Intro
Identify Hand Foot Mouth Disease symptoms, including rash, fever, and mouth sores, and learn about its causes, treatment, and prevention methods for a speedy recovery.
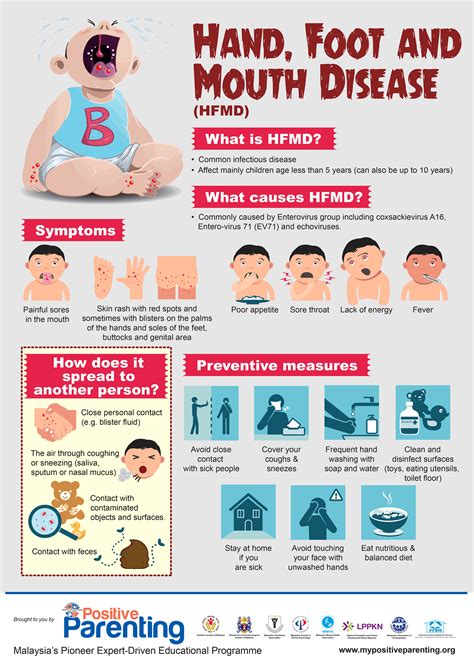
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common viral illness that affects individuals of all ages, but it is most prevalent among children under the age of 10. The disease is characterized by the appearance of sores or blisters on the hands, feet, and inside the mouth, as well as other symptoms such as fever, sore throat, and headache. Understanding the symptoms of HFMD is crucial for early detection, treatment, and prevention of complications. In this article, we will delve into the symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease, its causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
The symptoms of HFMD can vary from person to person, but they typically include a combination of the following: fever, sore throat, headache, fatigue, loss of appetite, and sores or blisters on the hands, feet, and inside the mouth. In some cases, individuals may also experience nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. The sores or blisters associated with HFMD are usually small, flat, and grayish-white, with a red ring around them. They can be painful and may cause discomfort when walking, eating, or drinking.
Introduction to Hand Foot Mouth Disease
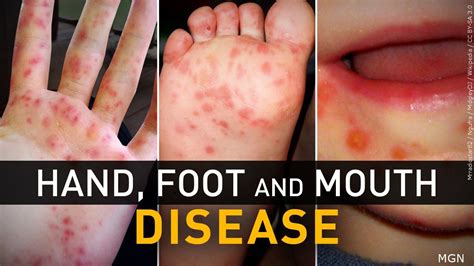
Causes of Hand Foot Mouth Disease
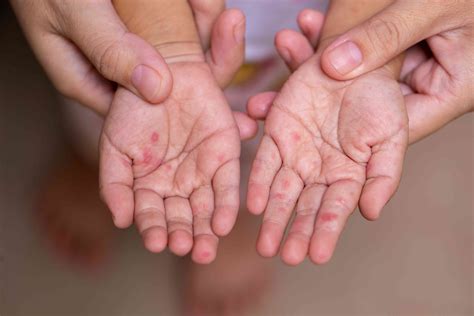
Symptoms of Hand Foot Mouth Disease
Types of Sores or Blisters
The sores or blisters associated with HFMD can appear in different locations, including: * On the palms of the hands * On the soles of the feet * Inside the mouth, including the tongue, roof of the mouth, and gums * On the buttocks or genital area These sores or blisters can be painful and may cause discomfort, especially when eating, drinking, or walking.Diagnosis of Hand Foot Mouth Disease
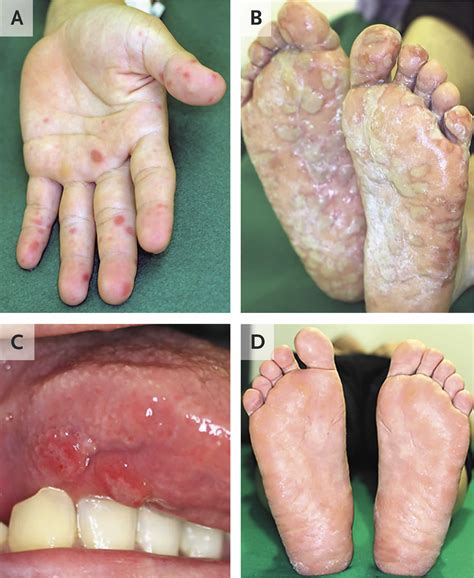
Treatment of Hand Foot Mouth Disease

Prevention of Hand Foot Mouth Disease
Complications of Hand Foot Mouth Disease

Long-Term Effects of Hand Foot Mouth Disease

What are the symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease?
+The symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease include fever, sore throat, headache, fatigue, loss of appetite, and sores or blisters on the hands, feet, and inside the mouth.
How is hand, foot, and mouth disease diagnosed?
+The diagnosis of hand, foot, and mouth disease is typically based on the symptoms and physical examination. Laboratory tests, such as a throat swab or stool sample, may also be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
How is hand, foot, and mouth disease treated?
+The treatment of hand, foot, and mouth disease is typically focused on relieving the symptoms and preventing complications. This can include over-the-counter pain medications, topical creams or ointments, rest, and hydration.
How can hand, foot, and mouth disease be prevented?
+The prevention of hand, foot, and mouth disease includes practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly, avoiding close contact with individuals who are infected, and cleaning and disinfecting surfaces and objects that may be contaminated with the virus.
What are the complications of hand, foot, and mouth disease?
+In some cases, hand, foot, and mouth disease can lead to complications, such as dehydration, bacterial superinfections, meningitis or encephalitis (in rare cases), and respiratory problems.
In conclusion, hand, foot, and mouth disease is a common viral illness that affects individuals of all ages. Understanding the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of HFMD is crucial for early detection, treatment, and prevention of complications. By practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with individuals who are infected, and seeking medical attention if symptoms worsen or if complications arise, individuals can reduce the risk of contracting HFMD and prevent long-term effects. We encourage readers to share their experiences with HFMD, ask questions, and seek medical attention if they suspect they or their loved ones have contracted the disease.
