Intro
Learn optimal fasting blood sugar rates and understand normal, high, and low levels with our comprehensive guide, covering targets, testing, and management strategies for healthy glucose control and diabetes prevention.
The importance of maintaining a healthy blood sugar level cannot be overstated. For individuals with diabetes, monitoring and controlling blood sugar levels is crucial to preventing complications and ensuring overall well-being. Even for those without diabetes, being aware of blood sugar levels can help identify potential health issues before they become severe. One key metric in assessing blood sugar health is the fasting blood sugar rate, which provides a snapshot of how the body manages glucose when it hasn't received any new intake. Understanding what this rate signifies, how it's measured, and what the results imply is essential for making informed decisions about health and lifestyle.
Maintaining a healthy fasting blood sugar rate is vital for preventing long-term damage to organs and blood vessels, which can lead to heart disease, kidney failure, and other serious conditions. High blood sugar levels over an extended period can damage blood vessels and the nerves that control the heart. Moreover, the kidneys may become overworked, trying to filter out the excess sugar from the blood, leading to potential kidney damage or disease. By understanding and managing fasting blood sugar levels, individuals can significantly reduce these risks and maintain a high quality of life.
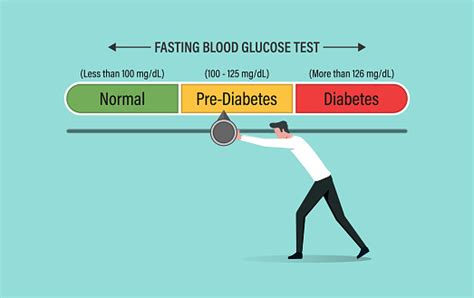
For individuals looking to understand their fasting blood sugar rate better, it's essential to delve into the specifics of what this measurement entails. The fasting blood sugar test, also known as the fasting glucose test, is a common diagnostic tool used to assess how well the body regulates blood sugar levels. This test requires an individual to fast for at least eight hours before the blood sample is taken, ensuring that the reading reflects the body's baseline glucose management without the influence of recent food intake. The results of this test can provide critical insights into glucose metabolism and help diagnose conditions like diabetes or prediabetes.
Understanding Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
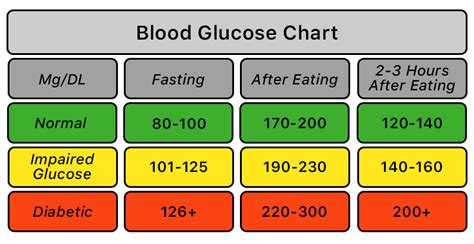
Understanding fasting blood sugar levels involves recognizing the normal ranges and what they signify. A normal fasting blood sugar level is typically below 100 mg/dL. Levels between 100 mg/dL and 125 mg/dL may indicate prediabetes, a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. A level of 126 mg/dL or higher suggests diabetes. These thresholds are crucial for diagnosing and managing diabetes and for preventing the onset of diabetes in those with prediabetes.
Factors Influencing Fasting Blood Sugar Rates
Several factors can influence fasting blood sugar rates, including diet, physical activity level, stress, and sleep patterns. For instance, consuming high amounts of simple carbohydrates and sugars before fasting can elevate fasting glucose levels. Similarly, lack of physical activity, high levels of stress, and inadequate sleep can also impact how the body regulates blood sugar, leading to higher fasting blood sugar rates. Understanding these factors is key to making lifestyle adjustments that can help manage and improve fasting blood sugar levels.Managing Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
Managing fasting blood sugar levels effectively involves a combination of dietary changes, increased physical activity, and, in some cases, medication. Dietary adjustments may include reducing intake of simple sugars and refined carbohydrates, increasing fiber intake, and eating regular, balanced meals. Physical activity, such as walking, jogging, or any form of exercise that raises heart rate and causes sweating, can significantly improve insulin sensitivity, helping the body to more effectively manage blood sugar levels.
