Intro
Discover foods rich in potassium, including bananas, leafy greens, and sweet potatoes, to boost heart health, lower blood pressure, and support muscle function with these potassium-rich diet essentials.
The importance of potassium in our diets cannot be overstated. As one of the essential minerals our bodies need to function properly, potassium plays a critical role in maintaining healthy blood pressure, promoting bone health, and supporting muscle function. Despite its significance, many of us do not consume enough potassium-rich foods, leading to potential health issues such as fatigue, weakness, and heart problems. Understanding the benefits of potassium and incorporating potassium-rich foods into our diets can significantly enhance our overall well-being.
Potassium is vital for maintaining the balance of fluids within our bodies, helping our nerves to function correctly, and enabling our muscles to contract. It also helps to reduce the risk of kidney stones, supports healthy bone mineral density, and may even lower blood pressure in individuals with hypertension. With so many benefits, it's crucial to know which foods are rich in potassium and how we can easily add them to our daily meals. From fresh fruits and vegetables to whole grains and lean proteins, there are numerous delicious and nutritious options available.
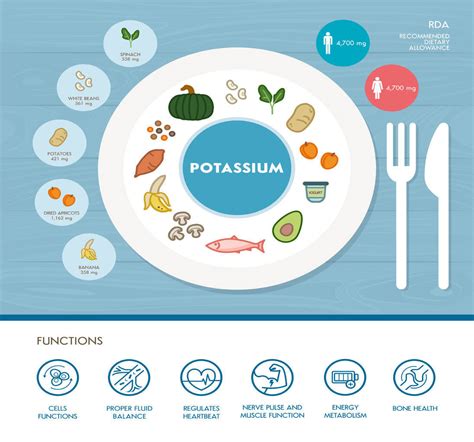
The average adult needs about 4,700 milligrams of potassium per day, according to the World Health Organization. Meeting this requirement can be achieved by consuming a variety of whole, unprocessed foods. For instance, bananas are one of the most well-known potassium-rich foods, but they are not the only option. Other fruits like avocados, apricots, and citrus fruits are also excellent sources of potassium. Leafy green vegetables, such as spinach and kale, are packed with potassium, as are sweet potatoes, squash, and other root vegetables. Even certain types of fish and dairy products can contribute to our daily potassium intake.
Potassium Benefits for Health

Potassium has numerous benefits for our health, ranging from reducing blood pressure to supporting bone health. One of the most significant advantages of consuming enough potassium is its effect on blood pressure. Studies have shown that a diet rich in potassium can help lower blood pressure in people with hypertension, reducing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. Potassium achieves this by balancing out the effects of sodium in the body and helping to relax the walls of blood vessels, which allows blood to flow more easily.
In addition to its impact on cardiovascular health, potassium plays a crucial role in muscle function. It helps muscles to contract and relax, making it essential for athletic performance and reducing the risk of muscle cramps and spasms. Potassium also supports bone health by reducing the amount of calcium excreted in the urine, which can help to prevent osteoporosis and fractures. Furthermore, potassium has been shown to have a positive effect on kidney health, reducing the risk of kidney stones and supporting overall kidney function.
Types of Potassium-Rich Foods
Potassium-rich foods can be broadly categorized into several groups, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy products. Each of these categories offers a variety of options, making it easy to incorporate potassium-rich foods into our diets. For example, fruits such as bananas, avocados, and apricots are all high in potassium, as are leafy green vegetables like spinach and kale. Whole grains, such as brown rice and quinoa, are also good sources of potassium, as are lean proteins like salmon and chicken.Some of the richest sources of potassium include:
- Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and collard greens
- Fresh fruits: Bananas, avocados, apricots, and citrus fruits
- Root vegetables: Sweet potatoes, squash, and carrots
- Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread
- Lean proteins: Salmon, chicken, and turkey
- Dairy products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese
Foods High in Potassium

