Intro
Discover 5 uses of Augmentin, a powerful antibiotic, for treating bacterial infections, pneumonia, skin infections, and more, with its amoxicillin and clavulanic acid combination, effective against various strains, including bronchitis and urinary tract infections.
The importance of antibiotics in modern medicine cannot be overstated. These medications have revolutionized the treatment of bacterial infections, saving countless lives and improving the quality of life for millions of people around the world. One such antibiotic that has gained widespread recognition for its effectiveness is Augmentin. Augmentin is a combination antibiotic consisting of amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium, and it is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. The versatility and efficacy of Augmentin have made it a staple in many medical practices, and its uses continue to expand as research and clinical experience accumulate.
The mechanism of action of Augmentin is what sets it apart from other antibiotics. Amoxicillin is a broad-spectrum penicillin-like antibiotic that works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria. However, many bacteria have developed resistance to amoxicillin by producing enzymes called beta-lactamases, which break down the antibiotic before it can take effect. Clavulanate potassium, the other component of Augmentin, is a beta-lactamase inhibitor that blocks the action of these enzymes, allowing amoxicillin to reach its target and effectively kill the bacteria. This dual mechanism of action makes Augmentin particularly effective against a wide range of bacterial infections, including those caused by beta-lactamase-producing strains.
The applications of Augmentin are diverse and continue to grow as new evidence emerges. From treating common infections like pneumonia and skin infections to more complex conditions such as urinary tract infections and septicemia, Augmentin has proven itself to be a reliable and potent antibiotic. Its ability to combat infections in various parts of the body, combined with its relatively favorable safety profile, has made it a preferred choice among healthcare providers for numerous clinical scenarios. Whether used in outpatient settings or in hospitals, Augmentin plays a critical role in the management of bacterial infections, underscoring its importance in contemporary healthcare.
Introduction to Augmentin
Uses of Augmentin
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
Augmentin is effective against a range of bacteria that cause lower respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia. Its broad-spectrum activity, combined with its ability to penetrate into respiratory tissues, makes it a valuable treatment option for community-acquired pneumonia.Skin and Skin Structure Infections
Benefits of Augmentin

Efficacy Against Beta-Lactamase-Producing Bacteria
One of the significant benefits of Augmentin is its ability to combat bacteria that produce beta-lactamase enzymes. This is crucial because many common pathogens, such as certain strains of E. coli, Klebsiella, and Staphylococcus aureus, have developed resistance to penicillins and other beta-lactam antibiotics through the production of these enzymes.Side Effects and Precautions

Contraindications and Warnings
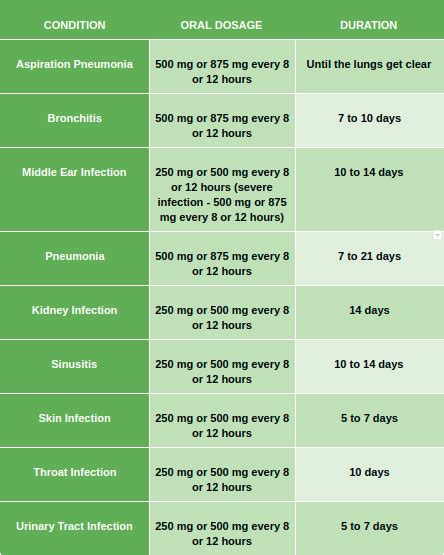
Augmentin is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to any component of the formulation. It should be used with caution in patients with renal impairment, as the dosage may need to be adjusted to prevent accumulation of the drug.Administration and Dosage

Dosage Adjustments
For patients with renal impairment, the dosage of Augmentin may need to be adjusted to prevent drug accumulation. This is particularly important in patients with severe renal impairment, where the half-life of the drug can be significantly prolonged.Conclusion and Future Directions

We invite you to share your thoughts on the uses and benefits of Augmentin, or to ask any questions you may have about this important antibiotic. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in helping us provide the most accurate and helpful information possible.
What is Augmentin used for?
+Augmentin is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including lower respiratory tract infections, skin and skin structure infections, urinary tract infections, and bacterial sinusitis.
How does Augmentin work?
+Augmentin works by combining amoxicillin, a broad-spectrum penicillin-like antibiotic, with clavulanate potassium, a beta-lactamase inhibitor. This combination allows Augmentin to overcome certain types of antibiotic resistance.
What are the side effects of Augmentin?
+Common side effects of Augmentin include gastrointestinal disturbances like diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Allergic reactions can also occur, ranging from mild rashes to severe anaphylaxis.
