Intro
Discover how Giant Cell Arthritis impacts daily life, causing inflammation, joint pain, and vision issues, affecting overall well-being and quality of life with symptoms and complications.
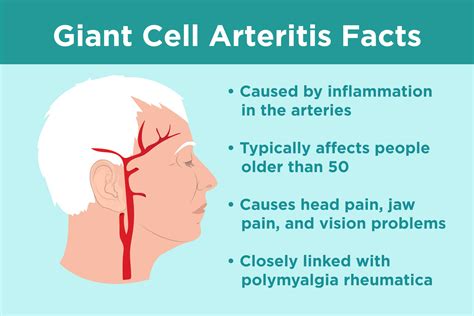
Giant cell arthritis, also known as giant cell arteritis, is a condition that affects the blood vessels, leading to inflammation and damage. This condition can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life, causing a range of symptoms and complications. Understanding the effects of giant cell arthritis is essential for individuals who have been diagnosed with the condition, as well as for their loved ones and healthcare providers. In this article, we will explore the various ways in which giant cell arthritis can affect an individual, including its impact on daily life, overall health, and emotional well-being.
The symptoms of giant cell arthritis can be debilitating, making it challenging for individuals to perform everyday tasks and maintain their independence. The condition can cause severe headaches, scalp tenderness, and jaw pain, which can be excruciating and disrupt a person's sleep patterns. Additionally, giant cell arthritis can lead to vision problems, including double vision, blurred vision, and even blindness. These symptoms can be frightening and affect a person's confidence and self-esteem. Furthermore, the condition can cause fatigue, fever, and weight loss, which can further compromise a person's overall health and well-being.
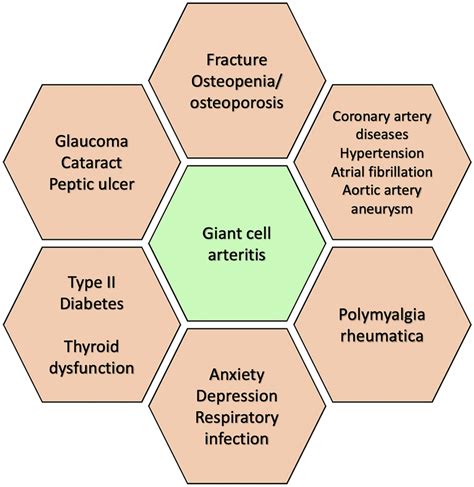
As giant cell arthritis progresses, it can lead to more severe complications, such as aortic aneurysm, stroke, and blindness. These complications can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention. It is essential for individuals with giant cell arthritis to work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their symptoms and prevent long-term damage. With proper treatment and care, individuals with giant cell arthritis can reduce their risk of complications and improve their quality of life. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the effects of giant cell arthritis and explore ways to manage the condition.
Understanding Giant Cell Arthritis
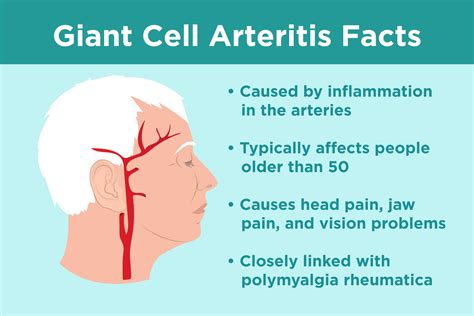
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of giant cell arthritis are not fully understood, but several risk factors have been identified. These include age, sex, and genetic predisposition. Individuals with a family history of giant cell arthritis are more likely to develop the condition. Additionally, people with certain medical conditions, such as polymyalgia rheumatica, are at a higher risk of developing giant cell arthritis. Other risk factors include smoking, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. By understanding these risk factors, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk of developing giant cell arthritis and improve their overall health.Symptoms and Diagnosis
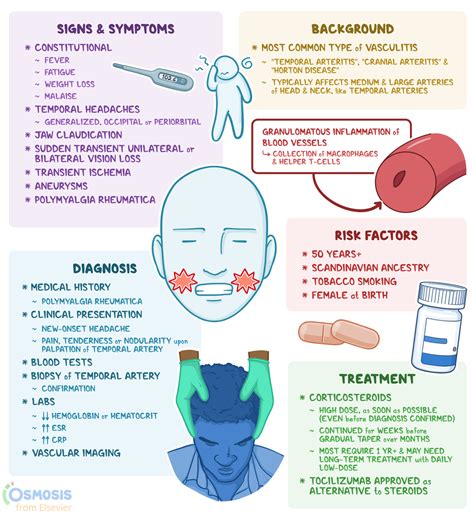
Diagnostic Tests
Several diagnostic tests can help confirm a diagnosis of giant cell arthritis. These include blood tests, such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP), which can detect inflammation in the body. Imaging studies, such as ultrasound, magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), and positron emission tomography (PET), can help visualize the blood vessels and detect any damage or inflammation. A biopsy of the temporal artery may also be performed to confirm the diagnosis. By using a combination of these diagnostic tests, healthcare providers can accurately diagnose giant cell arthritis and develop an effective treatment plan.Treatment and Management
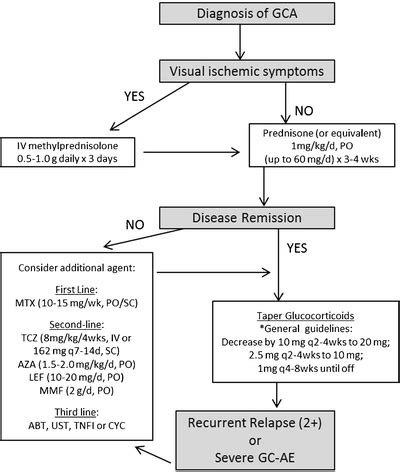
Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle modifications can help individuals with giant cell arthritis manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. This includes quitting smoking, which can reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications. Regular exercise, such as walking or swimming, can help improve overall health and reduce inflammation. Eating a healthy diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can also help manage the condition. Additionally, getting enough sleep, managing stress, and staying hydrated can help reduce symptoms and improve overall well-being. By making these lifestyle modifications, individuals with giant cell arthritis can take an active role in managing their condition and improving their health.Complications and Prognosis
