Intro
Discover gabapentin uses and benefits for nerve pain, epilepsy, and anxiety, highlighting its efficacy as an anticonvulsant and neuropathic pain reliever, with related treatments like fibromyalgia and restless leg syndrome management.
The world of pharmaceuticals is vast and complex, with numerous medications available to treat a wide range of health conditions. One such medication that has gained significant attention in recent years is gabapentin. Initially developed as an antiepileptic drug, gabapentin has shown immense potential in treating various neurological and psychiatric disorders. Its versatility and efficacy have made it a popular choice among healthcare professionals, and its benefits are being explored in various fields of medicine. In this article, we will delve into the uses and benefits of gabapentin, exploring its mechanisms, applications, and potential side effects.
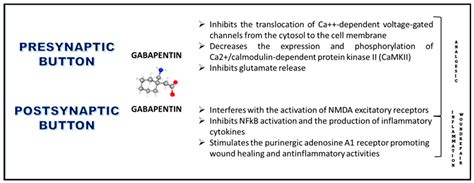
Gabapentin is a medication that belongs to the class of anticonvulsants, which are primarily used to treat seizure disorders. However, its therapeutic benefits extend far beyond epilepsy, and it is now widely used to manage conditions such as nerve pain, anxiety, and insomnia. The drug works by interacting with the brain's neurotransmitters, specifically gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which plays a crucial role in regulating nerve excitability. By modifying the activity of GABA, gabapentin helps to reduce abnormal electrical activity in the brain, thereby alleviating symptoms associated with various neurological and psychiatric conditions.
The uses of gabapentin are diverse and continue to expand as research uncovers its potential benefits. One of the primary applications of gabapentin is in the treatment of neuropathic pain, which is characterized by shooting, burning, or stabbing pain resulting from nerve damage. Conditions such as postherpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy, and fibromyalgia have shown significant improvement with gabapentin therapy. Additionally, gabapentin has been used to manage anxiety disorders, including social anxiety disorder and panic disorder, as well as insomnia and restless leg syndrome. Its anxiolytic properties make it an attractive alternative to traditional benzodiazepines, which can be habit-forming and have significant side effects.
Gabapentin Mechanism of Action
Gabapentin Uses in Neurology
Gabapentin Benefits in Psychiatry

Gabapentin Side Effects and Interactions

Gabapentin Dosage and Administration

Gabapentin Alternatives and Future Directions
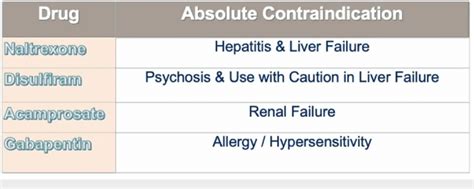
Gabapentin Contraindications and Warnings
Gabapentin Overdose and Toxicity

What is gabapentin used for?
+Gabapentin is used to treat various conditions, including epilepsy, neuropathic pain, anxiety disorders, insomnia, and restless leg syndrome.
How does gabapentin work?
+Gabapentin works by interacting with voltage-gated calcium channels and GABA receptors, reducing the release of excitatory neurotransmitters and promoting a calming effect on the nervous system.
What are the common side effects of gabapentin?
+Common side effects of gabapentin include dizziness, drowsiness, nausea, and fatigue. In rare cases, gabapentin can cause more serious side effects, such as suicidal thoughts, allergic reactions, and respiratory depression.
Can gabapentin be used in combination with other medications?
+Yes, gabapentin can be used in combination with other medications, but it is essential to monitor patients closely for any adverse reactions and adjust the dosage accordingly.
Is gabapentin addictive?
+Gabapentin can be habit-forming, and patients with a history of substance abuse or dependence should be monitored closely. However, the risk of addiction is generally lower compared to traditional benzodiazepines.
In conclusion, gabapentin is a versatile medication with a wide range of applications in neurology and psychiatry. Its benefits in treating neuropathic pain, anxiety disorders, and insomnia have made it a popular choice among healthcare professionals. While gabapentin can cause side effects and interact with other medications, its therapeutic effects make it a valuable treatment option for patients with various conditions. As research continues to uncover the potential benefits of gabapentin, it is essential to monitor patients closely and adjust the dosage accordingly to minimize the risk of adverse effects. We invite readers to share their experiences with gabapentin and explore its potential benefits in managing various health conditions.
