Intro
Discover key Inflammatory Breast Cancer facts, symptoms, and treatment options, including rare signs, aggressive forms, and targeted therapies for this rare breast cancer subtype.
Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) is a rare and aggressive form of breast cancer that accounts for approximately 1-5% of all breast cancer cases in the United States. Despite its rarity, IBC is a highly malignant disease that requires immediate medical attention. The importance of understanding IBC lies in its potential to cause significant harm if left untreated or misdiagnosed. It is essential to recognize the symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options available for IBC to ensure prompt and effective care.
The lack of awareness about IBC among the general public and even some healthcare professionals can lead to delayed diagnosis and poor outcomes. Therefore, it is crucial to educate oneself about the disease, its characteristics, and the latest research findings. By doing so, individuals can better navigate the complexities of IBC and make informed decisions about their health. Furthermore, increased awareness can also promote earlier detection and treatment, ultimately improving survival rates and quality of life for those affected by this devastating disease.
IBC is a unique form of breast cancer that presents distinct challenges in diagnosis, treatment, and management. Unlike other types of breast cancer, IBC often does not form a distinct lump or tumor. Instead, it causes the breast to become inflamed, swollen, and tender, which can be mistaken for an infection or other benign condition. This characteristic makes it essential to approach IBC with a comprehensive understanding of its clinical presentation, diagnostic criteria, and therapeutic options. By exploring the intricacies of IBC, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of this disease and the importance of multidisciplinary care.
Inflammatory Breast Cancer Symptoms
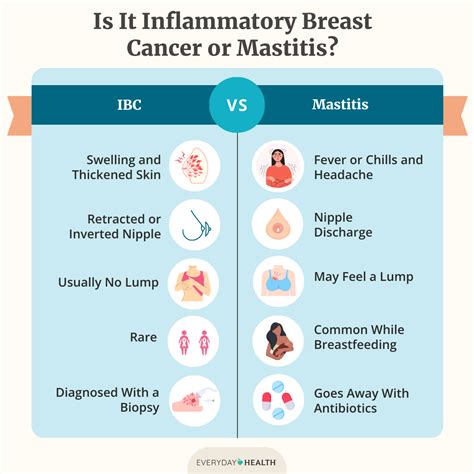
Risk Factors and Causes
The exact causes of IBC are not fully understood, but several risk factors have been identified. These include being female, as IBC is extremely rare in men, and having a family history of breast cancer. Other potential risk factors may include obesity, African American ethnicity, and a history of radiation exposure. While these factors can increase an individual's likelihood of developing IBC, they do not guarantee the disease will occur. Therefore, it is crucial to maintain a healthy lifestyle, undergo regular breast cancer screenings, and seek medical attention if any unusual symptoms or changes are detected.Inflammatory Breast Cancer Diagnosis
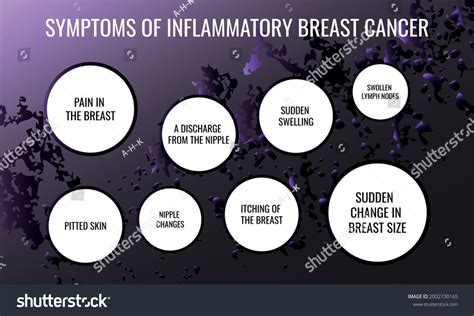
Staging and Classification
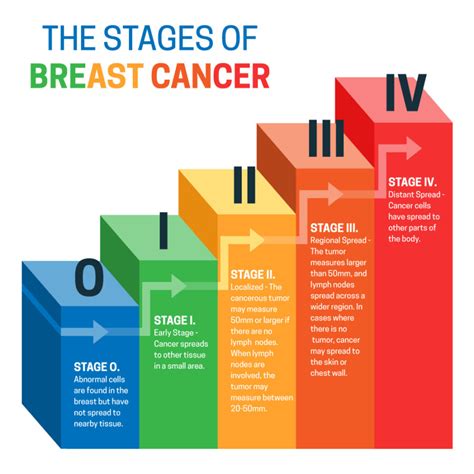
Once IBC is diagnosed, the disease is typically staged using the TNM system, which considers the size of the tumor (T), the spread to nearby lymph nodes (N), and the presence of distant metastasis (M). IBC is usually classified as stage III or stage IV, depending on the extent of the disease. This classification helps guide treatment decisions and predict outcomes. Understanding the stage and classification of IBC is essential for developing an effective treatment plan and improving survival rates.Inflammatory Breast Cancer Treatment

Palliative Care and Support
In addition to curative treatments, palliative care and support are essential for individuals with IBC. Palliative care focuses on alleviating symptoms, managing pain, and improving quality of life. This can include medication, physical therapy, and emotional support. Furthermore, support groups and counseling can help individuals cope with the emotional and psychological aspects of IBC. By addressing the physical, emotional, and social needs of those affected by IBC, healthcare providers can improve overall well-being and enhance the effectiveness of treatment.Inflammatory Breast Cancer Prognosis
Current Research and Developments
Ongoing research is focused on improving our understanding of IBC, developing more effective treatments, and enhancing patient outcomes. This includes investigating new chemotherapy regimens, targeted therapies, and immunotherapies. Additionally, researchers are exploring the genetic and molecular mechanisms underlying IBC, with the goal of identifying potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets. By staying up-to-date with the latest research findings and advances in IBC treatment, individuals can make informed decisions about their care and participate in clinical trials or other research studies.Inflammatory Breast Cancer Prevention

Genetic Counseling and Testing
Genetic counseling and testing can help identify individuals who are at increased risk of developing IBC due to inherited genetic mutations. The most common mutations associated with breast cancer are BRCA1 and BRCA2. Individuals who test positive for these mutations may consider preventive measures such as prophylactic mastectomy or enhanced screening. By understanding their genetic risk, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their likelihood of developing IBC and improve their overall health.Inflammatory Breast Cancer Awareness

Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, IBC is a complex and aggressive disease that requires prompt medical attention and comprehensive care. By understanding the symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of IBC, individuals can take an active role in managing their health and improving their chances of survival. It is essential to stay informed about the latest research findings, participate in awareness campaigns, and support those affected by IBC. Together, we can make a difference in the lives of individuals with IBC and work towards a future where this devastating disease is no longer a threat.What are the most common symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer?
+The most common symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer include breast swelling, redness, and warmth, which can be accompanied by itching, pain, or tenderness.
How is inflammatory breast cancer diagnosed?
+Inflammatory breast cancer is typically diagnosed using a combination of physical examinations, imaging studies, and biopsy.
What are the treatment options for inflammatory breast cancer?
+Treatment for inflammatory breast cancer usually involves a combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of inflammatory breast cancer. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others. By working together, we can raise awareness about IBC and improve the lives of those affected by this devastating disease.
