Intro
Identify severe dehydration symptoms, including excessive thirst, dark urine, and dizziness, and learn about dehydration causes, treatment, and prevention methods to stay hydrated and avoid heat-related illnesses.
Dehydration is a common and potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including excessive sweating, vomiting, diarrhea, and certain medical conditions. Severe dehydration symptoms can be alarming and require immediate attention. In this article, we will delve into the importance of understanding dehydration, its causes, and the severe symptoms that can arise if left untreated.
Dehydration can affect anyone, regardless of age or health status. However, certain groups are more susceptible to dehydration, such as older adults, young children, and people with underlying medical conditions. It is essential to recognize the signs and symptoms of dehydration to prevent severe complications. Mild dehydration can often be treated with oral rehydration solutions, but severe dehydration requires medical attention to prevent long-term damage.
The human body is composed of approximately 60% water, which plays a crucial role in maintaining various bodily functions, such as regulating body temperature, transporting nutrients, and removing waste products. When the body loses fluids, it can disrupt these functions, leading to a range of symptoms. Severe dehydration can cause serious complications, including organ failure, seizures, and even death. Therefore, it is vital to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for dehydration to prevent severe consequences.
Understanding Dehydration

Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, causing an imbalance in the body's water and electrolyte levels. Electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and chloride, play a crucial role in maintaining various bodily functions, including nerve and muscle function. When the body loses fluids, it also loses electrolytes, which can disrupt these functions. Dehydration can be classified into three categories: mild, moderate, and severe. Mild dehydration can often be treated with oral rehydration solutions, while moderate dehydration may require intravenous fluids. Severe dehydration, however, requires immediate medical attention.
Causes of Dehydration
Dehydration can be caused by a variety of factors, including: * Excessive sweating * Vomiting * Diarrhea * Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and kidney disease * Medications, such as diuretics * Climate and environment, such as hot and humid weatherSevere Dehydration Symptoms
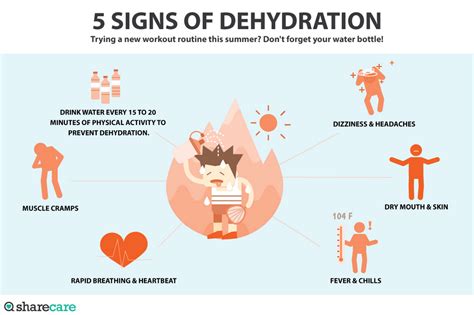
Severe dehydration symptoms can be alarming and require immediate attention. Some common symptoms of severe dehydration include:
- Excessive thirst
- Dark yellow or brown urine
- Decreased urine output
- Fatigue and weakness
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- Rapid heartbeat
- Low blood pressure
- Sunken eyes
- Decreased skin elasticity
- Seizures and coma
Treating Severe Dehydration
Treating severe dehydration requires immediate medical attention. The primary goal of treatment is to replenish fluids and electrolytes to restore balance in the body. Treatment options may include: * Intravenous fluids to replenish fluids and electrolytes * Oral rehydration solutions to help the body absorb fluids and electrolytes * Medications to treat underlying medical conditions * Hospitalization to monitor and manage severe dehydration symptomsPreventing Dehydration

Preventing dehydration is crucial to avoiding severe complications. Some tips to prevent dehydration include:
- Drinking plenty of water and electrolyte-rich beverages
- Avoiding excessive sweating and heat exposure
- Eating a balanced diet that includes electrolyte-rich foods
- Avoiding medications that can cause dehydration
- Monitoring urine output and color to ensure adequate hydration
Recognizing Dehydration in Vulnerable Populations
Certain populations, such as older adults and young children, are more susceptible to dehydration. It is essential to recognize the signs and symptoms of dehydration in these populations to prevent severe complications. Some tips to recognize dehydration in vulnerable populations include: * Monitoring urine output and color * Checking for signs of excessive sweating and heat exposure * Looking for signs of fatigue and weakness * Monitoring for decreased skin elasticity and sunken eyesComplications of Severe Dehydration
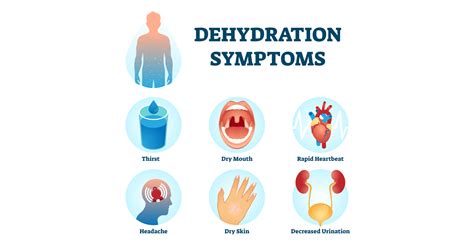
Severe dehydration can cause serious complications, including:
- Organ failure
- Seizures and coma
- Death
- Kidney damage
- Heart problems
- Electrolyte imbalances
Managing Severe Dehydration in Emergency Situations
In emergency situations, managing severe dehydration requires immediate attention. Some tips to manage severe dehydration in emergency situations include: * Calling emergency services * Providing oral rehydration solutions or intravenous fluids * Monitoring vital signs and urine output * Keeping the person cool and comfortableConclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, severe dehydration symptoms can be alarming and require immediate attention. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for dehydration is crucial to preventing severe complications. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of dehydration, providing prompt treatment, and taking preventive measures, we can reduce the risk of severe dehydration and its complications. If you or someone you know is experiencing severe dehydration symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately.
To learn more about dehydration and its management, we invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. You can also share this article with friends and family to raise awareness about the importance of hydration and dehydration prevention.
What are the common causes of dehydration?
+Dehydration can be caused by a variety of factors, including excessive sweating, vomiting, diarrhea, certain medical conditions, and medications.
How can I prevent dehydration?
+To prevent dehydration, drink plenty of water and electrolyte-rich beverages, avoid excessive sweating and heat exposure, eat a balanced diet, and monitor urine output and color.
What are the symptoms of severe dehydration?
+Severe dehydration symptoms include excessive thirst, dark yellow or brown urine, decreased urine output, fatigue and weakness, dizziness and lightheadedness, rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure, sunken eyes, and decreased skin elasticity.
How is severe dehydration treated?
+Severe dehydration is treated with intravenous fluids to replenish fluids and electrolytes, oral rehydration solutions, and medications to treat underlying medical conditions.
What are the complications of severe dehydration?
+Severe dehydration can cause serious complications, including organ failure, seizures and coma, death, kidney damage, heart problems, and electrolyte imbalances.
