Intro
Discover the normal glucose levels range and maintain healthy blood sugar levels. Learn about ideal glucose ranges, blood sugar monitoring, and diabetes management with related terms like fasting glucose, postprandial glucose, and glycemic control.
Maintaining normal glucose levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Glucose, a type of sugar, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When glucose levels are within a normal range, the body functions properly, and the risk of developing chronic diseases like diabetes is minimized. Normal glucose levels range is a topic of great interest, especially for individuals who are at risk of developing diabetes or those who have been diagnosed with the condition. Understanding the importance of normal glucose levels can help individuals take proactive steps to maintain a healthy lifestyle and prevent complications associated with diabetes.
The normal glucose levels range is typically measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). For individuals without diabetes, normal glucose levels are usually between 70 mg/dL and 99 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L to 5.5 mmol/L) when fasting, and less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) two hours after eating. It is essential to note that these values may vary slightly depending on the laboratory or testing method used. Healthcare providers often use these values as a reference point to diagnose and manage diabetes.
Glucose levels can fluctuate throughout the day, depending on various factors such as diet, physical activity, and medication. For instance, after eating a meal, glucose levels may rise, and then decrease as the body absorbs and utilizes the glucose. In individuals with diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin (a hormone that regulates glucose levels) or is unable to effectively use the insulin it produces, leading to high glucose levels. Understanding the normal glucose levels range and how it relates to overall health can help individuals make informed decisions about their diet, lifestyle, and treatment options.
Understanding Normal Glucose Levels Range
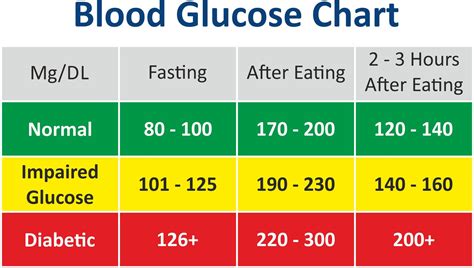
Normal glucose levels range is a critical aspect of maintaining overall health. When glucose levels are within a normal range, the body's cells receive the energy they need to function properly. Glucose is obtained from the food we eat, and the body regulates its levels through the production of insulin and glucagon, two hormones produced by the pancreas. Insulin helps to lower glucose levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose by cells, while glucagon raises glucose levels by stimulating the release of stored glucose (glycogen) into the bloodstream.
Factors Affecting Normal Glucose Levels Range
Several factors can affect normal glucose levels range, including: * Diet: Consuming high amounts of carbohydrates, especially those with a high glycemic index, can cause a spike in glucose levels. * Physical activity: Regular exercise can help to lower glucose levels by increasing the body's sensitivity to insulin. * Medication: Certain medications, such as steroids and certain psychiatric medications, can raise glucose levels. * Sleep: Poor sleep quality and duration can disrupt glucose regulation, leading to high glucose levels. * Stress: Chronic stress can raise glucose levels by stimulating the production of stress hormones like cortisol.Benefits of Maintaining Normal Glucose Levels Range
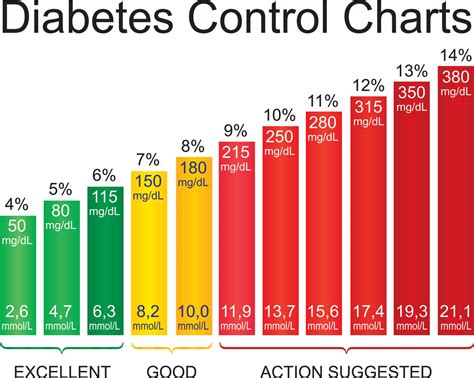
Maintaining normal glucose levels range has numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced risk of developing diabetes and its complications, such as heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage.
- Improved energy levels and mental clarity.
- Enhanced physical performance and endurance.
- Healthier weight management.
- Reduced risk of certain cancers, such as pancreatic cancer.