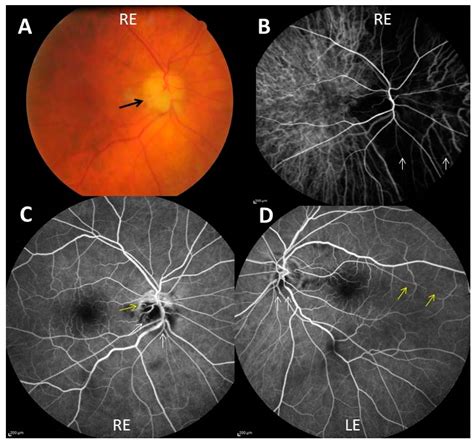
Long-Term Outlook
The long-term outlook for individuals with giant cell arthritis is generally good, especially if treatment is started early. With proper treatment and care, individuals can reduce their risk of complications and improve their quality of life. However, giant cell arthritis is a chronic condition, and individuals may need to take medications and make lifestyle modifications for the rest of their lives. By working closely with their healthcare providers and making healthy lifestyle choices, individuals with giant cell arthritis can manage their condition and improve their overall health and well-being.Coping and Support
Emotional Support
Emotional support is essential for individuals with giant cell arthritis. Talking to a therapist or counselor can help individuals cope with their emotions and develop strategies to manage stress and anxiety. Support groups, either in-person or online, can also provide a sense of community and connection with others who are experiencing similar challenges. Additionally, seeking support from family and friends can help individuals with giant cell arthritis feel less alone and more supported. By prioritizing emotional support, individuals with giant cell arthritis can improve their overall well-being and quality of life.Current Research and Future Directions
Future Directions
The future of giant cell arthritis research holds promise for improving treatment outcomes and reducing the risk of complications. Emerging therapies, such as stem cell therapy and nanotechnology, may offer new opportunities for treating the condition. Additionally, advances in imaging technologies and biomarkers may improve diagnosis and monitoring of giant cell arthritis. By continuing to invest in research and development, we can improve our understanding of giant cell arthritis and develop more effective treatments to improve the lives of individuals with the condition.What are the symptoms of giant cell arthritis?
+The symptoms of giant cell arthritis include severe headaches, scalp tenderness, jaw pain, fever, fatigue, and weight loss. In some cases, the condition can cause vision problems, including double vision, blurred vision, and even blindness.
How is giant cell arthritis diagnosed?
+Giant cell arthritis is diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Blood tests, such as ESR and CRP, can detect inflammation in the body, while imaging studies, such as ultrasound and MRA, can help visualize the blood vessels and detect any damage or inflammation.
What are the complications of giant cell arthritis?
+The complications of giant cell arthritis include aortic aneurysm, stroke, and blindness. These complications can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention. With prompt and proper treatment, individuals with giant cell arthritis can reduce their risk of complications and improve their quality of life.
How is giant cell arthritis treated?
+Treatment for giant cell arthritis typically involves a combination of medications and lifestyle changes. Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are often used to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms. Other medications, such as methotrexate and azathioprine, may be used to suppress the immune system and prevent further damage.
What is the prognosis for giant cell arthritis?
+The prognosis for giant cell arthritis varies depending on the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of treatment. With prompt and proper treatment, individuals with giant cell arthritis can reduce their risk of complications and improve their quality of life. However, if left untreated, the condition can lead to severe and potentially life-threatening complications.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of giant cell arthritis, its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and complications. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may be affected by giant cell arthritis, and to join online support groups to connect with others who are experiencing similar challenges. By working together, we can improve our understanding of giant cell arthritis and develop more effective treatments to improve the lives of individuals with the condition.
