Intro
Discover 5 key German Measles facts, including symptoms, causes, and prevention methods, to understand this viral infection, also known as Rubella, and its impact on pregnancy and infant health, with related conditions like congenital rubella syndrome.
German measles, also known as rubella, is a viral infection that was once a common childhood illness. Although it's now relatively rare in many parts of the world due to widespread vaccination, it's still important to understand the disease and its implications. German measles is typically mild, but it can have serious consequences for pregnant women and their unborn babies. In this article, we'll delve into the world of German measles, exploring its causes, symptoms, and prevention methods.
The importance of understanding German measles cannot be overstated. With the rise of anti-vaccination movements and the potential for outbreaks, it's crucial that we're aware of the risks and take steps to protect ourselves and our loved ones. By learning more about German measles, we can work together to prevent its spread and ensure that everyone has access to the information and resources they need to stay healthy. Whether you're a parent, a healthcare professional, or simply someone who wants to stay informed, this article is for you.
As we explore the world of German measles, we'll cover a range of topics, from the history of the disease to its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. We'll also discuss the importance of vaccination and the steps you can take to protect yourself and your loved ones. By the end of this article, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of German measles and be equipped with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions about your health.
What is German Measles?
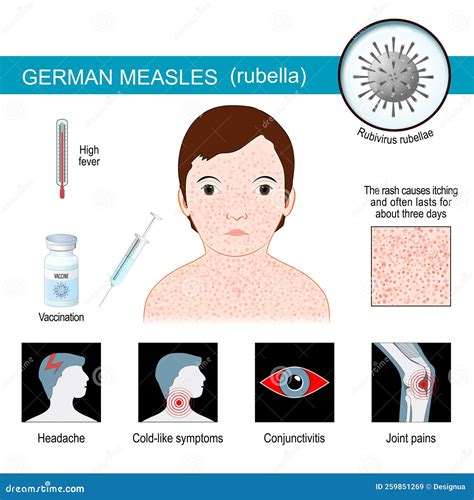
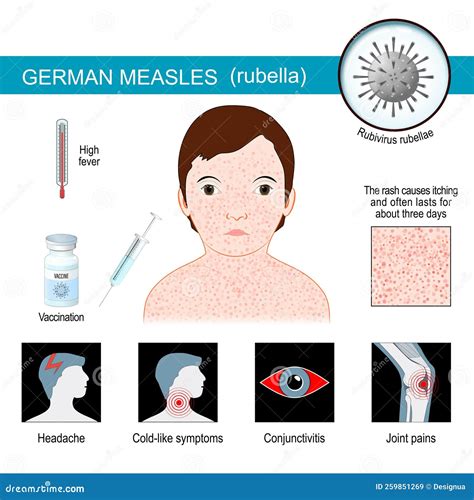
Symptoms of German Measles
The symptoms of German measles can vary from person to person, but they typically include a low-grade fever, sore throat, and a rash that starts on the face and spreads to the rest of the body. The rash is usually pink or red and can be itchy, but it's not typically severe. Other symptoms of German measles may include: * Headache * Fatigue * Loss of appetite * Swollen lymph nodes * Conjunctivitis (pinkeye)Causes and Risk Factors

Complications of German Measles
While German measles is typically a mild disease, it can have serious complications for pregnant women and their unborn babies. If a pregnant woman contracts German measles, it can increase the risk of: * Miscarriage * Stillbirth * Birth defects, such as deafness, blindness, or heart defects * Premature birthDiagnosis and Treatment
Vaccination and Prevention
The best way to prevent German measles is through vaccination. The measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine is a combined vaccine that protects against all three diseases. The vaccine is typically given to children at 12-15 months of age, with a booster shot at 4-6 years of age. Adults who haven't been vaccinated or who are at high risk of contracting the disease may also need to receive the vaccine.German Measles in Pregnancy

German Measles in Children
German measles is typically a mild disease in children, but it can still have serious consequences. Children with German measles may experience: * Fever * Rash * Sore throat * Headache * Fatigue Children with German measles should be kept home from school or daycare to prevent the spread of the disease. Parents can help relieve symptoms by: * Keeping their child hydrated * Using over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen * Applying cool compresses to reduce feverGerman Measles Outbreaks
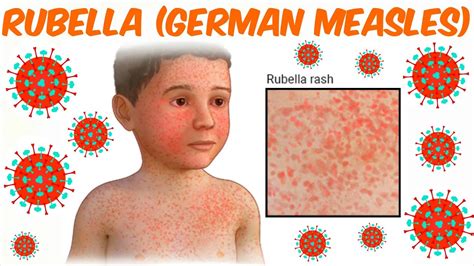
Preventing German Measles Outbreaks
Preventing German measles outbreaks requires a combination of vaccination, good hygiene, and public health measures. Some ways to prevent outbreaks include: * Maintaining high vaccination rates * Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly * Avoiding close contact with people who have German measles * Implementing public health measures, such as quarantine and contact tracingGerman Measles Facts and Statistics
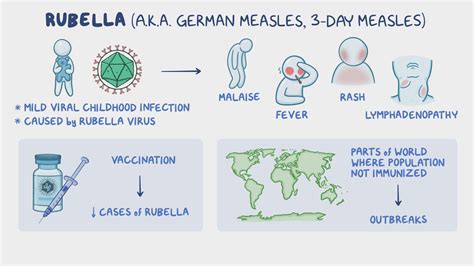
German Measles History
German measles has a long history, with the first recorded outbreak occurring in the 18th century. The disease was once a common childhood illness, but it's now relatively rare in many parts of the world due to widespread vaccination. Some notable events in the history of German measles include: * 1964: The first rubella vaccine is developed * 1969: The MMR vaccine is introduced * 1980s: German measles outbreaks occur in the United States and other countries due to low vaccination rates * 2005: The World Health Organization launches a global campaign to eliminate German measlesWhat is German measles?
+German measles, also known as rubella, is a viral infection that's characterized by a distinctive rash and mild fever.
How is German measles spread?
+German measles is typically spread through respiratory droplets or contact with contaminated surfaces.
Can German measles be prevented?
+Yes, German measles can be prevented through vaccination. The MMR vaccine is 97% effective in preventing the disease.
What are the complications of German measles?
+German measles can cause serious complications in pregnant women and their unborn babies, including miscarriage, stillbirth, and birth defects.
How is German measles diagnosed?
+German measles is typically diagnosed based on the presence of symptoms, such as the characteristic rash and fever. A blood test or swab test may be used to confirm the diagnosis.
We hope you've found this article informative and helpful in understanding German measles. By learning more about this disease, you can take steps to protect yourself and your loved ones. Remember to get vaccinated, practice good hygiene, and stay informed about the latest developments in the fight against German measles. If you have any questions or comments, please don't hesitate to reach out. Share this article with your friends and family to help spread awareness about German measles and the importance of vaccination. Together, we can work towards a healthier and safer future for everyone.
