discomfort, and vertigo or dizziness.
How can I prevent earwax blockages?
+To prevent earwax blockages, avoid using cotton swabs, use ear drops or earwax dissolvers to help soften and remove earwax, avoid using earplugs or hearing aids that can push earwax deeper into the ear canal, keep the ears clean and dry, and avoid sticking objects, such as fingers or cotton swabs, into the ear canal.
