Intro
Discover the versatile uses of Gabapentin, including nerve pain management, epilepsy treatment, and anxiety relief, exploring its benefits and applications in neurology and mental health.
Gabapentin is a medication that has been widely used for various medical conditions, primarily for its analgesic, anticonvulsant, and anxiolytic properties. Initially developed to mimic the structure of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), gabapentin has proven to be effective in treating a range of health issues. Its versatility and relatively favorable side effect profile have made it a popular choice among healthcare providers. Here, we will delve into five significant uses for gabapentin, exploring its applications, benefits, and the science behind its efficacy.
The importance of gabapentin lies in its ability to address conditions that are often challenging to manage. For instance, neuropathic pain, which results from damage to the nervous system, can be particularly difficult to treat. Traditional painkillers often fail to provide adequate relief, leaving patients to suffer from chronic pain. Gabapentin, with its unique mechanism of action, offers hope for these patients. Moreover, its use extends beyond pain management, playing a crucial role in the treatment of epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and other conditions. As research continues to uncover the potential benefits of gabapentin, its applications are likely to expand, offering new treatment options for patients.
One of the key aspects of gabapentin is its multifaceted approach to treating various conditions. By affecting the way that nerves send messages to the brain, gabapentin can reduce the occurrence of seizures, alleviate pain, and even help manage symptoms of anxiety. This broad spectrum of activity makes gabapentin an invaluable tool in the healthcare arsenal. Furthermore, its relatively long history of use has provided a wealth of data on its safety and efficacy, allowing healthcare providers to prescribe it with confidence. As we explore the five primary uses of gabapentin, it becomes clear that this medication has the potential to significantly improve the quality of life for many individuals.
Introduction to Gabapentin Uses

Pharmacological Mechanism
The exact mechanism through which gabapentin acts is not fully understood but is believed to involve the modulation of calcium channels, which play a critical role in the transmission of pain and the regulation of neuronal excitability. By binding to these channels, gabapentin reduces the release of excitatory neurotransmitters, thereby decreasing the abnormal electrical activity associated with conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain. This unique action distinguishes gabapentin from other medications, offering a novel approach to treating complex neurological and psychiatric disorders.Treatment of Neuropathic Pain
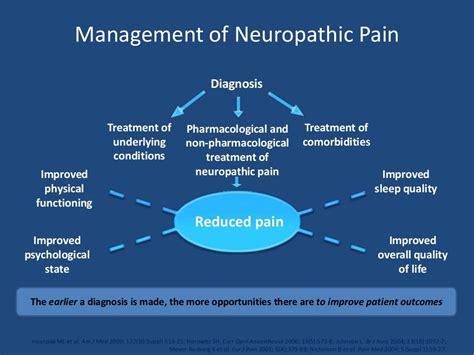
Efficacy in Neuropathic Pain Management
Clinical trials have consistently demonstrated the efficacy of gabapentin in reducing neuropathic pain. For example, a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine found that gabapentin significantly reduced pain intensity in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Another study focusing on postherpetic neuralgia showed similar results, with gabapentin providing substantial pain relief and improving the quality of life for patients. These findings underscore the importance of gabapentin in the management of neuropathic pain and highlight its potential to improve outcomes for patients with these conditions.Management of Epilepsy

Anticonvulsant Properties
The anticonvulsant effects of gabapentin are thought to result from its ability to modulate the activity of voltage-gated calcium channels. By reducing the influx of calcium ions into neurons, gabapentin decreases the release of excitatory neurotransmitters, which in turn reduces the excitability of neurons and the likelihood of seizure activity. This mechanism of action is distinct from that of other antiepileptic drugs, making gabapentin a valuable addition to the arsenal of treatments for epilepsy.Treatment of Anxiety Disorders

Anxiolytic Effects
The anxiolytic effects of gabapentin have been observed in both clinical and preclinical studies. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology found that gabapentin significantly reduced symptoms of anxiety in patients with generalized anxiety disorder. Another study focusing on social anxiety disorder showed that gabapentin improved social functioning and reduced anxiety symptoms in affected individuals. These findings suggest that gabapentin may be a useful adjunctive treatment for anxiety disorders, particularly in cases where traditional anxiolytics are ineffective or not tolerated.Treatment of Fibromyalgia

Management of Fibromyalgia Symptoms
The management of fibromyalgia symptoms often requires a multifaceted approach, incorporating pharmacological, non-pharmacological, and lifestyle interventions. Gabapentin, with its analgesic and sleep-enhancing properties, plays a critical role in this management strategy. Clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of gabapentin in reducing pain intensity and improving sleep quality in patients with fibromyalgia. For example, a study published in the journal Arthritis & Rheumatism found that gabapentin significantly reduced pain and improved sleep in patients with fibromyalgia.Treatment of Restless Legs Syndrome

Management of RLS Symptoms
The management of RLS symptoms typically involves lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise and avoidance of caffeine, as well as pharmacological interventions. Gabapentin, with its ability to modulate neurotransmitter activity, may help alleviate RLS symptoms by reducing the abnormal sensations and urges to move associated with the condition. While more research is needed to fully understand the role of gabapentin in RLS management, available data suggest that it may be a useful treatment option for patients who do not respond to traditional therapies.What is gabapentin primarily used for?
+Gabapentin is primarily used for the treatment of neuropathic pain, epilepsy, and anxiety disorders. It is also used off-label for the management of fibromyalgia, restless legs syndrome, and other conditions.
How does gabapentin work?
+Gabapentin works by modulating the activity of calcium channels and neurotransmitters in the brain, which helps to reduce pain, seizure activity, and anxiety symptoms.
What are the common side effects of gabapentin?
+Common side effects of gabapentin include dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, and nausea. In some cases, gabapentin can also cause mood changes, such as irritability or anxiety.
Can gabapentin be used for anxiety disorders?
+Yes, gabapentin can be used off-label for the treatment of anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and panic disorder.
Is gabapentin addictive?
+Gabapentin has a low potential for abuse and addiction. However, it can cause physical dependence and withdrawal symptoms if stopped abruptly after long-term use.
In conclusion, gabapentin is a versatile medication with a wide range of applications, from the management of neuropathic pain and epilepsy to the treatment of anxiety disorders and fibromyalgia. Its unique mechanism of action and relatively favorable side effect profile make it a valuable treatment option for patients with these conditions. As research continues to uncover the potential benefits of gabapentin, its role in the management of various health issues is likely to expand. If you are considering gabapentin for a medical condition, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to discuss the potential benefits and risks and determine the best course of treatment for your specific needs. We invite you to share your experiences with gabapentin or ask questions about its uses and effects in the comments below. Your input can help others better understand the role of gabapentin in managing various health conditions.
