Intro
Discover 5 crucial RSV disease facts, including symptoms, transmission, and prevention methods, to protect against Respiratory Syncytial Virus infections in vulnerable populations, such as infants and older adults, and learn about diagnosis and treatment options.
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common and highly contagious virus that affects people of all ages, but it's most severe in young children and older adults. RSV disease is a significant public health concern, and understanding its facts is crucial for prevention and management. The importance of RSV disease facts lies in their ability to inform and educate individuals about the risks, symptoms, and treatment options available. By knowing these facts, individuals can take proactive steps to protect themselves and their loved ones from the virus. Moreover, RSV disease facts highlight the need for continued research and development of effective treatments and prevention strategies.
RSV disease is a leading cause of hospitalization in children under the age of one, and it's estimated that nearly all children will have been infected with RSV by their second birthday. The virus spreads quickly and easily, making it a significant challenge for healthcare systems and families. RSV disease facts also underscore the importance of vaccination and prevention measures, such as proper hygiene and infection control practices. By understanding the facts about RSV disease, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and take steps to reduce their risk of infection.
The impact of RSV disease on public health is significant, with thousands of hospitalizations and deaths reported each year. RSV disease facts emphasize the need for increased awareness and education about the virus, as well as the importance of developing effective treatments and prevention strategies. By working together, healthcare professionals, researchers, and individuals can reduce the burden of RSV disease and improve health outcomes for those affected.
What is RSV Disease?
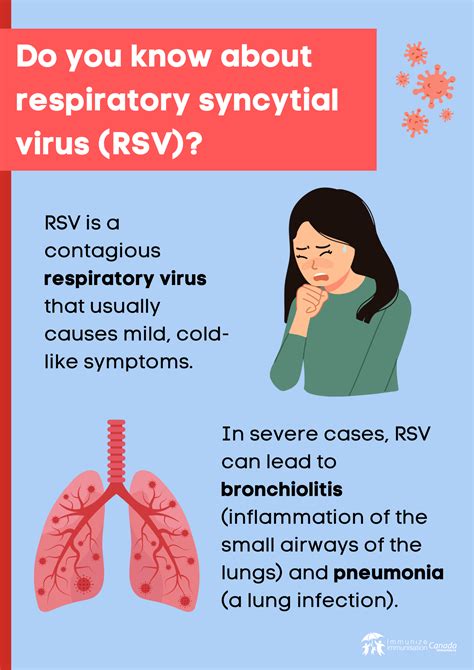
Types of RSV Disease
There are two main types of RSV disease: upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) and lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI). URTI is the most common type of RSV disease and is characterized by symptoms such as runny nose, coughing, and sneezing. LRTI is more severe and can lead to bronchiolitis and pneumonia. RSV disease can also be classified into different subtypes, including RSV-A and RSV-B, which can affect different age groups and populations.Causes and Risk Factors of RSV Disease
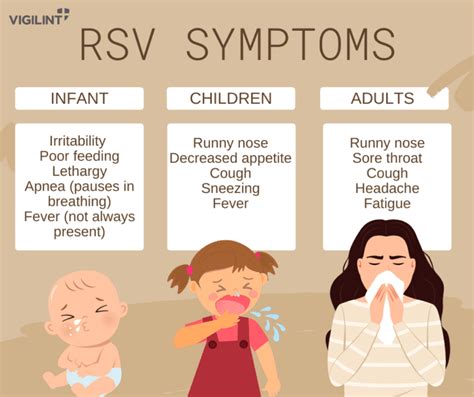
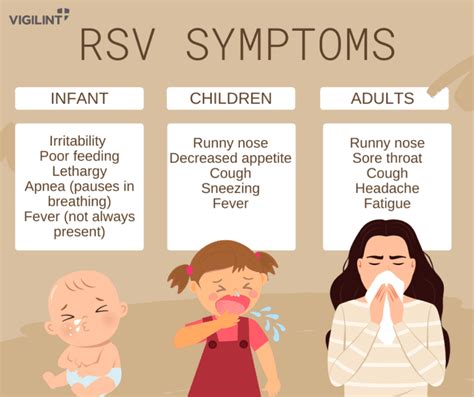
Risk Factors for Severe RSV Disease
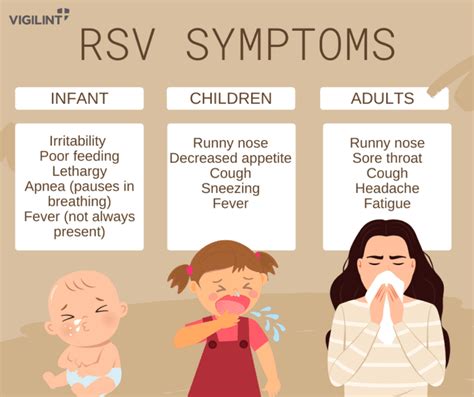
Certain populations are at higher risk for severe RSV disease, including premature infants, young children with underlying health conditions, and older adults with weakened immune systems. Other risk factors for severe RSV disease include heart disease, lung disease, and immunodeficiency. It's essential to take preventive measures to reduce the risk of RSV disease, especially for high-risk populations.Symptoms of RSV Disease
