Intro
Discover the ideal A1c level range for diabetes management, including target HbA1c values, blood sugar control, and glucose monitoring to achieve optimal health outcomes and reduce complications.
Maintaining an ideal A1c level range is crucial for individuals with diabetes to manage their condition effectively and prevent complications. The A1c test, also known as the hemoglobin A1c or HbA1c test, measures the average blood glucose levels over the past 2 to 3 months. It's a vital tool for assessing how well diabetes is being managed. For people without diabetes, the A1c level is typically below 5.7%, while for those with diabetes, the goal is often to keep it below 7%. However, the ideal range can vary depending on factors such as age, other health conditions, and the risk of hypoglycemia.
Understanding the A1c test and its implications is essential for everyone, especially those living with diabetes. It's not just about achieving a specific number but also about maintaining a lifestyle that supports overall health and wellness. The test provides a snapshot of glucose control, helping individuals and their healthcare providers make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication. For instance, if an A1c level is high, it may indicate the need for adjustments in the treatment plan, such as changing medications, increasing physical activity, or improving dietary habits.
The significance of maintaining an ideal A1c level range cannot be overstated. It's associated with a reduced risk of diabetes-related complications, such as heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage. Furthermore, achieving and maintaining tight blood glucose control can improve the quality of life, reduce the risk of hospitalizations, and decrease healthcare costs. Therefore, understanding what constitutes an ideal A1c level and how to achieve it is vital for effective diabetes management.
Ideal A1c Level Range for Different Groups
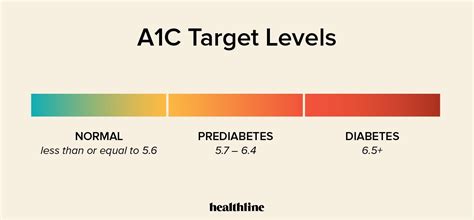
The ideal A1c level range can vary among different groups of people. For individuals without diabetes, an A1c level below 5.7% is considered normal. For those with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends an A1c goal of less than 7% for most adults. However, this target may be adjusted based on individual factors. For example, a less stringent A1c goal (such as <8%) may be appropriate for people with a history of severe hypoglycemia, limited life expectancy, or extensive insulin use. Pregnant women with diabetes are often advised to aim for an even tighter control, with an A1c level below 6.5% if it can be achieved safely.
Factors Influencing A1c Targets
Several factors can influence what constitutes an ideal A1c level for an individual. These include the duration of diabetes, the presence of other health conditions (comorbidities), the risk of hypoglycemia, disease duration, life expectancy, resources, and support system. For instance, younger individuals with type 1 diabetes may aim for tighter control to prevent long-term complications, while older adults with type 2 diabetes and significant comorbidities might have a higher target to balance the risk of hypoglycemia against the benefits of tight glucose control.Benefits of Achieving Ideal A1c Levels

Achieving and maintaining ideal A1c levels offers numerous benefits, including reduced risks of microvascular complications (such as diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy), macrovascular complications (like heart attacks and strokes), and improved quality of life. Tight blood glucose control can also reduce the risk of cognitive decline and depression, which are common among people with diabetes. Furthermore, managing diabetes effectively can decrease healthcare utilization and costs, as it reduces the need for hospitalizations, emergency department visits, and other medical interventions.
Strategies for Achieving Ideal A1c Levels
Several strategies can help individuals achieve and maintain ideal A1c levels. These include: - **Healthy Eating:** Following a balanced diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium, and high in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. - **Regular Physical Activity:** Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week. - **Medication Adherence:** Taking diabetes medications as prescribed by a healthcare provider. - **Monitoring Blood Glucose:** Regularly checking blood glucose levels to understand how different factors (like food, exercise, and stress) affect glucose levels. - **Stress Management:** Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, as stress can raise blood glucose levels.Challenges in Achieving Ideal A1c Levels

Despite the importance of achieving ideal A1c levels, several challenges can hinder success. These include socioeconomic barriers (such as lack of access to healthy food, healthcare, or affordable medications), psychological factors (like diabetes distress or depression), and physical limitations (such as mobility issues that make exercise difficult). Additionally, the complexity of diabetes management, with its multiple daily tasks (like glucose monitoring, insulin administration, and carbohydrate counting), can be overwhelming for some individuals.
Overcoming Challenges
To overcome these challenges, individuals with diabetes can benefit from: - **Multidisciplinary Care Teams:** Working with a team of healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, dietitians, and pharmacists, who can provide comprehensive care and support. - **Patient Education:** Participating in diabetes education programs to learn about diabetes management, nutrition, and lifestyle changes. - **Support Groups:** Joining support groups, either in-person or online, to connect with others who are living with diabetes, share experiences, and learn from each other. - **Technology and Apps:** Utilizing digital tools, such as glucose monitoring apps, insulin pumps, and continuous glucose monitors, to streamline diabetes management and improve adherence to treatment plans.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, achieving and maintaining an ideal A1c level range is a critical aspect of diabetes management. It requires a comprehensive approach that includes healthy lifestyle choices, adherence to medication regimens, and regular monitoring of blood glucose levels. By understanding the factors that influence A1c targets and implementing strategies to overcome challenges, individuals with diabetes can improve their quality of life and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications. Future directions in diabetes care may include the development of more personalized treatment plans, the integration of advanced technologies (like artificial intelligence and wearable devices) into diabetes management, and a greater emphasis on preventive care and early intervention.
Final Thoughts
As research and technology continue to evolve, the management of diabetes is likely to become more sophisticated and tailored to individual needs. However, the core principles of achieving ideal A1c levels—through a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication adherence, and ongoing education and support—will remain essential. By staying informed, engaged, and committed to their care, individuals with diabetes can look forward to better health outcomes and an improved quality of life.
What is the ideal A1c level for someone with diabetes?
+The ideal A1c level for most adults with diabetes is less than 7%, but this target may be adjusted based on individual factors such as age, other health conditions, and the risk of hypoglycemia.
How often should I get an A1c test?
+The frequency of A1c testing depends on the individual's diabetes management plan and their healthcare provider's recommendations. Generally, the test is done at least twice a year if diabetes is well-controlled, and more frequently if changes are made to the treatment plan or if control is poor.
Can I achieve ideal A1c levels through diet and exercise alone?
+For some individuals, especially those with prediabetes or newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, lifestyle changes such as healthy eating and regular physical activity may be sufficient to achieve ideal A1c levels. However, many people with diabetes will also require medication to manage their condition effectively.
We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions about achieving ideal A1c levels in the comments below. Your engagement can help others understand the complexities and challenges of diabetes management and inspire collective efforts towards better health outcomes.
