Intro
Identify 5 signs of high triglycerides, a key indicator of heart health, and learn about symptoms, causes, and risks associated with elevated triglyceride levels, including cardiovascular disease and pancreatitis.
High triglycerides, a type of fat found in the blood, can significantly increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions. It is essential to recognize the signs and symptoms of high triglycerides to take proactive steps towards managing and reducing their levels. In this article, we will delve into the world of triglycerides, exploring what they are, why they are crucial, and most importantly, the signs that indicate their elevated levels.
Triglycerides are an important source of energy for the body, but when their levels become too high, they can pose serious health risks. The American Heart Association suggests that high triglycerides, combined with high LDL cholesterol and low HDL cholesterol, can lead to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries, potentially resulting in heart attacks and strokes. Given the severity of these potential outcomes, it is vital to understand the indicators of high triglycerides.
Recognizing the signs of high triglycerides can be challenging, as they often do not present with clear symptoms in the early stages. However, there are several key indicators that individuals should be aware of to assess their risk and take necessary precautions. These signs can range from physical symptoms to lifestyle factors, all of which play a crucial role in determining an individual's overall health and risk profile.
Understanding Triglycerides
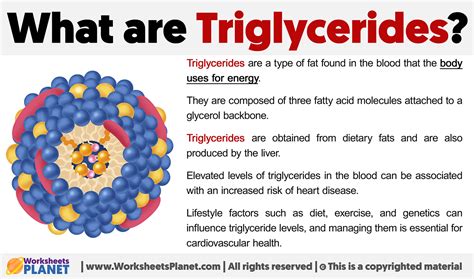
To grasp the concept of high triglycerides, it is essential to understand what triglycerides are and their role in the body. Triglycerides are a type of fat (lipid) found in the blood. When you eat, your body converts any calories it doesn't need to use right away into triglycerides, which are stored in your fat cells. Later, hormones release triglycerides for energy between meals. However, if you regularly consume more calories than you burn, particularly from high-fat, high-carbohydrate foods, you may have high triglycerides (hypertriglyceridemia).
Signs of High Triglycerides

Several signs can indicate that an individual has high triglycerides. These signs often manifest as a result of the underlying health issues that contribute to elevated triglyceride levels. Some of the most common signs include:
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can lead to higher levels of triglycerides. This is because excess body fat, particularly around the abdominal area, can lead to insulin resistance, a condition where the body's cells do not respond effectively to insulin, resulting in higher blood sugar levels and increased triglyceride production.
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is another indicator of potential high triglycerides. High blood pressure can damage blood vessels, making them more susceptible to the buildup of plaque, which is exacerbated by high triglyceride levels.
- Elevated Blood Sugar: Individuals with high blood sugar levels, especially those with diabetes, are at a higher risk of developing high triglycerides. Insulin resistance, a common feature of type 2 diabetes, contributes to increased triglyceride production in the liver.
- Fatigue and Weakness: High triglycerides can lead to a decrease in the body's ability to transport oxygen and nutrients to cells and organs, potentially causing fatigue and weakness.
- Pancreatitis: Extremely high levels of triglycerides can cause inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), which is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Risk Factors for High Triglycerides

Understanding the risk factors for high triglycerides is crucial for prevention and management. Some of the key risk factors include:
- Diet High in Saturated and Trans Fats: Consuming foods high in saturated and trans fats can increase triglyceride levels.
- Lack of Physical Activity: A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to obesity and insulin resistance, both of which are linked to high triglycerides.
- Smoking: Smoking can damage the cardiovascular system and increase the risk of heart disease, which is linked to high triglyceride levels.
- Age: Triglyceride levels tend to rise with age.
- Family History: A family history of high cholesterol or heart disease can increase an individual's risk of developing high triglycerides.
Diagnosis and Treatment of High Triglycerides

Diagnosing high triglycerides involves a simple blood test that measures the levels of triglycerides and other lipids in the blood. The treatment for high triglycerides typically involves lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication. Lifestyle modifications include:
- Dietary Changes: Adopting a diet low in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol, and high in fiber and omega-3 fatty acids can help lower triglyceride levels.
- Weight Loss: Losing weight, especially around the abdominal area, can significantly reduce triglyceride levels.
- Increased Physical Activity: Regular exercise, such as walking, can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce triglyceride levels.
- Quitting Smoking: Stopping smoking can reduce the risk of heart disease and help manage triglyceride levels.
Managing High Triglycerides with Diet

Diet plays a crucial role in managing high triglycerides. Here are some dietary recommendations:
- Increase Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, can help lower triglycerides.
- Choose Healthy Fats: Focus on unsaturated fats found in foods like avocados, nuts, and olive oil.
- Limit Carbohydrates: Reduce intake of sugary drinks, refined grains, and saturated fats.
- Increase Fiber Intake: Soluble fiber found in foods like oats, barley, fruits, vegetables, and legumes can help lower triglycerides.
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, recognizing the signs of high triglycerides and understanding their implications is the first step towards a healthier lifestyle. By acknowledging the risk factors and implementing dietary and lifestyle changes, individuals can significantly reduce their triglyceride levels and lower their risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular conditions. It is essential to maintain open communication with healthcare providers, monitor triglyceride levels regularly, and adhere to treatment plans to ensure effective management of high triglycerides.
We invite our readers to share their experiences and insights on managing high triglycerides. Your comments and questions can provide valuable information for others who are seeking to understand and address this critical health issue. Additionally, consider sharing this article with friends and family who may benefit from this information, and don't hesitate to reach out to healthcare professionals for personalized advice on reducing triglyceride levels and improving overall cardiovascular health.
What are the common symptoms of high triglycerides?
+Common symptoms include obesity, high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar, fatigue, and weakness. In severe cases, extremely high triglycerides can cause pancreatitis.
How can I lower my triglyceride levels through diet?
+To lower triglyceride levels through diet, focus on consuming foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, healthy fats, and fiber. Limit your intake of carbohydrates, especially sugary drinks and refined grains, and avoid saturated and trans fats.
What are the risk factors for developing high triglycerides?
+Risk factors include a diet high in saturated and trans fats, lack of physical activity, smoking, age, and family history of high cholesterol or heart disease.
