Intro
Discover 5 effective ways value-based care works, improving patient outcomes through accountable, patient-centered, and cost-effective healthcare models, enhancing population health management and care coordination.
The healthcare industry has been undergoing a significant transformation in recent years, shifting from a traditional fee-for-service model to a value-based care approach. This change is driven by the need to improve patient outcomes, reduce costs, and enhance the overall quality of care. Value-based care is a healthcare delivery model that focuses on providing high-quality, patient-centered care while controlling costs. In this article, we will delve into the world of value-based care, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and key components.
The importance of value-based care cannot be overstated. With the rising costs of healthcare, it has become essential to find ways to deliver high-quality care while reducing expenses. Value-based care achieves this by incentivizing healthcare providers to prioritize patient outcomes and efficiency. This approach has been shown to improve patient satisfaction, reduce hospital readmissions, and lower costs. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, it is crucial to understand the principles and practices of value-based care.
The shift towards value-based care is not without its challenges. Healthcare providers must adapt to new payment models, invest in technology and infrastructure, and develop new skills to succeed in this environment. However, the benefits of value-based care far outweigh the challenges. By focusing on patient-centered care, healthcare providers can improve outcomes, reduce costs, and enhance the overall quality of care. In the following sections, we will explore the key components of value-based care, including its benefits, working mechanisms, and best practices.
Introduction to Value-Based Care
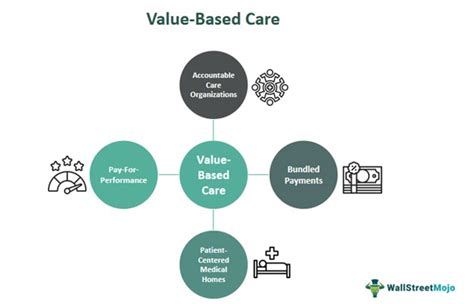
Key Principles of Value-Based Care
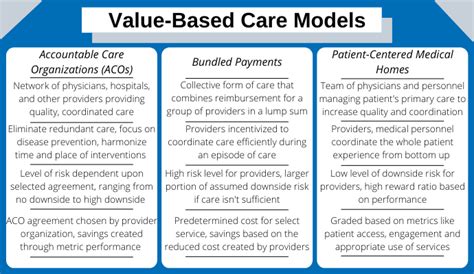
The key principles of value-based care include: * Patient engagement: Encouraging patients to take an active role in their care * Care coordination: Coordinating care across different settings and providers * Population health management: Managing the health of populations to improve outcomes and reduce costs * Quality measurement: Measuring and reporting quality metrics to improve care * Cost control: Controlling costs while maintaining qualityBenefits of Value-Based Care

Working Mechanisms of Value-Based Care
Value-based care works by incentivizing healthcare providers to prioritize patient outcomes and efficiency. This approach uses various payment models, including: * Pay-for-performance: Paying providers based on their performance on quality metrics * Bundled payments: Paying providers a fixed fee for a bundle of services * Capitation: Paying providers a fixed fee per patientKey Components of Value-Based Care
Best Practices for Implementing Value-Based Care
Some best practices for implementing value-based care include: * Developing a clear strategy and vision * Investing in technology and infrastructure * Building a strong care team * Engaging patients and families * Continuously measuring and improving qualityChallenges and Opportunities in Value-Based Care

Overcoming Challenges in Value-Based Care
To overcome the challenges of value-based care, healthcare providers can: * Develop a clear strategy and vision * Invest in technology and infrastructure * Build a strong care team * Engage patients and families * Continuously measure and improve qualityFuture of Value-Based Care

Trends in Value-Based Care
Some trends in value-based care include: * Increased use of data analytics * Growing importance of patient engagement * Expanding role of care coordination * Emerging importance of population health managementConclusion and Next Steps

We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with value-based care in the comments below. What do you think are the most significant benefits and challenges of value-based care? How can healthcare providers overcome the challenges of implementing value-based care? Share this article with your colleagues and friends to continue the conversation.
What is value-based care?
+Value-based care is a healthcare delivery model that prioritizes patient outcomes and quality of care.
What are the benefits of value-based care?
+The benefits of value-based care include improved patient outcomes, reduced costs, and enhanced patient satisfaction.
How does value-based care work?
+Value-based care works by incentivizing healthcare providers to prioritize patient outcomes and efficiency, using various payment models such as pay-for-performance, bundled payments, and capitation.
What are the key components of value-based care?
+The key components of value-based care include data analytics, care coordination, patient engagement, and population health management.
What are the challenges of implementing value-based care?
+The challenges of implementing value-based care include changing payment models, investing in technology, and developing new skills.
