Intro
Learn effective food poisoning treatment and prevention methods, including symptom relief, home remedies, and medical interventions to combat foodborne illnesses and bacterial infections.
Food poisoning is a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide every year. It occurs when we consume contaminated or spoiled food, which can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to life-threatening complications. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for food poisoning is essential to prevent and manage this condition effectively. In this article, we will delve into the world of food poisoning, exploring its types, symptoms, and treatment options, as well as providing valuable tips on how to prevent it.
Food poisoning can be caused by a variety of factors, including bacteria, viruses, parasites, and toxins. Some of the most common culprits behind food poisoning are Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria. These microorganisms can contaminate food at any stage of production, processing, or preparation, making it crucial to handle and cook food safely. Moreover, food poisoning can also be caused by consuming spoiled or expired food, which can harbor harmful bacteria and toxins.
The symptoms of food poisoning can vary depending on the type and severity of the contamination. Common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and fever. In severe cases, food poisoning can lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and even organ failure. It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if symptoms persist or worsen over time. A healthcare professional can diagnose food poisoning through a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as stool cultures and blood tests.
Understanding Food Poisoning

To understand food poisoning, it is crucial to know the different types of contamination that can occur. There are several types of food poisoning, including bacterial, viral, parasitic, and toxic. Bacterial food poisoning is the most common type, accounting for the majority of cases. It is caused by bacteria such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria, which can contaminate food through various means, including poor handling and cooking practices.
Types of Food Poisoning
Bacterial food poisoning can be further divided into several subtypes, including: * Salmonella poisoning: caused by the Salmonella bacteria, which can contaminate food such as poultry, eggs, and dairy products. * E. coli poisoning: caused by the E. coli bacteria, which can contaminate food such as ground beef, unpasteurized juice, and raw produce. * Listeria poisoning: caused by the Listeria bacteria, which can contaminate food such as hot dogs, deli meats, and soft cheeses.Treatment Options for Food Poisoning
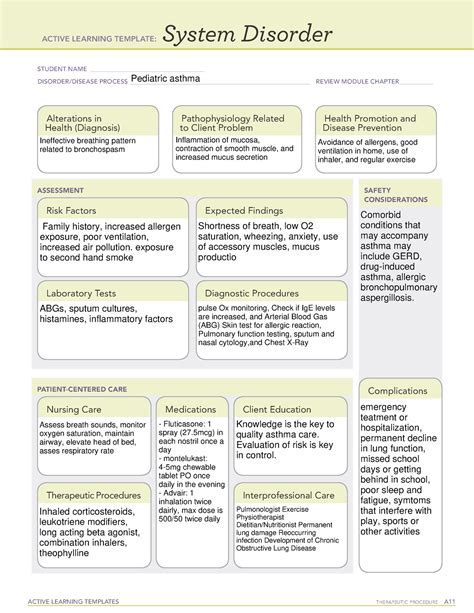
The treatment for food poisoning depends on the severity and type of contamination. In most cases, food poisoning can be treated at home with rest, hydration, and a bland diet. However, in severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to manage dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and other complications. Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat bacterial food poisoning, while anti-diarrheal medications can help manage symptoms such as diarrhea and abdominal cramps.
Home Remedies for Food Poisoning
There are several home remedies that can help manage food poisoning symptoms, including: * Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids, such as water, clear broth, and electrolyte-rich beverages like coconut water or sports drinks. * Eating a bland diet, such as bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast (BRAT diet). * Avoiding spicy, fatty, or heavy foods that can irritate the stomach. * Getting plenty of rest to help the body recover from the infection.Prevention is Key

Preventing food poisoning is crucial to avoid the risk of contamination and subsequent health complications. There are several ways to prevent food poisoning, including:
- Handling and cooking food safely, such as washing hands frequently, separating raw and cooked food, and cooking food to the recommended internal temperature.
- Avoiding high-risk foods, such as raw or undercooked meat, poultry, and eggs, as well as unpasteurized dairy products and juices.
- Storing food properly, such as refrigerating perishable food promptly and freezing food at 0°F (-18°C) or below.
- Being aware of food recalls and outbreaks, and taking necessary precautions to avoid contaminated food.
Food Safety Tips
Here are some additional food safety tips to prevent food poisoning: * Wash hands frequently with soap and water, especially after handling raw food, before eating, and after using the bathroom. * Separate raw and cooked food to prevent cross-contamination. * Cook food to the recommended internal temperature, such as 165°F (74°C) for poultry and 145°F (63°C) for beef, pork, and lamb. * Refrigerate perishable food promptly, such as within two hours of cooking or purchasing.Complications of Food Poisoning

In severe cases, food poisoning can lead to complications such as dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and organ failure. Dehydration can occur when the body loses too much fluid and electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and chloride. Electrolyte imbalance can lead to muscle weakness, fatigue, and heart arrhythmias. Organ failure, such as kidney or liver failure, can occur in severe cases of food poisoning, especially in people with underlying health conditions.
Risk Factors for Complications
Certain groups of people are at higher risk of developing complications from food poisoning, including: * Older adults: people over 65 years old may be more susceptible to dehydration and electrolyte imbalance due to age-related decline in physical function. * Pregnant women: pregnant women may be more susceptible to food poisoning due to changes in their immune system and digestive tract. * Young children: children under 5 years old may be more susceptible to dehydration and electrolyte imbalance due to their small body size and developing immune system. * People with underlying health conditions: people with conditions such as diabetes, kidney disease, and liver disease may be more susceptible to complications from food poisoning.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, food poisoning is a common health issue that can be prevented and managed with proper knowledge and precautions. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for food poisoning, we can take steps to protect ourselves and our loved ones from this condition. Remember to always handle and cook food safely, avoid high-risk foods, and store food properly to prevent contamination. If you suspect you have food poisoning, seek medical attention immediately to prevent complications and promote recovery.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with food poisoning in the comments below. Have you or a loved one ever had food poisoning? What steps do you take to prevent food poisoning in your daily life? Share your tips and advice with our community to help us create a safer and healthier food environment for everyone.
What are the most common symptoms of food poisoning?
+The most common symptoms of food poisoning include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and fever.
How can I prevent food poisoning at home?
+To prevent food poisoning at home, handle and cook food safely, avoid high-risk foods, and store food properly. Wash your hands frequently, separate raw and cooked food, and cook food to the recommended internal temperature.
What should I do if I suspect I have food poisoning?
+If you suspect you have food poisoning, seek medical attention immediately. Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids, and avoid solid foods until your symptoms subside. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to manage dehydration and electrolyte imbalance.
