Intro
Discover effective knee effusion treatment options, including drainage, physical therapy, and medication, to alleviate swelling, pain, and inflammation, and restore knee function and mobility with various therapeutic approaches.
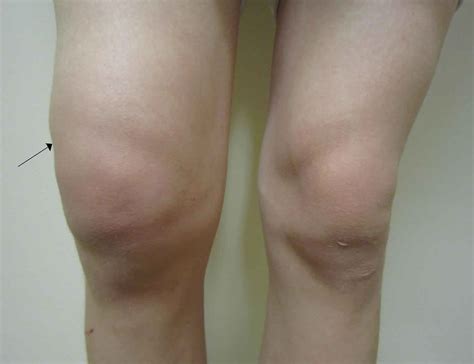
Knee effusion, also known as water on the knee, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of excess fluid in the knee joint. This condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, infection, or underlying medical conditions such as arthritis. The symptoms of knee effusion can range from mild to severe and may include pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited mobility. As the condition can significantly impact daily activities and overall quality of life, it is essential to explore the various treatment options available.
The importance of seeking medical attention for knee effusion cannot be overstated. If left untreated, the condition can lead to further complications, such as chronic pain, limited mobility, and increased risk of infection. Moreover, knee effusion can be a symptom of an underlying condition that requires prompt medical attention. Therefore, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and to discuss the most suitable treatment options.
Knee effusion treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause, severity, and individual patient needs. In general, treatment aims to reduce pain and inflammation, promote healing, and restore normal knee function. A comprehensive treatment plan may involve a combination of conservative management strategies, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgical intervention. By understanding the available treatment options and their benefits, individuals can make informed decisions about their care and work towards achieving optimal knee health.
Knee Effusion Causes and Risk Factors

To develop an effective treatment plan, it is essential to understand the underlying causes and risk factors associated with knee effusion. The condition can result from various factors, including traumatic injuries, overuse or repetitive strain, infection, and underlying medical conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or gout. Identifying the underlying cause of knee effusion is critical in determining the most suitable treatment approach. A healthcare professional will typically conduct a physical examination, review medical history, and may order diagnostic tests such as X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential causes.
Conservative Management Strategies

Conservative management strategies are often the first line of treatment for knee effusion. These approaches aim to reduce pain and inflammation, promote healing, and restore normal knee function. Common conservative management strategies include:
- Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) to reduce pain and inflammation
- Pain relief medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen
- Physical therapy to improve range of motion, strength, and flexibility
- Assistive devices such as crutches or a cane to reduce stress on the knee joint
- Lifestyle modifications such as weight loss, exercise, and activity modification to reduce stress on the knee joint
These strategies can be effective in managing mild to moderate knee effusion. However, in more severe cases or when conservative management strategies are ineffective, further intervention may be necessary.
Physical Therapy for Knee Effusion
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the treatment of knee effusion. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to improve range of motion, strength, and flexibility. The goals of physical therapy for knee effusion include:
- Reducing pain and inflammation
- Improving range of motion and flexibility
- Strengthening the muscles surrounding the knee joint
- Enhancing proprioception and balance
- Promoting normal knee function and mobility
A physical therapist may use various techniques, including exercise, manual therapy, and modalities such as heat, cold, or electrical stimulation, to achieve these goals. By incorporating physical therapy into the treatment plan, individuals can improve their overall knee health and reduce the risk of future complications.
Aspiration and Injection Therapies
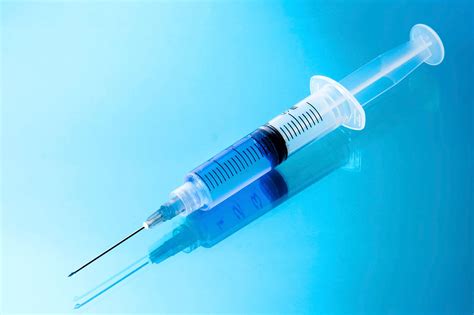
In some cases, aspiration and injection therapies may be necessary to manage knee effusion. Aspiration involves removing excess fluid from the knee joint using a needle and syringe. This procedure can help reduce pain and inflammation and improve mobility. Injection therapies, such as corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections, can also be used to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Aspiration and injection therapies can be effective in managing knee effusion, especially when combined with conservative management strategies and physical therapy. However, these procedures should only be performed by a qualified healthcare professional to minimize the risk of complications.
