Intro
Boost iron intake with foods high in iron, including leafy greens, beans, and lean meats, to combat iron deficiency and anemia, improving overall health and wellbeing with essential nutrients.
Iron is a vital nutrient that plays a central role in the production of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to different parts of the body. Without sufficient iron, the body may not be able to produce enough healthy oxygen-carrying red blood cells, leading to a condition known as iron deficiency anemia. This condition can cause fatigue, weakness, pale skin, and shortness of breath, among other symptoms. Therefore, consuming foods high in iron is essential to maintain good health and prevent iron deficiency anemia.
Iron deficiency is a common nutritional disorder worldwide, affecting millions of people. It is particularly prevalent among pregnant women, young children, and individuals with certain medical conditions, such as celiac disease or ulcerative colitis. A diet that includes a variety of iron-rich foods can help prevent iron deficiency and ensure that the body has enough iron to function properly. There are two types of dietary iron: heme iron, which is found in animal-based foods, and non-heme iron, which is found in plant-based foods. Heme iron is more easily absorbed by the body than non-heme iron.
A well-planned diet that includes a mix of iron-rich foods can provide adequate iron intake and reduce the risk of iron deficiency. Iron-rich foods include red meat, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, nuts, seeds, and fortified cereals. Vitamin C can enhance iron absorption, so consuming foods high in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits, bell peppers, and tomatoes, along with iron-rich foods, can help increase iron absorption. Cooking in cast-iron cookware can also increase iron intake, especially when cooking acidic foods like tomatoes.
Iron-Rich Foods

Iron-rich foods can be categorized into two main groups: animal-based foods and plant-based foods. Animal-based foods, such as red meat, poultry, and fish, are rich in heme iron, which is more easily absorbed by the body than non-heme iron found in plant-based foods. Plant-based foods, such as beans, lentils, and fortified cereals, are rich in non-heme iron. Some of the richest sources of iron include clams, oysters, beef liver, spinach, and fortified breakfast cereals.
Animal-Based Iron-Rich Foods
Animal-based foods are some of the richest sources of iron. These foods include: * Red meat: Beef, lamb, and pork are all good sources of iron. * Poultry: Chicken and turkey are good sources of iron, especially if consumed with the skin. * Fish and seafood: Fish like sardines, anchovies, and shellfish like clams, oysters, and mussels are rich in iron. * Organ meats: Beef liver, chicken liver, and pork liver are all rich in iron.Plant-Based Iron-Rich Foods
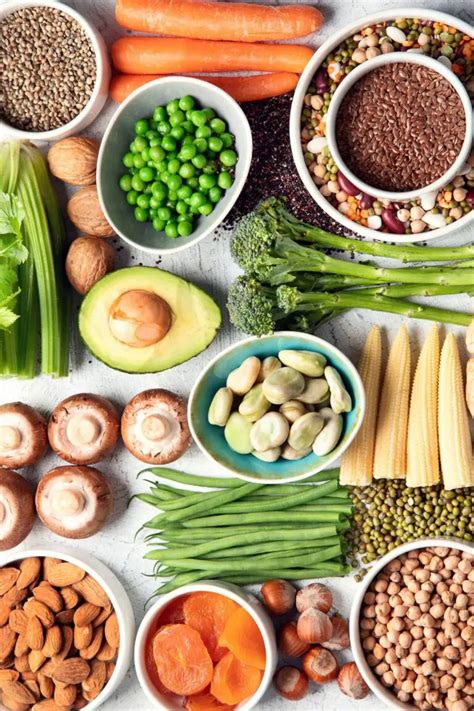

