Intro
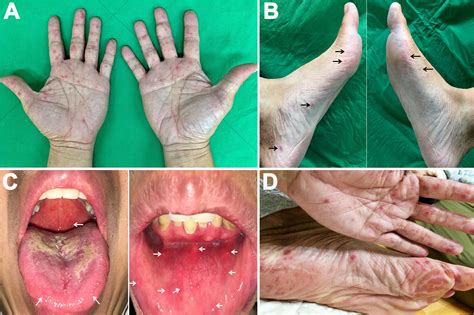
Identify Foot Mouth Disease symptoms, including fever, blisters, and sore throat, to manage hand, foot, and mouth disease effectively.
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) is a highly contagious viral disease that affects cloven-hoofed animals, such as cattle, pigs, sheep, and goats. The disease is characterized by the appearance of lesions on the feet and in the mouth of infected animals, which can lead to significant economic losses for farmers and the livestock industry as a whole. Understanding the symptoms of FMD is crucial for early detection and prevention of the disease.
The symptoms of FMD can vary depending on the species of animal affected, but they typically include fever, loss of appetite, and the appearance of lesions on the feet and in the mouth. These lesions can be painful and can cause difficulty walking and eating, leading to weight loss and reduced productivity. In addition to the economic impact, FMD can also have significant animal welfare implications, as infected animals can suffer from pain and discomfort.
The importance of recognizing the symptoms of FMD cannot be overstated, as prompt identification and reporting of the disease are critical for preventing its spread. Farmers, veterinarians, and animal health officials must be aware of the signs of FMD and take swift action to contain outbreaks and prevent the disease from spreading to other farms or regions. This includes implementing biosecurity measures, such as restricting movement of animals and personnel, and conducting regular surveillance and monitoring of animal health.
Introduction to Foot-and-Mouth Disease
Causes and Transmission of FMD
The FMD virus is highly contagious and can be transmitted through various routes, including direct contact with infected animals, contaminated feed and water, and through the air. The virus can also survive on surfaces and in the environment for extended periods, making it difficult to eradicate. The transmission of FMD can be facilitated by human activity, such as the movement of animals and personnel, and the sharing of equipment and supplies.Symptoms of Foot-and-Mouth Disease

Diagnosis and Treatment of FMD
Diagnosing FMD can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other diseases. However, a combination of clinical examination, laboratory testing, and epidemiological investigation can help confirm the diagnosis. There is no specific treatment for FMD, but supportive care, such as providing pain relief and ensuring access to food and water, can help alleviate the symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.Prevention and Control of FMD

Vaccination Against FMD
Vaccination is a critical component of FMD prevention and control. There are several types of FMD vaccines available, including inactivated and live attenuated vaccines. Vaccination can help reduce the risk of infection and prevent the spread of the disease, but it is not a guarantee against infection.Economic and Social Impacts of FMD
Global Efforts to Control FMD
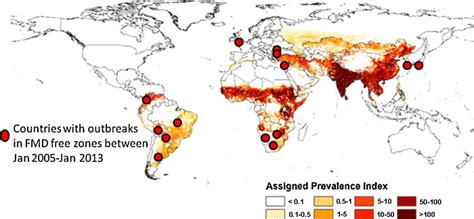
Controlling FMD requires a global effort, as the disease can spread rapidly across borders and regions. International organizations, such as the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations, play a critical role in coordinating global efforts to control FMD. This includes providing technical assistance, supporting research and development, and facilitating international cooperation and collaboration.Conclusion and Future Directions
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with FMD in the comments section below. Have you been affected by FMD, or do you have questions about the disease? Share your stories and ask your questions, and we will do our best to provide helpful information and support.
What are the symptoms of foot-and-mouth disease?
+The symptoms of FMD include fever, loss of appetite, lesions on the feet and in the mouth, difficulty walking and eating, weight loss, and reduced productivity.
How is foot-and-mouth disease transmitted?
+FMD is transmitted through direct contact with infected animals, contaminated feed and water, and through the air.
Can foot-and-mouth disease be prevented?
+Yes, FMD can be prevented through a combination of biosecurity measures, vaccination, and regular surveillance and monitoring of animal health.
What are the economic impacts of foot-and-mouth disease?
+The economic impacts of FMD can be significant, including reduced productivity and income for farmers, increased costs for veterinary care and disease control, and loss of livelihoods and food security.
What is being done to control foot-and-mouth disease globally?
+International organizations, such as the OIE and FAO, are working to control FMD through coordinated global efforts, including providing technical assistance, supporting research and development, and facilitating international cooperation and collaboration.
