Intro
Learn about gallstones, a common medical condition causing abdominal pain, nausea, and inflammation. Discover symptoms, treatment options, and prevention methods for gallstone disease and related digestive disorders.
The medical condition of gallstones is a common and often painful issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a condition where small, hard deposits form in the gallbladder, a small organ located under the liver that stores bile, a digestive fluid. These deposits, known as gallstones, can be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball, and they can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe pain. In this article, we will delve into the world of gallstones, exploring what they are, how they form, and what treatments are available.
Gallstones are a significant health concern, as they can lead to serious complications if left untreated. The gallbladder is a vital organ that plays a crucial role in digestion, and when gallstones block the flow of bile, it can cause a range of problems, including inflammation, infection, and even cancer. Therefore, it is essential to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for gallstones, as well as the ways to prevent them from forming in the first place.
The formation of gallstones is a complex process that involves a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. One of the primary causes of gallstones is an imbalance of bile salts, cholesterol, and bilirubin, which are the main components of bile. When the balance of these substances is disrupted, it can lead to the formation of small, hard deposits that can grow and accumulate over time. Other factors that can contribute to the formation of gallstones include obesity, diabetes, and a diet high in fat and cholesterol.
Gallstones Symptoms and Diagnosis
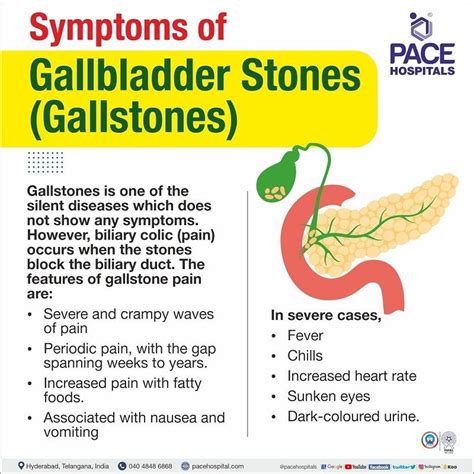
The symptoms of gallstones can vary widely, depending on the size and location of the stones. Some people may experience no symptoms at all, while others may experience severe pain, nausea, and vomiting. The most common symptoms of gallstones include abdominal pain, particularly in the upper right quadrant, nausea and vomiting, fever, and jaundice, which is a yellowing of the skin and eyes. In some cases, gallstones can also cause pancreatitis, which is an inflammation of the pancreas that can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Diagnosing gallstones typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests. The most common imaging tests used to diagnose gallstones are ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI scans. These tests can help doctors visualize the gallbladder and detect any blockages or abnormalities. In some cases, a doctor may also perform an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), which is a procedure that uses a flexible tube with a camera and light on the end to visualize the bile ducts and gallbladder.
Gallstones Treatment Options
The treatment options for gallstones depend on the size, location, and number of stones, as well as the severity of symptoms. In some cases, gallstones may not require treatment, especially if they are small and not causing any symptoms. However, if gallstones are causing severe pain, nausea, and vomiting, or if they are blocking the flow of bile, treatment may be necessary. The most common treatment options for gallstones include watchful waiting, medication, and surgery.
Watchful waiting is a treatment approach that involves monitoring the gallstones and symptoms over time to see if they change or worsen. This approach is often used for people who have small gallstones that are not causing any symptoms. Medication may also be used to treat gallstones, especially if they are causing pain and discomfort. The most common medications used to treat gallstones are pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, and medications that help dissolve the stones, such as ursodiol.
Surgery is often the most effective treatment option for gallstones, especially if they are large or numerous. The most common surgical procedure used to treat gallstones is a cholecystectomy, which is the removal of the gallbladder. This procedure can be performed laparoscopically, which involves making small incisions in the abdomen and using a camera and instruments to remove the gallbladder. In some cases, an open cholecystectomy may be necessary, which involves making a larger incision in the abdomen to remove the gallbladder.
Gallstones Prevention and Lifestyle Changes

