Intro
Discover how fish oil thins blood, reducing inflammation and improving heart health with omega-3 fatty acids, EPA, and DHA, naturally preventing blood clots and strokes.
The importance of maintaining good cardiovascular health cannot be overstated. One of the key factors in ensuring the well-being of our hearts is the management of blood viscosity and clotting. Fish oil, rich in omega-3 fatty acids, has been widely recognized for its beneficial effects on heart health, including its ability to thin blood and reduce the risk of thrombosis. This article delves into the mechanisms by which fish oil exerts its anti-coagulant effects, exploring the biochemical pathways and clinical evidence that support its use as a natural blood thinner.
Fish oil supplementation has become increasingly popular due to its broad range of health benefits, from reducing inflammation and improving brain function to supporting heart health. The omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil, particularly EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), are key players in these beneficial effects. When it comes to blood thinning, understanding how these compounds interact with the body's physiological processes is crucial. By influencing various aspects of blood clotting and vessel wall function, fish oil can help prevent the formation of harmful blood clots that could lead to heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events.
The interaction between fish oil and blood viscosity is complex, involving multiple biochemical pathways and cellular mechanisms. Essentially, the omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil work to reduce inflammation in the body, which is a major contributor to the development of atherosclerosis (the buildup of plaques in arteries) and subsequent thrombosis. By mitigating inflammatory responses, fish oil helps maintain the integrity of blood vessels and prevents excessive clotting. Moreover, omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to improve blood lipid profiles, further contributing to the reduction of cardiovascular risk. As research continues to uncover the full scope of fish oil's benefits, its potential as a natural adjunct to conventional anti-coagulant therapies becomes increasingly evident.
Introduction to Fish Oil and Blood Thinning

Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Their Role in Blood Thinning
The primary omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil, EPA and DHA, exert their blood-thinning effects through several mechanisms: - **Inhibition of Platelet Aggregation:** Omega-3 fatty acids reduce the stickiness of platelets, which are small blood cells that play a key role in clot formation. By inhibiting platelet aggregation, fish oil supplementation can prevent the initial steps of clot formation. - **Reduction of Inflammatory Markers:** Chronic inflammation is a known risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Omega-3 fatty acids have potent anti-inflammatory properties, reducing the levels of inflammatory markers in the body and thereby decreasing the risk of thrombosis. - **Improvement of Blood Vessel Function:** Fish oil helps in maintaining the flexibility and health of blood vessels, improving blood flow and reducing blood pressure, all of which contribute to a lower risk of clot formation.Mechanisms of Fish Oil in Blood Thinning
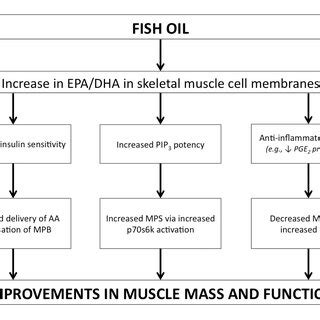
Clinical Evidence Supporting Fish Oil's Blood-Thinning Effects
Numerous clinical trials and observational studies have investigated the relationship between fish oil supplementation and cardiovascular health. While the evidence is not uniform and some studies have reported mixed results, the overall consensus supports the notion that fish oil can contribute to a reduced risk of heart disease, including a decrease in blood clotting tendency. For instance, studies have shown that individuals consuming higher amounts of fish oil have lower levels of triglycerides, a type of fat in the blood that can contribute to clotting, and improved ratios of omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acids, which is associated with better cardiovascular outcomes.Benefits of Using Fish Oil as a Natural Blood Thinner

Practical Considerations for Fish Oil Supplementation
For those considering fish oil supplementation as a means to support cardiovascular health and blood thinning, several practical considerations are important: - **Dosage:** The optimal dose of fish oil for blood thinning effects is not universally agreed upon, but most studies suggest benefits with daily intakes of 1-2 grams of combined EPA and DHA. - **Source:** The quality of fish oil supplements can vary widely. Look for products that are certified by third-party organizations and have been purified to remove contaminants such as mercury and PCBs. - **Interactions:** Individuals on anti-coagulant medications should consult with their healthcare provider before starting fish oil supplementation, as the combination may increase the risk of bleeding.Potential Risks and Side Effects of Fish Oil Supplementation

Future Directions in Fish Oil Research
The ongoing research into the effects of fish oil on cardiovascular health and blood thinning is expected to uncover new insights into its mechanisms of action and potential therapeutic applications. Future studies may focus on optimizing dosing regimens, exploring the benefits of fish oil in specific patient populations, and investigating its use in combination with other natural compounds or conventional medications to achieve synergistic effects. As our understanding of omega-3 fatty acids and their role in human health evolves, the potential for fish oil to play a significant role in preventive and therapeutic strategies against cardiovascular disease will likely continue to grow.Conclusion and Recommendations

Final Thoughts on Integrating Fish Oil into Your Health Routine
Integrating fish oil into your daily routine can be a simple yet effective step towards better cardiovascular health. Whether through dietary changes that include more fatty fish, or through supplementation with high-quality fish oil products, the potential benefits of omega-3 fatty acids are clear. By combining fish oil with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and other healthy lifestyle choices, individuals can take a proactive approach to protecting their heart health and reducing the risk of blood clots and other cardiovascular events.What are the primary omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil?
+The primary omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil are EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), which are key players in its beneficial effects on heart health and blood thinning.
How does fish oil affect blood clotting?
+Fish oil affects blood clotting by reducing the stickiness of platelets, inhibiting the production of pro-coagulant eicosanoids, and improving blood vessel function, all of which contribute to a reduced risk of thrombosis.
What are the recommended daily doses of fish oil for blood thinning effects?
+The recommended daily doses of fish oil for blood thinning effects vary, but most studies suggest benefits with intakes of 1-2 grams of combined EPA and DHA per day.
We hope this comprehensive overview has provided valuable insights into the role of fish oil in blood thinning and its potential benefits for cardiovascular health. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with fish oil supplementation, please don't hesitate to comment below. Your feedback and engagement are invaluable in helping us create more informative and helpful content for our readers. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from learning about the natural health benefits of fish oil.