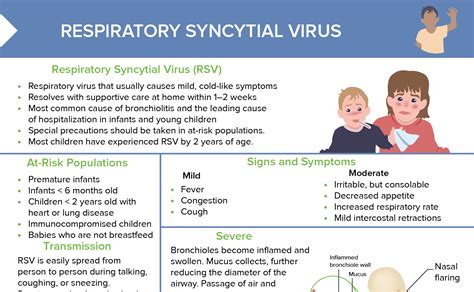
Diagnosis of RSV Disease
RSV disease is typically diagnosed based on symptoms and physical examination. A healthcare provider may also perform tests such as a rapid antigen test or a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test to confirm the diagnosis. In some cases, a chest X-ray or other imaging tests may be necessary to rule out other conditions.Treatment and Management of RSV Disease
Prevention of RSV Disease
Prevention is key to reducing the risk of RSV disease. Measures such as: * Washing hands frequently * Avoiding close contact with people who are sick * Avoiding touching surfaces and objects that may have the virus * Getting vaccinated * Practicing good hygiene and infection control practices can help prevent the spread of RSV disease.Complications of RSV Disease
Long-term Effects of RSV Disease
RSV disease can have long-term effects on the respiratory system, particularly in young children. Some studies suggest that RSV disease may increase the risk of developing asthma and other respiratory conditions later in life.Current Research and Developments in RSV Disease
Future Directions in RSV Disease Research
Future research directions in RSV disease include the development of more effective vaccines, the exploration of new treatment options, and the improvement of diagnostic tests. Researchers are also working to better understand the mechanisms of RSV disease and to identify new targets for therapy.What is RSV disease?
+RSV disease is a respiratory illness caused by the Respiratory Syncytial Virus. It's a common and highly contagious virus that affects people of all ages, but it's most severe in young children and older adults.
How is RSV disease spread?
+RSV disease is spread through close contact with an infected person, touching surfaces and objects that have the virus on them, and then touching the mouth, nose, or eyes.
What are the symptoms of RSV disease?
+The symptoms of RSV disease can range from mild to severe and may include runny nose, coughing, sneezing, fever, wheezing, apnea, poor appetite, vomiting, and diarrhea.
How is RSV disease diagnosed?
+RSV disease is typically diagnosed based on symptoms and physical examination. A healthcare provider may also perform tests such as a rapid antigen test or a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test to confirm the diagnosis.
What is the treatment for RSV disease?
+There is no specific treatment for RSV disease, but symptoms can be managed with over-the-counter medications and home remedies. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to provide supportive care such as oxygen therapy and mechanical ventilation.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of RSV disease facts. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out. Share this article with your friends and family to help spread awareness about RSV disease. Together, we can work towards reducing the burden of RSV disease and improving health outcomes for those affected. Take action today by learning more about RSV disease and taking steps to protect yourself and your loved ones from this common and highly contagious virus.
