Intro
Discover 5 ways ganglion cyst surgery can relieve wrist pain, numbness, and limited mobility, using minimally invasive techniques, surgical excision, and arthroscopic methods to treat ganglion cysts, wrist tumors, and joint disorders, promoting optimal recovery and rehabilitation.
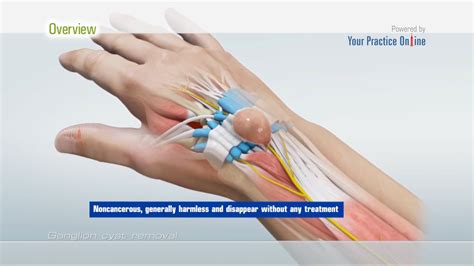
Ganglion cysts are common lumps that develop under the skin, often on the wrist or hand. They are usually harmless but can cause discomfort and pain, especially if they press on surrounding nerves or tendons. In some cases, ganglion cysts can limit mobility and interfere with daily activities. For people experiencing symptoms or those who are concerned about the appearance of a ganglion cyst, surgery is a viable option. Understanding the different approaches to ganglion cyst surgery is crucial for making informed decisions about treatment.
The decision to undergo surgery for a ganglion cyst is typically made after other treatments have been tried without success. These treatments can include watching and waiting to see if the cyst goes away on its own, using a splint to immobilize the affected area, or aspirating the cyst to drain its fluid content. However, if the cyst persists, is painful, or interferes with function, surgical removal may be recommended. It's essential to discuss the potential benefits and risks of surgery with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
Surgery for ganglion cysts is generally effective, with a low risk of complications. The procedure involves removing the cyst and, in some cases, the tendon sheath that the cyst is attached to. This can be done through an open incision or arthroscopically, using smaller incisions and a camera to visualize the area. The choice between these methods depends on the size and location of the cyst, as well as the surgeon's preference and experience. Each approach has its advantages and potential drawbacks, which should be carefully considered by patients and their healthcare providers.
Overview of Ganglion Cyst Surgery
Types of Anesthesia Used
The type of anesthesia used for ganglion cyst surgery depends on several factors, including the size and location of the cyst, the patient's health status, and the surgeon's preference. Local anesthesia numbs the area where the cyst is located, allowing the patient to remain awake during the procedure. Regional anesthesia numbs a larger area, such as the entire arm, and may be used in conjunction with sedation to help the patient relax. General anesthesia, which puts the patient to sleep, is typically reserved for more complex cases or when the patient prefers to be unconscious during the surgery.Open Excision of Ganglion Cysts
Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of open excision include its effectiveness in removing the cyst and the relatively straightforward nature of the procedure. However, it may result in a larger scar and potentially longer recovery times compared to arthroscopic methods. The risk of complications, such as infection or nerve damage, is also present, although these are rare.Arthroscopic Ganglion Cyst Removal
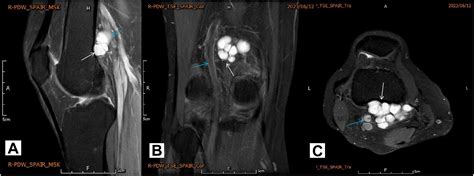
Indications and Limitations
Arthroscopic removal is indicated for cysts that are accessible through this method and in patients who are good candidates for minimally invasive surgery. However, the success of arthroscopic removal can depend on the surgeon's experience and the specific location and size of the cyst. In some cases, arthroscopy may not be feasible, and open excision may be recommended instead.Aspiration and Injection Therapy
Efficacy and Risks
The efficacy of aspiration and injection therapy varies, with some patients experiencing significant relief, while others may see the cyst return. The risks are generally low but can include infection, nerve damage, or temporary worsening of symptoms. These methods are often used as a first line of treatment or in patients who are not good candidates for surgery.Recovery and Rehabilitation

Postoperative Care and Complications
Postoperative care includes monitoring for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or increased pain, and following a wound care regimen as instructed by the healthcare provider. Complications, although rare, can include infection, nerve damage, or recurrence of the cyst. It's essential for patients to attend follow-up appointments to ensure proper healing and address any concerns.Preventing Recurrence

Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to surgical treatment, certain lifestyle modifications can help manage symptoms and potentially reduce the risk of recurrence. These can include avoiding repetitive activities that may have contributed to the cyst's formation, using proper ergonomics to reduce strain on the wrists and hands, and maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on joints.What are the common symptoms of a ganglion cyst?
+Common symptoms include a visible lump under the skin, pain or discomfort, especially when the cyst is pressed or when the affected area is moved, and limited mobility if the cyst is large or in a sensitive location.
How long does it take to recover from ganglion cyst surgery?
+Recovery times can vary but generally range from a few weeks to a few months. The initial healing process usually takes about 2-4 weeks, after which physical therapy may be recommended to regain full strength and mobility.
Can ganglion cysts be prevented?
+While there is no proven method to completely prevent ganglion cysts, avoiding repetitive strain on the wrists and hands, maintaining good posture, and taking regular breaks during activities that involve repetitive motions may help reduce the risk.
In conclusion, ganglion cyst surgery is an effective treatment option for individuals suffering from these lumps, offering relief from symptoms and the potential for full recovery. By understanding the different surgical approaches, including open excision and arthroscopic removal, and the importance of postoperative care and rehabilitation, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment. Whether you're considering surgery for a ganglion cyst or simply looking for more information on the topic, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider to discuss the best course of action for your specific situation. We invite you to share your experiences or ask questions in the comments below, and don't forget to share this article with anyone who might find it helpful.