Surgical Intervention for Knee Effusion
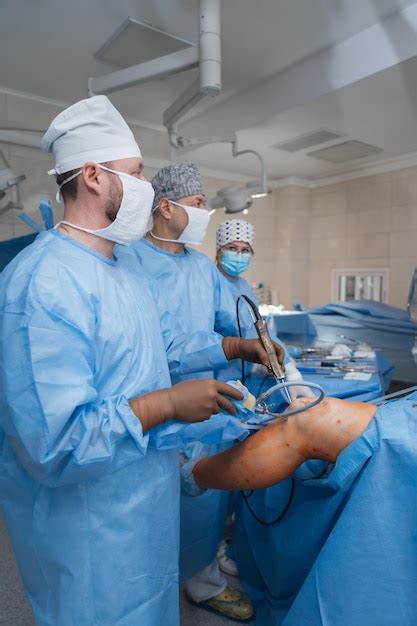
In severe cases of knee effusion or when conservative management strategies are ineffective, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options for knee effusion include:
- Arthroscopy: a minimally invasive procedure that involves inserting a camera and surgical instruments into the knee joint to remove damaged tissue and repair any underlying damage
- Open surgery: a more invasive procedure that involves making an incision in the knee to access the joint and repair any underlying damage
- Joint replacement surgery: a procedure that involves replacing the damaged joint with an artificial one
Surgical intervention should only be considered after conservative management strategies and physical therapy have been exhausted. A healthcare professional can help determine the most suitable surgical option based on individual needs and medical history.
Benefits and Risks of Surgical Intervention
Surgical intervention for knee effusion can offer several benefits, including:- Reduced pain and inflammation
- Improved range of motion and mobility
- Enhanced quality of life
- Reduced risk of future complications
However, surgical intervention also carries risks, including:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Nerve damage
- Adverse reaction to anesthesia
It is essential to discuss the benefits and risks of surgical intervention with a healthcare professional to make an informed decision about treatment.
Recovery and Rehabilitation after Knee Effusion Treatment
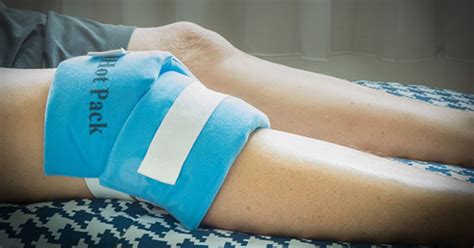
Recovery and rehabilitation after knee effusion treatment are crucial in achieving optimal outcomes. The recovery process typically involves a combination of rest, physical therapy, and pain management. A healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance on the recovery process, including:
- Pain management strategies
- Physical therapy exercises to improve range of motion and strength
- Lifestyle modifications to reduce stress on the knee joint
- Follow-up appointments to monitor progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed
By following a comprehensive recovery and rehabilitation plan, individuals can reduce the risk of complications, promote healing, and achieve optimal knee health.
Importance of Follow-up Care
Follow-up care is essential in monitoring progress and adjusting the treatment plan as needed. A healthcare professional can:- Monitor the knee joint for signs of infection or other complications
- Adjust the treatment plan to optimize outcomes
- Provide guidance on lifestyle modifications to reduce stress on the knee joint
- Address any concerns or questions about the recovery process
By prioritizing follow-up care, individuals can ensure a smooth and successful recovery.
What are the common causes of knee effusion?
+Knee effusion can be caused by various factors, including traumatic injuries, overuse or repetitive strain, infection, and underlying medical conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or gout.
What are the symptoms of knee effusion?
+The symptoms of knee effusion can range from mild to severe and may include pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited mobility.
What are the treatment options for knee effusion?
+Treatment options for knee effusion include conservative management strategies, physical therapy, aspiration and injection therapies, and surgical intervention.
How long does it take to recover from knee effusion treatment?
+The recovery time for knee effusion treatment varies depending on the individual and the severity of the condition. A healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance on the recovery process.
Can knee effusion be prevented?
+While knee effusion cannot be completely prevented, individuals can reduce their risk by maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, and avoiding activities that put excessive stress on the knee joint.
In conclusion, knee effusion is a condition that requires prompt medical attention to prevent further complications and promote optimal outcomes. By understanding the available treatment options and their benefits, individuals can make informed decisions about their care and work towards achieving optimal knee health. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of knee effusion, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and to discuss the most suitable treatment options. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with knee effusion treatment in the comments below and to share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