Benefits of Healthy Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining healthy fasting blood sugar levels has numerous benefits, ranging from reducing the risk of diabetes complications to improving overall energy levels and mental clarity. By managing blood sugar effectively, individuals can prevent the damage high blood sugar causes to blood vessels and nerves, reducing the risk of heart disease, kidney disease, and vision problems. Furthermore, stable blood sugar levels contribute to better weight management, improved mood, and enhanced cognitive function.Monitoring and Testing Fasting Blood Sugar
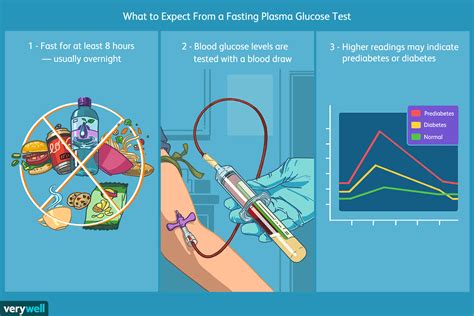
Monitoring and testing fasting blood sugar levels regularly is crucial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. This involves using a glucometer, a small device that measures blood glucose levels from a drop of blood obtained through a finger prick. Regular monitoring helps in adjusting diet, exercise, and medication to maintain blood sugar levels within the target range. It also provides immediate feedback on how different factors, such as specific foods or activities, affect blood sugar levels.
Interpreting Test Results
Interpreting fasting blood sugar test results requires understanding the different ranges and what they indicate. - **Normal**: Less than 100 mg/dL - **Prediabetes**: 100 mg/dL to 125 mg/dL - **Diabetes**: 126 mg/dL or higher Understanding these ranges helps individuals and healthcare providers make informed decisions about treatment and lifestyle adjustments.Lifestyle Adjustments for Better Blood Sugar Control

Making lifestyle adjustments is a critical component of managing fasting blood sugar levels. Key adjustments include:
- Dietary Changes: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Physical Activity: Engage in regular exercise, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week.
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Sleep Hygiene: Ensure adequate sleep, aiming for 7-8 hours per night, to help regulate blood sugar levels.
Role of Medication
For some individuals, lifestyle adjustments alone may not be sufficient to manage fasting blood sugar levels, and medication may be necessary. Medications for diabetes work in various ways, such as stimulating insulin release, improving insulin sensitivity, or delaying glucose absorption. The decision to start medication should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider, who can determine the best course of treatment based on individual needs and health status.Natural Remedies and Supplements

Several natural remedies and supplements have been studied for their potential in helping manage fasting blood sugar levels. These include:
- Berberine: A compound found in several plants, known for its ability to lower blood sugar levels.
- Chromium: A mineral that enhances the action of insulin, improving glucose metabolism.
- Cinnamon: A spice that has been shown to have a moderate effect in lowering blood sugar levels.
- Alpha-Lipoic Acid: An antioxidant that may help reduce insulin resistance and improve insulin sensitivity.
Precautions and Considerations
While considering natural remedies and supplements, it's essential to approach with caution. Not all supplements are safe for everyone, especially for individuals with certain health conditions or those taking medications. It's crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before adding any supplements to the regimen, to discuss potential benefits, risks, and interactions with other medications.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, managing fasting blood sugar levels is a multifaceted approach that involves lifestyle adjustments, monitoring, and when necessary, medication. By understanding the factors that influence fasting blood sugar rates and taking proactive steps to manage them, individuals can significantly improve their health outcomes. As research continues to uncover new insights into glucose metabolism and diabetes management, staying informed and adaptable will be key to navigating the complexities of blood sugar control.
Call to Action
For those looking to take control of their fasting blood sugar levels, the first step is often the most challenging. Whether it's scheduling a doctor's appointment, starting a new exercise routine, or simply being more mindful of dietary choices, every action counts. By sharing this article with others and engaging in conversations about blood sugar health, we can work together to raise awareness and support one another in our journeys towards better health.What is a normal fasting blood sugar level?
+A normal fasting blood sugar level is typically below 100 mg/dL.
How often should I test my fasting blood sugar?
+The frequency of testing fasting blood sugar depends on your health status and whether you have diabetes. Consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Can lifestyle changes alone manage fasting blood sugar levels?
+For some individuals, especially those with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise can effectively manage fasting blood sugar levels. However, for others, medication may also be necessary.