Strategies for Maintaining Normal Glucose Levels Range
To maintain normal glucose levels range, individuals can follow these strategies: * Eat a balanced diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and refined carbohydrates. * Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, or cycling. * Get adequate sleep and practice stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga. * Monitor glucose levels regularly, especially if you have a family history of diabetes or are at risk of developing the condition. * Consider working with a registered dietitian or a healthcare provider to develop a personalized meal plan and exercise program.Diagnosing and Managing Diabetes

Diagnosing and managing diabetes requires a comprehensive approach that involves lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring of glucose levels. The main goals of diabetes management are to:
- Achieve and maintain normal glucose levels range.
- Prevent complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage.
- Improve quality of life and overall health.
Types of Diabetes
There are several types of diabetes, including: * Type 1 diabetes: An autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. * Type 2 diabetes: A metabolic disorder in which the body becomes resistant to insulin, leading to high glucose levels. * Gestational diabetes: A type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy, usually in the second or third trimester. * LADA (Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults): A type of diabetes that is similar to type 1 diabetes but develops in adults.Treatment Options for Diabetes
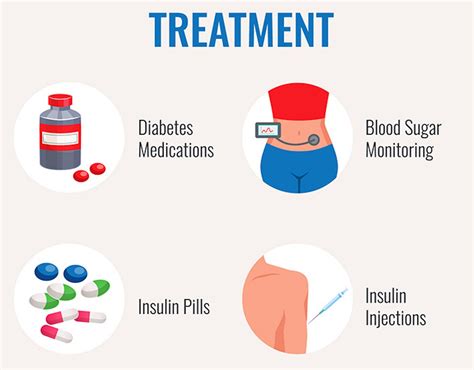
Treatment options for diabetes depend on the type and severity of the condition. Common treatment options include:
- Lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise.
- Medication, such as metformin, sulfonylureas, and insulin.
- Insulin therapy, which involves injecting insulin into the body to regulate glucose levels.
- Bariatric surgery, which can help individuals with type 2 diabetes achieve significant weight loss and improve glucose regulation.
Monitoring Glucose Levels
Monitoring glucose levels is an essential aspect of diabetes management. Individuals with diabetes can use a variety of methods to monitor their glucose levels, including: * Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) tests. * Oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTTs). * Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) tests. * Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems. * Blood glucose meters.Preventing Complications Associated with Diabetes

Preventing complications associated with diabetes requires a comprehensive approach that involves lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring of glucose levels. Common complications associated with diabetes include:
- Heart disease.
- Kidney disease.
- Nerve damage.
- Blindness.
- Amputations.
Strategies for Preventing Complications
To prevent complications associated with diabetes, individuals can follow these strategies: * Maintain normal glucose levels range. * Monitor blood pressure and cholesterol levels. * Engage in regular physical activity. * Eat a balanced diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and refined carbohydrates. * Get adequate sleep and practice stress-reducing techniques.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, maintaining normal glucose levels range is crucial for overall health and well-being. By understanding the factors that affect glucose levels, following strategies for maintaining normal glucose levels range, and working with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan, individuals can reduce their risk of developing diabetes and its complications. If you have any questions or concerns about normal glucose levels range or diabetes management, we encourage you to comment below or share this article with a friend or family member who may benefit from this information.
What is the normal glucose levels range for individuals without diabetes?
+For individuals without diabetes, normal glucose levels are usually between 70 mg/dL and 99 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L to 5.5 mmol/L) when fasting, and less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) two hours after eating.
What are the benefits of maintaining normal glucose levels range?
+Maintaining normal glucose levels range has numerous benefits, including reduced risk of developing diabetes and its complications, improved energy levels and mental clarity, enhanced physical performance and endurance, and healthier weight management.
How can individuals maintain normal glucose levels range?
+Individuals can maintain normal glucose levels range by eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, getting adequate sleep, practicing stress-reducing techniques, and monitoring glucose levels regularly.
What are the common complications associated with diabetes?
+Common complications associated with diabetes include heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, blindness, and amputations.
How can individuals prevent complications associated with diabetes?
+Individuals can prevent complications associated with diabetes by maintaining normal glucose levels range, monitoring blood pressure and cholesterol levels, engaging in regular physical activity, eating a balanced diet, and getting adequate sleep and practicing stress-reducing techniques.