Among the foods high in potassium, some stand out for their exceptionally high content. For instance, a single medium-sized sweet potato can provide over 700 milligrams of potassium, while a cup of cooked spinach can offer over 800 milligrams. Avocados are another potassium-rich food, with a single medium-sized avocado providing around 708 milligrams. Even certain types of fish, such as salmon and tuna, are good sources of potassium, with a 3-ounce serving providing around 500 milligrams.
To give you a better idea, here are some specific foods and their potassium content per serving:
- Banana (1 medium): 422 milligrams
- Avocado (1 medium): 708 milligrams
- Spinach (1 cup cooked): 840 milligrams
- Sweet potato (1 medium): 542 milligrams
- Salmon (3 ounces): 534 milligrams
- Apricots (1 cup dried): 1,478 milligrams
How to Increase Potassium Intake
Increasing potassium intake can be achieved through simple dietary changes. One of the most effective ways is to focus on whole, unprocessed foods, which tend to be naturally rich in potassium. This includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy products. Another strategy is to incorporate potassium-rich foods into every meal, such as adding spinach to omelets, having an avocado as a side dish, or snacking on bananas and apricots.For those who find it challenging to get enough potassium from their diet alone, supplements are available. However, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplements, as excessive potassium intake can lead to adverse health effects. Generally, a balanced diet that includes a wide range of whole foods can provide all the potassium the body needs.
Potassium Deficiency Symptoms
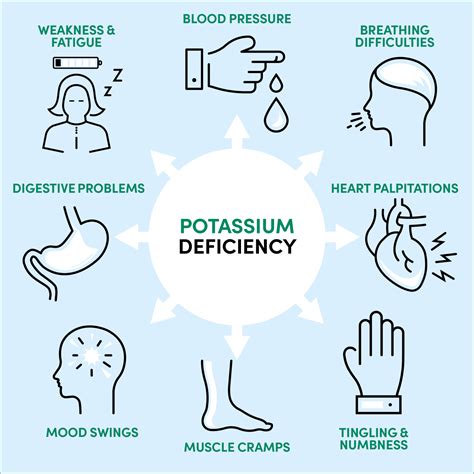
A potassium deficiency, also known as hypokalemia, can lead to a range of symptoms. Mild cases may cause fatigue, weakness, and muscle cramps, while more severe deficiencies can result in heart arrhythmias, muscle paralysis, and respiratory failure. Other symptoms of potassium deficiency include:
- Constipation
- Abdominal cramping
- Bloating and water retention
- Palpitations
- Muscle spasms
It's crucial to recognize these symptoms early and seek medical attention if they persist or worsen. Treatment for potassium deficiency typically involves dietary changes to increase potassium intake, and in severe cases, may require intravenous potassium supplementation.
Potassium and Blood Pressure
The relationship between potassium and blood pressure is well-documented. Potassium helps to lower blood pressure by counteracting the effects of sodium and relaxing the walls of blood vessels. This makes potassium an essential mineral for individuals with hypertension or those at risk of developing high blood pressure.Studies have consistently shown that a diet rich in potassium can help to reduce blood pressure in people with hypertension. For example, the DASH diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension), which emphasizes potassium-rich foods, has been proven to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Potassium-Rich Recipes

Incorporating potassium-rich foods into your diet can be easy and delicious. Here are some simple recipes to get you started:
- Spinach and Feta Stuffed Chicken: Stuff boneless chicken breasts with a mixture of spinach, feta cheese, and lemon juice, then bake until cooked through.
- Avocado and Banana Smoothie: Blend together avocado, banana, milk, and a sprinkle of cinnamon for a potassium-packed smoothie.
- Sweet Potato and Black Bean Tacos: Fill tacos with roasted sweet potato, black beans, and a sprinkle of cheese for a flavorful and nutritious meal.
- Grilled Salmon with Roasted Vegetables: Grill salmon and serve with a variety of roasted vegetables, such as Brussels sprouts and sweet potatoes, for a potassium-rich dinner.
These recipes demonstrate how easy it is to incorporate potassium-rich foods into your meals, ensuring you meet your daily potassium needs and reap the many health benefits associated with this essential mineral.
Potassium Supplements
While dietary changes are the preferred method for increasing potassium intake, supplements are available for those who need them. Potassium supplements come in various forms, including potassium gluconate, potassium citrate, and potassium chloride. However, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen, as excessive potassium intake can lead to adverse health effects.Supplements may be necessary for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease or those taking certain medications that cause potassium loss. Additionally, athletes or individuals who engage in strenuous physical activity may require potassium supplements to replenish lost electrolytes.
Potassium and Athletic Performance

