Intro
Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (sJIA) is a rare and chronic autoimmune disease that affects children and adolescents. It is characterized by inflammation in multiple joints and other parts of the body, such as the skin, eyes, and internal organs. The symptoms of sJIA can vary widely from one person to another, but they often include fever, rash, and joint pain. In this article, we will delve into the world of sJIA, exploring its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies.
The importance of understanding sJIA cannot be overstated, as it is a complex and multifaceted disease that requires a comprehensive approach to management. By recognizing the symptoms and signs of sJIA, healthcare providers can diagnose and treat the condition early, reducing the risk of long-term damage and improving the quality of life for affected individuals. Furthermore, research into the causes and mechanisms of sJIA is ongoing, and a better understanding of the disease is crucial for the development of effective treatments and therapies.
As we explore the world of sJIA, it becomes clear that the disease is not just a medical condition, but also a personal and emotional journey for those affected. The symptoms of sJIA can be debilitating and disruptive, affecting not only the individual but also their family and friends. Therefore, it is essential to approach the topic with sensitivity and compassion, recognizing the human impact of the disease and the need for support and understanding.
Introduction to sJIA
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact causes of sJIA are not fully understood, but research suggests that it is an autoimmune disease, in which the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues and organs. Several genetic and environmental factors may contribute to the development of sJIA, including genetic predisposition, infections, and exposure to certain toxins. Additionally, some studies suggest that sJIA may be triggered by an abnormal immune response to a viral or bacterial infection.Symptoms of sJIA
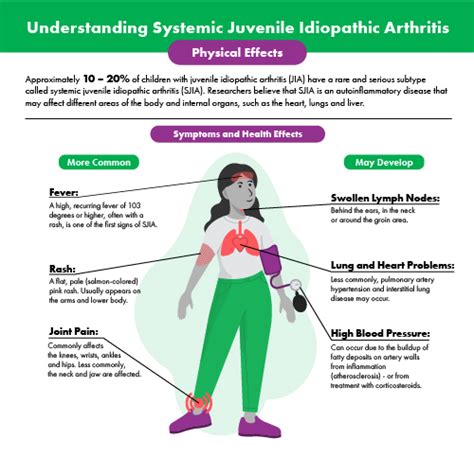
Diagnosis and Diagnostic Criteria
Diagnosing sJIA can be challenging, as the symptoms are often nonspecific and may resemble those of other conditions. A diagnosis of sJIA is typically made based on a combination of clinical features, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. The diagnostic criteria for sJIA include: * Fever for at least 2 weeks * Arthritis in one or more joints * One or more of the following: rash, lymphadenopathy, serositis, or splenomegaly * Elevated inflammatory markers, such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) * Presence of autoantibodies, such as rheumatoid factor and antinuclear antibodiesTreatment and Management
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medical treatment, lifestyle modifications can play an essential role in managing sJIA. These may include: * Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce stress on joints * Engaging in regular exercise, such as swimming or cycling, to improve joint mobility and strength * Getting adequate sleep and rest to reduce fatigue and stress * Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to support overall health * Avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke to reduce the risk of complicationsComplications and Prognosis
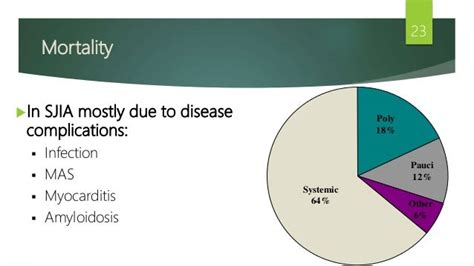
The prognosis for sJIA varies widely depending on the severity of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment. With prompt and aggressive treatment, many children with sJIA can experience significant improvement in symptoms and quality of life. However, some individuals may continue to experience persistent disease activity and complications, highlighting the need for ongoing research and development of more effective treatments.
Current Research and Future Directions
Research into sJIA is ongoing, with a focus on understanding the underlying causes and mechanisms of the disease. Current studies are exploring the role of genetic and environmental factors, as well as the potential for new treatments and therapies. Some promising areas of research include: * Gene therapy to modify the immune system and reduce inflammation * Stem cell therapy to repair damaged tissues and joints * Biologic agents targeting specific components of the immune system * Personalized medicine approaches to tailor treatment to individual needs and characteristicsWhat is the difference between sJIA and other forms of JIA?
+sJIA is a subtype of JIA characterized by systemic inflammation, whereas other forms of JIA may be limited to joint inflammation. sJIA is also often accompanied by fever, rash, and lymphadenopathy, which are not typical features of other JIA subtypes.
How is sJIA diagnosed?
+sJIA is diagnosed based on a combination of clinical features, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. The diagnostic criteria include fever, arthritis, and one or more of the following: rash, lymphadenopathy, serositis, or splenomegaly.
What are the treatment options for sJIA?
+The treatment of sJIA typically involves a combination of medications, including NSAIDs, corticosteroids, DMARDs, and biologic agents. Physical therapy and lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular exercise, can also play an essential role in managing the disease.
What are the potential complications of sJIA?
+sJIA can lead to several complications, including joint damage and deformity, eye problems, osteoporosis, growth retardation, and increased risk of infections and sepsis. Macrophage activation syndrome (MAS) is a life-threatening condition that can occur in some individuals with sJIA.
What is the prognosis for sJIA?
+The prognosis for sJIA varies widely depending on the severity of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment. With prompt and aggressive treatment, many children with sJIA can experience significant improvement in symptoms and quality of life. However, some individuals may continue to experience persistent disease activity and complications.
As we conclude our exploration of sJIA, we hope that readers have gained a deeper understanding of this complex and multifaceted disease. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions in the comments section below. If you or someone you know is affected by sJIA, we encourage you to seek out resources and support from healthcare providers, patient organizations, and online communities. Together, we can work towards a better understanding of sJIA and the development of more effective treatments and therapies.