Plant-based foods are also rich in iron, although the iron in these foods is non-heme iron, which is not as easily absorbed by the body as heme iron. Some of the richest plant-based sources of iron include:
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and peas are all good sources of iron.
- Nuts and seeds: Pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds, and sunflower seeds are all good sources of iron.
- Whole grains: Quinoa, brown rice, and whole-wheat bread are all good sources of iron.
- Fortified cereals: Many breakfast cereals are fortified with iron, making them a good source of this nutrient.
Increasing Iron Absorption
To increase iron absorption, it is essential to consume iron-rich foods along with foods that enhance iron absorption, such as vitamin C-rich foods. Some of the best foods to consume along with iron-rich foods include: * Citrus fruits: Oranges, grapefruits, and lemons are all high in vitamin C. * Bell peppers: Green, red, and yellow bell peppers are all high in vitamin C. * Tomatoes: Fresh and cooked tomatoes are both high in vitamin C. * Cruciferous vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts are all high in vitamin C.Cooking and Iron Intake

Cooking can also affect iron intake. Cooking in cast-iron cookware can increase iron intake, especially when cooking acidic foods like tomatoes. Additionally, cooking methods like stir-frying and sautéing can help retain more iron in foods than methods like boiling.
Iron Supplements
While a well-planned diet can provide adequate iron intake, some individuals may require iron supplements to prevent or treat iron deficiency anemia. Iron supplements are available in various forms, including ferrous sulfate, ferrous gluconate, and ferric citrate. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any iron supplements, as excessive iron intake can cause adverse effects.Preventing Iron Deficiency

Preventing iron deficiency requires a combination of a well-planned diet, a healthy lifestyle, and regular health check-ups. Some of the ways to prevent iron deficiency include:
- Consuming a variety of iron-rich foods
- Cooking in cast-iron cookware
- Avoiding excessive tea and coffee consumption, which can inhibit iron absorption
- Avoiding excessive milk consumption, which can inhibit iron absorption
- Getting regular health check-ups to monitor iron levels
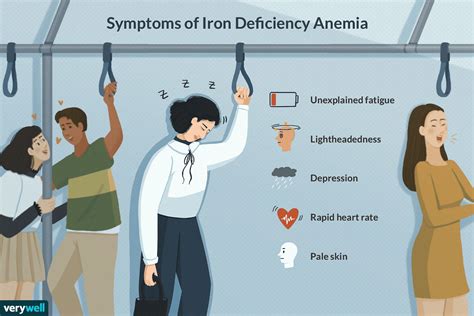
Iron Deficiency Symptoms
Iron deficiency can cause a range of symptoms, including: * Fatigue and weakness * Pale skin * Shortness of breath * Headaches * Dizziness * Cold hands and feet * Poor appetite * Hair lossTreatment of Iron Deficiency
Treatment of iron deficiency typically involves a combination of dietary changes and iron supplements. In severe cases, iron deficiency may require intravenous iron therapy or blood transfusions. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for iron deficiency.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, iron is a vital nutrient that plays a central role in maintaining good health. Consuming a variety of iron-rich foods, cooking in cast-iron cookware, and avoiding excessive tea and coffee consumption can help prevent iron deficiency. Regular health check-ups can help monitor iron levels and prevent iron deficiency anemia. If you are experiencing symptoms of iron deficiency, consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment.What are the symptoms of iron deficiency?
+The symptoms of iron deficiency include fatigue and weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, headaches, dizziness, cold hands and feet, poor appetite, and hair loss.
What are the richest sources of iron?
+The richest sources of iron include clams, oysters, beef liver, spinach, and fortified breakfast cereals.
How can I increase iron absorption?
+You can increase iron absorption by consuming iron-rich foods along with foods that enhance iron absorption, such as vitamin C-rich foods like citrus fruits, bell peppers, and tomatoes.
Do I need to take iron supplements?
+It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine if you need to take iron supplements. While a well-planned diet can provide adequate iron intake, some individuals may require iron supplements to prevent or treat iron deficiency anemia.
How can I prevent iron deficiency?
+You can prevent iron deficiency by consuming a variety of iron-rich foods, cooking in cast-iron cookware, avoiding excessive tea and coffee consumption, and getting regular health check-ups to monitor iron levels.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable information about iron-rich foods and how to prevent iron deficiency. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, please consider sharing it with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the importance of iron in our diets.
