Intro
Discover how pleural effusion impacts lung function, causing respiratory issues like shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing, affecting overall lung health and potentially leading to complications.
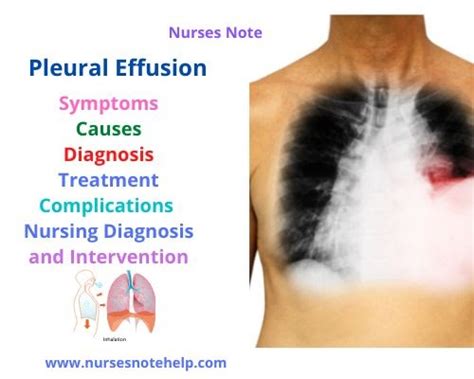
Pleural effusion is a condition characterized by the accumulation of excess fluid in the pleural space, which is the area between the lungs and the chest wall. This condition can have significant effects on the lungs, impacting their ability to function properly. Understanding the ways in which pleural effusion affects the lungs is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes. The importance of addressing pleural effusion lies in its potential to compromise respiratory function, leading to symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing. As the condition progresses, it can lead to more severe complications, including respiratory failure. Therefore, it is essential to explore the various aspects of pleural effusion and its impact on lung health.
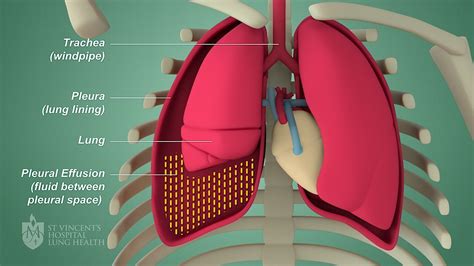
The lungs are delicate organs that play a critical role in maintaining overall health. They are responsible for exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide through the process of respiration. Any condition that affects the lungs, such as pleural effusion, can have far-reaching consequences for the body as a whole. Pleural effusion can result from a variety of underlying causes, including infections, cancers, and inflammatory diseases. Regardless of the cause, the accumulation of fluid in the pleural space can lead to increased pressure on the lungs, reducing their ability to expand and contract properly. This, in turn, can impair gas exchange, leading to inadequate oxygenation of the blood and tissues.
Pleural effusion is a condition that requires prompt medical attention to prevent long-term damage to the lungs. The effects of pleural effusion on the lungs can be multifaceted, involving changes in lung mechanics, gas exchange, and overall respiratory function. As the fluid accumulates in the pleural space, it can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to life-threatening complications. The severity of the condition depends on the amount of fluid present, the underlying cause, and the individual's overall health status. By understanding the mechanisms by which pleural effusion affects the lungs, healthcare providers can develop targeted interventions to alleviate symptoms, address underlying causes, and improve patient outcomes.
Introduction to Pleural Effusion

Causes of Pleural Effusion
The causes of pleural effusion can be diverse, including infections, cancers, inflammatory diseases, and heart failure. Infections such as pneumonia can lead to pleural effusion by causing inflammation and fluid accumulation in the pleural space. Similarly, cancers such as lung cancer and breast cancer can metastasize to the pleura, resulting in fluid accumulation. Inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus can also cause pleural effusion by promoting inflammation and fluid buildup in the pleural space.Effects of Pleural Effusion on Lung Function

Impact on Gas Exchange
The impact of pleural effusion on gas exchange is a critical aspect of the condition. Gas exchange refers to the process by which oxygen is transferred from the lungs to the blood and carbon dioxide is removed. Pleural effusion can impair gas exchange by reducing the surface area available for gas exchange and increasing the distance between the alveoli and the pulmonary capillaries. This can lead to hypoxemia, a condition characterized by low oxygen levels in the blood, which can have far-reaching consequences for the body.Diagnosis and Treatment of Pleural Effusion

Treatment Options
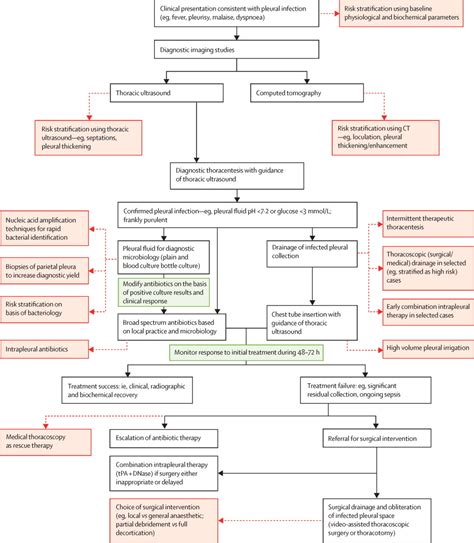
Treatment options for pleural effusion depend on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. For small, asymptomatic effusions, observation and monitoring may be sufficient. However, for larger effusions or those causing significant symptoms, drainage of the fluid may be necessary. This can be achieved through thoracentesis, a procedure in which a needle is inserted into the pleural space to remove fluid. In some cases, a chest tube may be inserted to allow for continuous drainage of the fluid.Complications of Pleural Effusion
Prevention and Management
Prevention and management of pleural effusion involve addressing the underlying cause and reducing the risk of complications. For individuals with underlying conditions like heart failure or cancer, managing these conditions can help prevent pleural effusion. Reducing the risk of infections, such as pneumonia, through vaccination and practicing good hygiene can also play a role in prevention. Management of pleural effusion may involve a multidisciplinary approach, including pulmonary, oncology, and infectious disease specialists, to address the condition and its underlying cause effectively.Living with Pleural Effusion
Coping Strategies
Coping strategies for individuals with pleural effusion include stress management, breathing exercises, and pulmonary rehabilitation. Stress management techniques, such as meditation and yoga, can help reduce anxiety and improve overall well-being. Breathing exercises, including diaphragmatic breathing, can help improve lung function and increase oxygenation. Pulmonary rehabilitation programs, which include exercise training, education, and support, can help individuals with pleural effusion and other respiratory conditions improve their lung function and quality of life.Future Directions in Pleural Effusion Management
Emerging Therapies
Emerging therapies for pleural effusion include the use of pleural catheters for continuous fluid drainage and the development of new pharmacological agents to reduce fluid accumulation. Pleural catheters can provide a minimally invasive means of managing pleural effusion, reducing the need for repeated thoracenteses and hospital admissions. New pharmacological agents, such as those targeting the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathway, may help reduce fluid accumulation and improve symptoms in individuals with pleural effusion.Conclusion and Recommendations
As we reflect on the complexities of pleural effusion and its impact on lung health, it becomes clear that a comprehensive approach is necessary to address this condition. By combining medical treatment with lifestyle modifications and support, individuals with pleural effusion can navigate the challenges of this condition and improve their overall well-being. We invite readers to share their experiences, ask questions, and seek guidance from healthcare professionals to better understand and manage pleural effusion.
What are the common causes of pleural effusion?
+Pleural effusion can result from a variety of underlying causes, including infections, cancers, inflammatory diseases, and heart failure. The specific cause can influence the treatment approach and outcome.
How is pleural effusion diagnosed?
+Diagnosis of pleural effusion typically involves a combination of physical examination, imaging studies like chest X-rays and CT scans, and laboratory tests, including pleural fluid analysis.
What are the treatment options for pleural effusion?
+Treatment options for pleural effusion depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition, ranging from observation and monitoring for small, asymptomatic effusions to drainage of the fluid through thoracentesis or chest tube insertion for larger effusions or those causing significant symptoms.
