Intro
Understand your H Pylori lab test result, including symptoms, treatment, and diagnosis of Helicobacter Pylori infection, with related tests and analysis for accurate interpretation.
The presence of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) in the stomach can lead to various gastrointestinal issues, including peptic ulcers and gastric cancer. As a result, diagnosing and treating H. pylori infections has become a crucial aspect of healthcare. One of the primary methods for detecting H. pylori is through laboratory tests, which can provide accurate and reliable results. In this article, we will delve into the world of H. pylori lab test results, exploring the different types of tests, their procedures, and the implications of the results.
The importance of H. pylori lab tests cannot be overstated. These tests enable healthcare professionals to diagnose H. pylori infections, monitor the effectiveness of treatments, and prevent potential complications. With the rise of antibiotic resistance, accurate diagnosis and treatment have become more critical than ever. By understanding the different types of H. pylori lab tests and their results, individuals can take a proactive approach to their health, working closely with their healthcare providers to manage and prevent H. pylori-related issues.
H. pylori lab tests are typically performed when an individual exhibits symptoms of a gastrointestinal infection, such as abdominal pain, bloating, or nausea. These tests can also be conducted as part of a routine check-up or to monitor the effectiveness of treatment. The most common types of H. pylori lab tests include the urea breath test, stool antigen test, blood tests, and endoscopy. Each of these tests has its unique characteristics, advantages, and limitations, which will be discussed in detail later in this article.
H. Pylori Lab Test Types
There are several types of H. pylori lab tests, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The choice of test depends on various factors, including the individual's symptoms, medical history, and the availability of testing facilities.
Urea Breath Test
The urea breath test is a non-invasive and widely used method for detecting H. pylori. This test measures the amount of carbon dioxide in the breath, which is produced when H. pylori bacteria break down urea. The test involves drinking a special liquid containing urea, followed by a breath test to measure the levels of carbon dioxide.Stool Antigen Test
The stool antigen test is another non-invasive method that detects the presence of H. pylori antigens in the stool. This test is often used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and to confirm the eradication of the bacteria.Blood Tests
Blood tests can detect the presence of antibodies against H. pylori in the blood. These tests are often used to diagnose H. pylori infections, but they may not be as accurate as other methods, such as the urea breath test or stool antigen test.Endoscopy
Endoscopy is a more invasive procedure that involves inserting a flexible tube with a camera into the stomach to visualize the mucosa and collect tissue samples. This test can detect the presence of H. pylori and other gastrointestinal issues, such as ulcers or inflammation.Understanding H. Pylori Lab Test Results
Interpreting H. pylori lab test results requires a thorough understanding of the different types of tests and their limitations. A positive test result typically indicates the presence of H. pylori, while a negative result suggests that the bacteria are not present. However, false-positive and false-negative results can occur, and it is essential to consider the individual's medical history, symptoms, and other test results when interpreting the results.
Positive Test Results
A positive test result indicates the presence of H. pylori, and treatment is usually necessary to eradicate the bacteria. The choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the severity of symptoms, the presence of complications, and the individual's medical history.Negative Test Results
A negative test result suggests that H. pylori is not present, but it does not rule out other gastrointestinal issues. Further testing or evaluation may be necessary to determine the underlying cause of symptoms.False-Positive and False-Negative Results
False-positive and false-negative results can occur due to various factors, such as recent antibiotic use, bleeding disorders, or technical errors. It is essential to consider these possibilities when interpreting test results and to consult with a healthcare professional for guidance.Treatment and Management of H. Pylori Infections
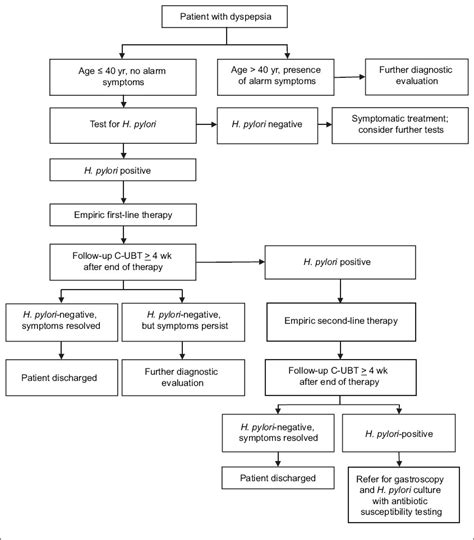
Treatment of H. pylori infections typically involves a combination of antibiotics and acid-reducing medications. The goal of treatment is to eradicate the bacteria, reduce symptoms, and prevent complications.
Antibiotic Treatment
Antibiotic treatment is usually necessary to eradicate H. pylori. The choice of antibiotics depends on various factors, including the severity of symptoms, the presence of complications, and the individual's medical history.Acid-Reducing Medications
Acid-reducing medications, such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), can help reduce stomach acid and alleviate symptoms. These medications are often used in combination with antibiotics to enhance treatment efficacy.Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes, stress reduction, and smoking cessation, can help manage H. pylori symptoms and prevent complications.Prevention of H. Pylori Infections
Preventing H. pylori infections requires a combination of good hygiene practices, dietary modifications, and lifestyle changes.
Good Hygiene Practices
Good hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing, can help reduce the transmission of H. pylori.Dietary Modifications
Dietary modifications, such as avoiding contaminated food and water, can help prevent H. pylori infections.Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes, such as stress reduction and smoking cessation, can help manage H. pylori symptoms and prevent complications.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, H. pylori lab tests play a crucial role in diagnosing and managing H. pylori infections. Understanding the different types of tests, their procedures, and the implications of the results is essential for individuals and healthcare professionals. By working together, we can improve diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of H. pylori-related issues, ultimately reducing the burden of gastrointestinal disease.
As research continues to advance, new diagnostic methods and treatment options may become available. It is essential to stay informed about the latest developments and to consult with healthcare professionals for guidance on H. pylori diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
What are the common symptoms of H. pylori infections?
+Common symptoms of H. pylori infections include abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, and vomiting. In severe cases, H. pylori can cause peptic ulcers, gastric cancer, and other complications.
How is H. pylori diagnosed?
+H. pylori is diagnosed through laboratory tests, including the urea breath test, stool antigen test, blood tests, and endoscopy. The choice of test depends on various factors, including the individual's symptoms, medical history, and the availability of testing facilities.
What is the treatment for H. pylori infections?
+Treatment of H. pylori infections typically involves a combination of antibiotics and acid-reducing medications. The goal of treatment is to eradicate the bacteria, reduce symptoms, and prevent complications.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of H. pylori lab test results and their implications. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others. By working together, we can improve our understanding of H. pylori and reduce the burden of gastrointestinal disease.