Preventing gallstones is often easier than treating them, and there are several lifestyle changes that can help reduce the risk of developing gallstones. One of the most effective ways to prevent gallstones is to maintain a healthy weight, as obesity is a significant risk factor for gallstones. Eating a healthy diet that is low in fat and cholesterol can also help reduce the risk of gallstones. Foods that are high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help promote digestive health and reduce the risk of gallstones.
Regular exercise is also an important way to prevent gallstones, as it can help improve digestion and reduce the risk of obesity. Avoiding certain foods, such as fatty meats, dairy products, and processed foods, can also help reduce the risk of gallstones. Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water is also essential, as dehydration can increase the concentration of bile and make it more likely to form gallstones.
Gallstones Complications and Risks
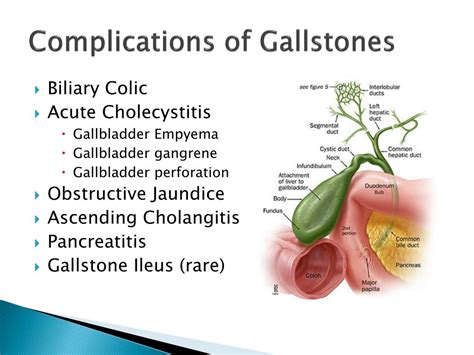
Gallstones can cause a range of complications and risks, especially if they are left untreated. One of the most common complications of gallstones is inflammation of the gallbladder, which is known as cholecystitis. This condition can cause severe pain, nausea, and vomiting, and can lead to more serious complications, such as infection and abscess formation.
Gallstones can also cause pancreatitis, which is an inflammation of the pancreas that can be life-threatening if left untreated. Pancreatitis can cause severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting, and can lead to more serious complications, such as organ failure and death. In some cases, gallstones can also cause jaundice, which is a yellowing of the skin and eyes that can be a sign of a more serious underlying condition.
Gallstones and Other Medical Conditions

Gallstones can be associated with other medical conditions, such as diabetes, obesity, and high blood pressure. People with these conditions are more likely to develop gallstones, and may require more aggressive treatment and management. In some cases, gallstones can also be a sign of a more serious underlying condition, such as liver disease or pancreatic cancer.
Therefore, it is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time. A doctor can diagnose gallstones and develop a treatment plan that takes into account any underlying medical conditions. With proper treatment and management, it is possible to reduce the risk of complications and improve overall health and well-being.
Gallstones and Pregnancy

Gallstones can be a concern during pregnancy, as they can increase the risk of complications and affect the health of the mother and baby. Pregnant women are more likely to develop gallstones due to hormonal changes and increased pressure on the gallbladder. Symptoms of gallstones during pregnancy can be similar to those experienced by non-pregnant women, but may also include more severe abdominal pain and nausea.
Treatment of gallstones during pregnancy depends on the severity of symptoms and the stage of pregnancy. In some cases, watchful waiting may be recommended, while in other cases, surgery may be necessary. It is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that takes into account the unique needs and risks of pregnancy.
Gallstones and Nutrition

Nutrition plays a critical role in the prevention and management of gallstones. A healthy diet that is low in fat and cholesterol can help reduce the risk of gallstones, while a diet high in fiber and antioxidants can help promote digestive health and reduce inflammation. Foods that are high in fat and cholesterol, such as fatty meats and dairy products, can increase the risk of gallstones and should be avoided.
In addition to dietary changes, certain supplements and nutrients may also be beneficial in preventing and managing gallstones. Vitamin C, for example, can help reduce the risk of gallstones by promoting the production of bile and improving digestion. Other nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids and probiotics, may also be beneficial in reducing inflammation and promoting digestive health.
Gallstones and Alternative Therapies
Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture and herbal medicine, may also be beneficial in preventing and managing gallstones. These therapies can help promote digestive health, reduce inflammation, and improve overall well-being. However, it is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that takes into account the unique needs and risks of each individual.
In conclusion, gallstones are a common and often painful medical condition that can have serious complications if left untreated. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for gallstones, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk and improve their overall health and well-being. Whether through lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, or alternative therapies, there are many ways to prevent and manage gallstones.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with gallstones in the comments below. Have you or a loved one been diagnosed with gallstones? What treatment options have you explored, and what have been the results? By sharing our knowledge and experiences, we can work together to promote greater understanding and awareness of this common medical condition.
What are the symptoms of gallstones?
+The symptoms of gallstones can vary widely, but may include abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, fever, and jaundice.
How are gallstones diagnosed?
+Gallstones are typically diagnosed using a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests, such as ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI scans.
What are the treatment options for gallstones?
+The treatment options for gallstones depend on the size, location, and number of stones, as well as the severity of symptoms, and may include watchful waiting, medication, and surgery.
Can gallstones be prevented?
+Yes, gallstones can be prevented by maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, and avoiding certain foods and substances that can increase the risk of gallstones.
What are the complications of gallstones?
+The complications of gallstones can include inflammation of the gallbladder, pancreatitis, and jaundice, and can be life-threatening if left untreated.
