Intro
Discover 5 effective ways to stop twitching, including stress reduction, muscle relaxation, and lifestyle changes, to alleviate involuntary muscle spasms and twitching symptoms, promoting overall nervous system health and wellness.
Twitching can be a frustrating and embarrassing experience, especially when it happens in public or at inopportune moments. Whether it's a twitching eye, a twitching muscle, or a full-blown tic, it can be distracting and disrupt daily life. The good news is that there are ways to stop twitching and manage its symptoms. In this article, we'll explore the possible causes of twitching, its effects on daily life, and provide practical tips on how to stop twitching.
Twitching can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, fatigue, caffeine, and certain medical conditions. It can also be a symptom of underlying neurological disorders, such as dystonia or Tourette's syndrome. Understanding the underlying cause of twitching is crucial in developing an effective treatment plan. By identifying the triggers and underlying causes, individuals can take steps to manage their symptoms and prevent future episodes.
In addition to its physical effects, twitching can also have a significant impact on a person's mental and emotional well-being. It can cause anxiety, embarrassment, and self-consciousness, making it challenging to interact with others or engage in daily activities. By addressing the root causes of twitching and developing strategies to manage its symptoms, individuals can regain control over their bodies and improve their overall quality of life.
Understanding Twitching
Types of Twitching
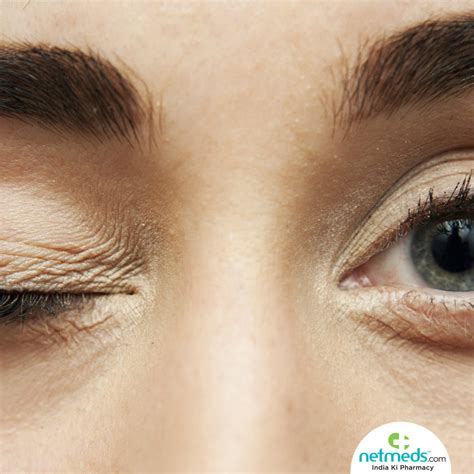
There are several types of twitching, including: * Muscle twitching: This is the most common type of twitching and occurs when a muscle contracts involuntarily. * Nerve twitching: This type of twitching occurs when a nerve is damaged or irritated, causing muscle contractions. * Eye twitching: This is a common type of twitching that occurs when the muscles around the eye contract involuntarily. * Facial twitching: This type of twitching occurs when the muscles in the face contract involuntarily, causing twitching or spasms.Causes of Twitching

Diagnosing Twitching
Diagnosing twitching typically involves a physical examination and a review of medical history. A doctor may also order tests, such as electromyography (EMG) or nerve conduction studies, to rule out underlying medical conditions. In some cases, a doctor may refer a patient to a specialist, such as a neurologist, for further evaluation and treatment.Treatment Options

Managing Symptoms
Managing symptoms of twitching involves a combination of medical treatment and lifestyle changes. Some tips for managing symptoms include: * Reducing stress: Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation or yoga, can help manage symptoms of twitching. * Getting regular exercise: Regular exercise can help reduce muscle tension and improve overall health. * Getting enough sleep: Getting enough sleep can help reduce fatigue and improve overall health. * Avoiding triggers: Avoiding triggers, such as caffeine and nicotine, can help manage symptoms of twitching.5 Ways to Stop Twitching
Additional Tips
Additional tips for stopping twitching include: * Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help reduce muscle contractions and improve overall health. * Eating a balanced diet: Eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce muscle contractions and improve overall health. * Avoiding certain medications: Certain medications, such as stimulants and certain antidepressants, can cause twitching. Avoiding these medications or talking to a doctor about alternative treatments can help manage symptoms of twitching.Conclusion and Next Steps

We encourage you to share your experiences with twitching in the comments below. Have you found any effective ways to manage your symptoms? What triggers your twitching episodes? Share your stories and help others who may be struggling with similar issues.
What are the most common causes of twitching?
+The most common causes of twitching include stress and anxiety, fatigue, caffeine, and certain medical conditions. In some cases, twitching can be a symptom of an underlying neurological disorder.
How can I stop twitching?
+To stop twitching, try reducing stress and anxiety, getting regular exercise, getting enough sleep, avoiding triggers, and practicing relaxation techniques. In some cases, medication or alternative therapies may be necessary to manage symptoms.
Can twitching be a sign of an underlying medical condition?
+Yes, twitching can be a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, or dystonia. If you're experiencing twitching, talk to a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
How can I manage stress and anxiety to reduce twitching?
+To manage stress and anxiety, try engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation or yoga, getting regular exercise, and getting enough sleep. Avoiding triggers, such as caffeine and nicotine, can also help reduce stress and anxiety.
Can alternative therapies help manage symptoms of twitching?
+Yes, alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage, and physical therapy, can help manage symptoms of twitching. Talk to a doctor or a licensed therapist to learn more about alternative therapies and how they can help manage your symptoms.
