Intro
Elevated lactic acid levels explained: Understand causes, symptoms, and effects of high lactate, metabolic acidosis, and lactate threshold, and learn how to manage and reduce lactic acid build-up for improved health and athletic performance.
Elevated lactic acid levels are a common concern for many individuals, particularly athletes and those who engage in strenuous physical activities. Lactic acid, also known as lactate, is a naturally occurring compound that is produced by the body as a byproduct of muscle metabolism. When the body's energy demands exceed its oxygen supply, it resorts to anaerobic metabolism, resulting in the production of lactic acid. In this article, we will delve into the world of lactic acid, exploring its causes, effects, and implications for overall health and wellness.
Lactic acid has long been misunderstood as a waste product that contributes to muscle fatigue and soreness. However, recent research has shed new light on the importance of lactic acid, revealing its role as a vital energy source for the body. During intense physical activity, the body's muscles rely on anaerobic metabolism to generate energy, resulting in the production of lactic acid. This process allows the body to maintain energy production, even in the absence of sufficient oxygen. As a result, elevated lactic acid levels are a common occurrence in individuals who engage in high-intensity activities, such as sprinting, weightlifting, or endurance sports.
The implications of elevated lactic acid levels extend beyond the realm of athletic performance, as they can also have significant effects on overall health and wellness. Elevated lactic acid levels have been linked to various health conditions, including metabolic disorders, cardiovascular disease, and even certain types of cancer. Furthermore, chronic elevations in lactic acid levels can lead to muscle fatigue, weakness, and decreased exercise performance. Therefore, it is essential to understand the causes and effects of elevated lactic acid levels, as well as the strategies for managing and reducing them.
What is Lactic Acid?
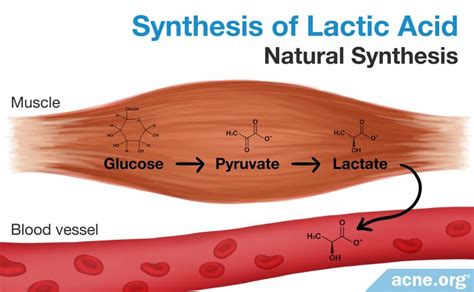
Causes of Elevated Lactic Acid Levels
Elevated lactic acid levels can be caused by a variety of factors, including intense physical activity, poor diet, and certain medical conditions. Some of the most common causes of elevated lactic acid levels include: * Intense physical activity: Engaging in high-intensity activities, such as sprinting, weightlifting, or endurance sports, can lead to elevated lactic acid levels. * Poor diet: Consuming a diet that is high in sugar and refined carbohydrates can lead to elevated lactic acid levels. * Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as metabolic disorders, cardiovascular disease, and cancer, can lead to elevated lactic acid levels. * Dehydration: Failure to stay hydrated can lead to elevated lactic acid levels, as the body's muscles rely on water to function properly.Effects of Elevated Lactic Acid Levels
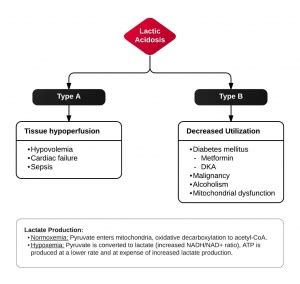
Strategies for Managing Elevated Lactic Acid Levels
Managing elevated lactic acid levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and supplements. Some of the most effective strategies for managing elevated lactic acid levels include: * Dietary changes: Consuming a diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help to reduce lactic acid levels. * Hydration: Staying hydrated is essential for maintaining healthy lactic acid levels. * Exercise: Engaging in regular exercise can help to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce lactic acid levels. * Supplements: Certain supplements, such as vitamin D, magnesium, and omega-3 fatty acids, can help to reduce lactic acid levels.Role of Lactic Acid in Athletic Performance

Benefits of Lactic Acid for Athletes
Lactic acid has several benefits for athletes, including: * Improved energy production: Lactic acid allows the body to maintain energy production, even in the absence of sufficient oxygen. * Enhanced endurance: Elevated lactic acid levels can improve endurance and delay the onset of fatigue. * Increased strength: Lactic acid can help to increase strength and power, particularly in high-intensity activities.Measuring Lactic Acid Levels

Interpreting Lactic Acid Test Results
Interpreting lactic acid test results requires a comprehensive understanding of the underlying physiology and biochemistry. Some of the key factors to consider when interpreting lactic acid test results include: * Normal ranges: Normal lactic acid levels typically range from 0.5 to 2.2 mmol/L. * Elevated levels: Elevated lactic acid levels can indicate a variety of conditions, including metabolic disorders, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. * Decreased levels: Decreased lactic acid levels can indicate a variety of conditions, including hypoglycemia and liver disease.Reducing Lactic Acid Levels

Supplements for Reducing Lactic Acid Levels
Some of the most effective supplements for reducing lactic acid levels include: * Vitamin D: Vitamin D can help to reduce lactic acid levels by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing inflammation. * Magnesium: Magnesium can help to reduce lactic acid levels by improving muscle function and reducing inflammation. * Omega-3 fatty acids: Omega-3 fatty acids can help to reduce lactic acid levels by reducing inflammation and improving heart health.What are the symptoms of elevated lactic acid levels?
+The symptoms of elevated lactic acid levels can include muscle fatigue, weakness, and decreased exercise performance. In severe cases, elevated lactic acid levels can lead to metabolic disorders, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.
How can I reduce lactic acid levels?
+Reducing lactic acid levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and supplements. Some of the most effective strategies for reducing lactic acid levels include consuming a diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, staying hydrated, engaging in regular exercise, and taking supplements such as vitamin D, magnesium, and omega-3 fatty acids.
What are the benefits of lactic acid for athletes?
+Lactic acid has several benefits for athletes, including improved energy production, enhanced endurance, and increased strength. Elevated lactic acid levels can improve endurance and delay the onset of fatigue, allowing athletes to perform at a higher level for longer periods.
In
Final Thoughts