Potassium plays a critical role in athletic performance, particularly in endurance sports. It helps to regulate fluid balance, support muscle function, and maintain nerve function, all of which are essential for optimal performance.
During intense physical activity, potassium levels can drop, leading to muscle cramps, fatigue, and decreased performance. Athletes can replenish lost potassium by consuming potassium-rich foods or supplements. Bananas, avocados, and coconut water are popular choices among athletes due to their high potassium content.
Potassium-Rich Snacks
Snacking on potassium-rich foods can help to maintain optimal potassium levels throughout the day. Here are some healthy snack options: - Fresh fruits: Bananas, avocados, and apricots - Nuts and seeds: Almonds, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds - Vegetables: Carrot sticks with hummus, cucumber slices, and cherry tomatoes - Dairy products: Yogurt, milk, and cheeseThese snacks are not only rich in potassium but also provide a range of other essential nutrients, making them a great addition to a balanced diet.
Potassium and Bone Health
Potassium has been shown to have a positive effect on bone health, particularly in older adults. It helps to reduce the amount of calcium excreted in the urine, which can help to prevent osteoporosis and fractures.
A diet rich in potassium, combined with adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, can support healthy bone mineral density. Foods rich in potassium, such as leafy greens, fruits, and whole grains, are also rich in other nutrients essential for bone health, making them a great addition to a balanced diet.
Potassium and Kidney Health
Potassium is essential for maintaining healthy kidneys. It helps to regulate fluid balance, support blood pressure, and reduce the risk of kidney stones.Individuals with kidney disease may need to limit their potassium intake, as their kidneys may not be able to effectively remove excess potassium from the body. However, for those with healthy kidneys, a diet rich in potassium can help to support kidney function and reduce the risk of kidney disease.
Potassium and Heart Health

The relationship between potassium and heart health is well-established. Potassium helps to lower blood pressure, reduce the risk of heart disease, and support overall cardiovascular health.
A diet rich in potassium, combined with regular physical activity and a healthy lifestyle, can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease. Foods rich in potassium, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, are also rich in other nutrients essential for heart health, making them a great addition to a balanced diet.
Potassium-Rich Foods for Vegetarians
Vegetarians can easily meet their potassium needs by consuming a variety of plant-based foods. Here are some potassium-rich options: - Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and collard greens - Fresh fruits: Bananas, avocados, and apricots - Legumes: White beans, lentils, and chickpeas - Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread - Nuts and seeds: Almonds, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seedsThese foods are not only rich in potassium but also provide a range of other essential nutrients, making them a great addition to a balanced vegetarian diet.
What are the symptoms of potassium deficiency?
+Potassium deficiency can cause a range of symptoms, including fatigue, weakness, muscle cramps, and heart arrhythmias. In severe cases, it can lead to muscle paralysis and respiratory failure.
How can I increase my potassium intake?
+You can increase your potassium intake by consuming a variety of whole, unprocessed foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy products. Supplements are also available, but it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.
What are some potassium-rich foods for vegetarians?
+Vegetarians can meet their potassium needs by consuming a variety of plant-based foods, including leafy greens, fresh fruits, legumes, whole grains, and nuts and seeds. Some examples include spinach, bananas, white beans, brown rice, and almonds.
In conclusion, potassium is an essential mineral that plays a critical role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. By understanding the benefits of potassium and incorporating potassium-rich foods into our diets, we can significantly reduce the risk of chronic diseases, support healthy blood pressure, and promote bone health. Whether you're an athlete looking to improve performance or simply seeking to maintain a balanced diet, potassium-rich foods are a great addition to any meal plan. We invite you to share your favorite potassium-rich recipes, ask questions about potassium deficiency, or discuss the importance of potassium in the comments below. Together, let's prioritize our health and well-being by making informed dietary choices.
